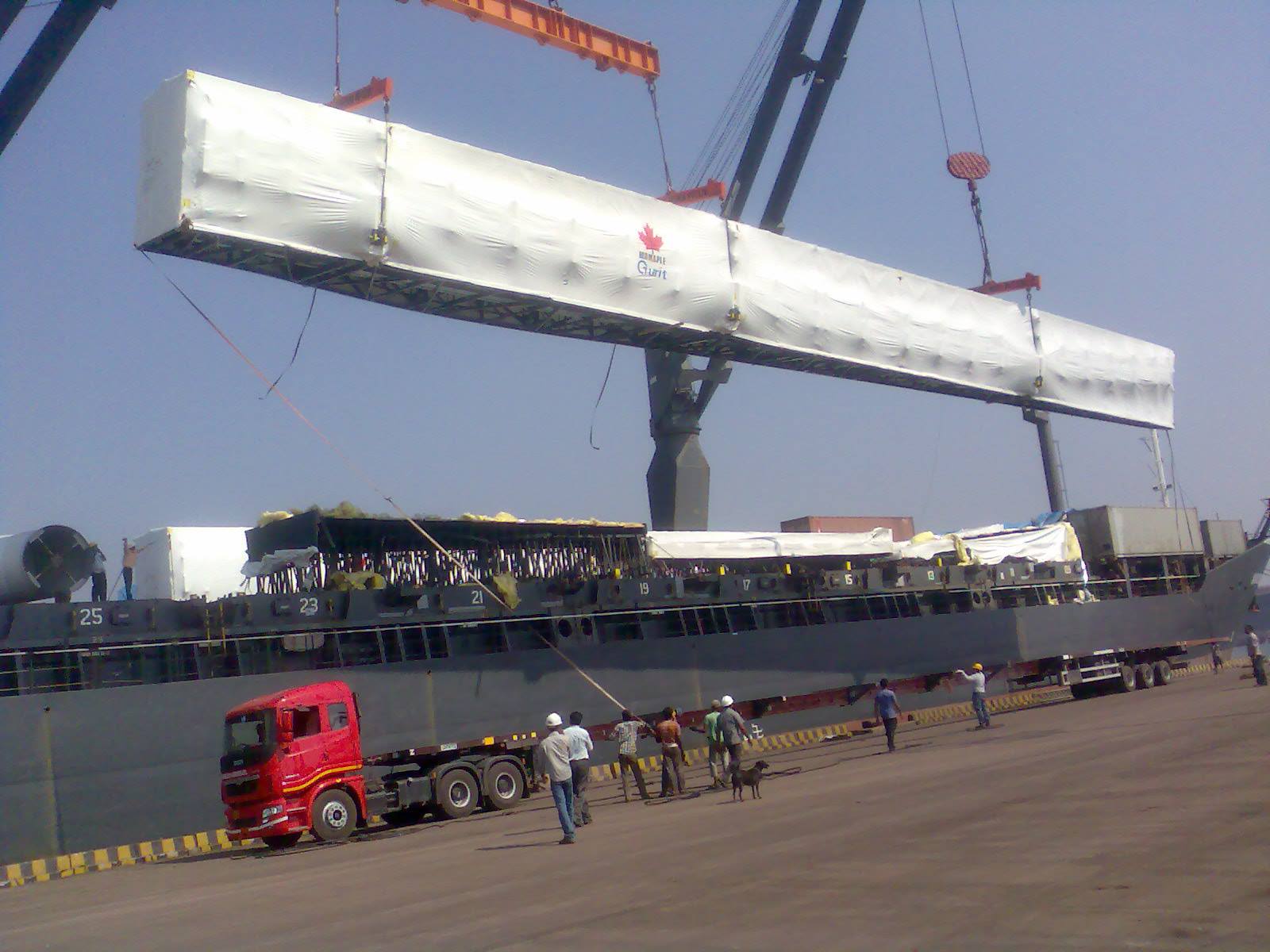
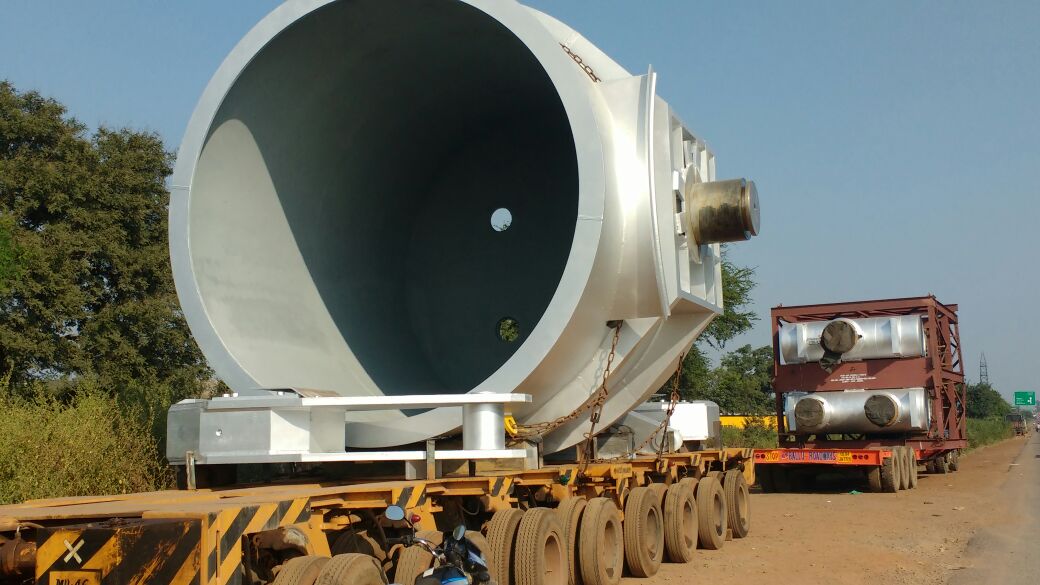
Different elements, both internal and external to the company, intervene in surveying a logistics transport route. Logistics Profile is a predominant trend regarding highway use as the main route of logistics distribution. However, the poor quality of our highways and their limited availability represent a challenge for land logistics transport and the Selection of different types of transport routes. This context makes it even more necessary to optimise the planning and design of transport routes to have efficient logistics distribution processes.
Why required road route survey

A transport route is a route that the carrier takes during the distribution and delivery of merchandise.
In this sense, the transport route should function so that the company can minimise transport costs and the use of the fleet as much as possible. Also, it should allow optimally reducing the distance and travelling time of the point-to-point route.
Related :-
Warehouse and Small Temporary Storage Rental Services
Truck Rental Services
Crane Rental Services
Types of transport routes
The types of transport routes can be organised into two categories according to the destination:
Capillary distribution transport route:
in this type of route, the transport of goods reaches the end customer. This last-mile delivery logistics takes place within urban centres.
Long-distance transport route:
these are those over dimensional cargo transport routes where large quantities of the product are transported by trucks or other means, nationally and internationally.
On the other hand, according to the planning strategy, the types of transport routes can be:
Fixed transport routes:
these are closed-loop routes that are not subject to change, where collection points and delivery points can be continuous or discontinuous for a specified time.
Dynamic transport routes:
these routes meet the different changing needs of the customer, with the possibility of being reprogrammed. In other words, time, distances traveled, and the product transport unit is better used.
Related :-
Advantages of road transport :- Please Click
Disadvantages of road transport :- Please Click
Oversized Load Transportation Problems :- Please Click
Keys for the survey and Selection of the transport route
The correct design of a transport route for the delivery of products is decisive to achieve effectiveness and efficiency on the part of the company, thus avoiding any problem in transport logistics. However, despite its extreme importance, organizations often make errors in route planning, which affects the quality of service and, therefore, the reputation of the brand.
Next, the primary keys for the correct planning of transport routes are the following:
- Selection of vehicles for the transport route
- transport route types
Some companies use the same type of vehicle in all their logistics routes without considering how to travel or the product to be transported.
When this happens, the tuck can suffer unnecessary wear if it travels on roads for which it was not designed. It may also not have the capacity to satisfy all the deliveries that need to be executed. It may not have the conditions to transport certain products, such as fragile goods, or depend on a cold chain.
Given these scenarios, it is essential that the vehicle chosen for each delivery is the most appropriate, taking into account both the type of transport route to be traveled and the type of products to be delivered. For example, if the products are small, the journey is short, and the roads are paved, the company can use bicycles to cover these logistical transport routes, thus promoting fuel savings and speed in goods deliveries. Other types of vehicles to consider depending on transportation are trucks, vans, pickup trucks, cars, or motorcycles.
Survey and Selection of which transport routes are available

Every transportation route is different. There are long, short, steep, flat, unpaved, urban, rural routes, among many others. That said, some companies do not plan their transport routes based on the type of journey. Therefore, carriers tend to travel roads that are not in the best condition, which ends up deteriorating the vehicles, causing delays in deliveries and even affecting the condition of the goods.
On the other hand, when the survey of the over dimensional cargo transport route is made based on the conditions and characteristics of the roads. There is the possibility of choosing routes that do not involve so much fuel consumption, wear and tear on the vehicle, overwork for the driver, or mistreatment of products. All this represents significant savings for the company and a considerable improvement in deliveries since adequate route control means using only the routes that offer the best delivery performance.
Selection of which are the transports routes with less traffic

Logistics in these types of situations become much more complex. The problem is exacerbated when transport companies do not analyze the roads with less traffic when selecting the transport route. When this mistake is made, drivers are more likely to get stuck in traffic jams, causing the product to arrive late at its destination, or worse, unable to deliver.
Caution in planning the logistics transport route is the solution to this problem. By evaluating which roads are with minor traffic congestion and selecting the transportation route based on that information, you will save drivers time on the road. This generates a competitive advantage that deliveries are made promptly. There are significant savings in fuel, and the possibility of making more trips and more deliveries in less time is increased.
Transportation route survey and planning with alternate routes

When companies select transportation routes, they forget to create a “plan B” for transportation logistics. So when planned routes are not available or transit is complex, the carrier must resort to intuition to select a random path that can get it to its destination on time, creating uncertainty about delivery.
The planning of transport routes should address the main roads and those that serve as a contingency method in the event of any eventuality. In this way, if the driver observes a lot of traffic, an accident, or an unfavorable climate to travel through a particular distribution route. With the authorization of his logistics team, he can divert to an alternative route already planned.
Transport route planning digitally routes of transport. Digital mapping has impacted the logistics sector in customer service and experience, digitizing logistics operations and facing demanding markets that differ from new customers proactively.
In recent years, orders have been increasing due to the e-commerce boom, and logistics is gradually strengthening. This requires the sector to meet the expectations of clients and the current market.
As part of the survey sampling design, it is necessary to clarify whether the sampling unit is the driver or everyone in the vehicle. The survey method (including equipment design) must take this into account.
It depends heavily on the purpose of the survey. For example, the choice of route is primarily determined by the driver. Still, other travel decisions (such as destination and time of day) can be determined by all passengers, not just the driver.
Some organisations still use such outdated resources as paper plans for transportation route planning, significantly reducing the effectiveness of their strategy. The design of the transport route on paper makes it challenging to carry out any change or optimisation in the design and prevents them from objectively and accurately assessing the conditions of the roads or managing delivery times. Hence, the team ends making plans based on intuitive arguments or assumptions.
Therefore, to achieve optimal over dimensional cargo route survey and planning, it is advisable to implement specialised transport software in distribution logistics, which digitises the Selection of transport routes and offers analysis functions routes, route assignment, or real-time monitoring of road haulers.
Recommended :-
Transport Department :- Please Click
History of Transportation :- Please Click
Importance of transport system :- Please Click
Survey the transport route according to external variables
Heavy rains, traffic accidents, caravans, protests, and events in public areas are just some of the external variables that a driver may encounter when carrying out a logistics transport route. In most cases, the logistics manager does not monitor these variables and, then, the driver comes across them unexpectedly, thus affecting delivery performance.
To avoid this type of “surprises” along the way, it is necessary to monitor these factors from the operational center constantly to be able to plan the routes taking into account strategic detours, alternate routes, schedules that are before or after the event to be avoided, etc. For example, on holidays, the logistics manager must investigate what time and where the different public events will take place to design transport routes avoiding those roads during those times.
Tool for the survey of transport routes
Different errors in the Selection of transport routes can be avoided using specialised software in distribution logistics. For example, The digital survey platform from which you can plan the transport route digitally and track all deliveries in real-time, thus preventing or solving problems proactively. In this way, the company will reduce its margins of error, improve its distribution routes, and guarantee quality service in the last mile.
The international transport of goods involves the entire network of large tonnage vehicles, airplanes, or large ships that move daily. A whole logistics network made up of thousands of units with a value of millions of currency. For this reason, route optimization is essential for the management of this transport.
Optimise transportation routes with cost
Logistics comprises all those actions aimed at placing merchandise in the agreed place, time, and conditions, to achieve maximum customer satisfaction. Still, achieving perfection is not easy.
Benefits of the Route Survey
Cost savings

The costs in logistics are the ones that most affect the income statement since they can make the difference between obtaining benefits or not in the balance sheet at the end of the year. It is worth highlighting certain advantages of having a well-studied logistics strategy. It also improves the increased government revenue.
Improved fleet management

The fleet is one of the essential elements if we want to use transport routes for industrial development. Therefore, if we develop a route organization that adapts to our needs and those of our clients, we will avoid the wear and tear of your vehicles and the number of cars used every day.
Optimal service level
This service improvement consists of using fewer vehicles to carry out the same number of transports or trips as before.
Most satisfied customers

Due to all of the above, that is, the savings in time thanks to the organization of routes and the offer of investment in research and development, customers will be more satisfied with the service provided by our business.
Time-saving

The survey and preparation of over dimensional cargo routes allow more significant savings in all times related to the distribution of our products due to the automation of tasks that avoid incidents.
International freight transport
When it comes to surveying an international logistics strategy, the expenses that this implies must be considered, taking variables as a reference regarding the regularity and quantity of products that have to be transported. International transport can be an excellent ally of an ambitious company. Good management is what makes the difference.
Obtaining experienced advice in the field of international goods movement is critical. On the other, due to the possibility of allowing two or more companies to divide or share the transport to have compatible destinations. Finally, due to the savings in personnel, fleet, and infrastructure that this implies.
Disadvantage
Use maximum time and cost in transport.
The survey of transport route is very time-consuming. It takes a lot of time to analyze the study, conducting the study. The road survey also brings lots of money.
Inefficiency
The road survey is insufficient to tell the on-time, i.e., actual time condition of the routes.
Related :-
Trucks Truckers and Trucking
Goods Transportation Problems
Logistics Overview
Logistics Park
Conclusion
Route optimization makes much more sense in the international arena for a simple logical reason the more kilometres we travel, the more possibilities we will have to optimize the road. In this sense, determining the approximate time it will take on an international route usually is very difficult since many aspects can upset the forecasts that we initially have.
Due to this, the most appropriate thing will always be to use a margin of time so that we always have a space that allows us to act before the different inconveniences that may arise along the way.
For the international transfer of goods, you should pay special attention to optimising your routes so that planning the time it will take for your shipment to arrive is much easier. In addition, you will ensure that your drivers will travel the fewest kilometres possible.
Click and follow our page for regular upgraded and latest news about Road Transportation Service :- Please Click
Sample of route survey report for odc cargo transportation
Route Survey Report for ODC Cargo Transportation
Date: [Insert Date]
Project Details:
Project Name: [Insert Project Name]
Client: [Insert Client Name]
Cargo Description: Over-Dimensional Cargo (ODC) Transportation
Origin: [Insert Origin Location]
Destination: [Insert Destination Location]
Introduction: The purpose of this route survey report is to assess the feasibility and safety of transporting the over-dimensional cargo from the origin site to the destination. The survey was conducted by a team of experienced professionals to identify potential challenges and recommend suitable measures to ensure the successful transportation of the ODC cargo.
Scope of Survey: The survey covered the entire transport route, including highways, bridges, and critical passages. Key factors such as road conditions, traffic volume, overhead clearances, road width, and potential obstacles were evaluated.
Route Findings: During the survey, the team observed the following critical points:
Road Conditions: The majority of the roads on the selected route are in good condition, with well-maintained surfaces. However, certain stretches might require minor repairs due to small potholes and surface irregularities.
Width Restrictions: Some sections of the route have narrow roads that may pose a challenge for the safe passage of the ODC cargo, especially during overtaking or maneuvering tight turns.
Bridge Capacity: The bridge at [Insert Bridge Location] has a weight limit that is lower than the total weight of the ODC cargo. Alternative routes should be considered to avoid crossing this bridge.
Overhead Clearances: Several overhead obstructions, such as low-hanging cables and tree branches, were identified along the route. These obstructions may require temporary removal or raising to accommodate the height of the ODC cargo.
Traffic Congestion: The survey identified potential areas of heavy traffic congestion, especially during peak hours. Proper coordination with local authorities will be necessary to minimize delays and ensure smooth transportation.
Recommendations: Based on the route survey findings, the following recommendations are made:
Road Repairs: Conduct necessary repairs and maintenance on the identified road sections to ensure a smoother and safer passage for the ODC cargo.
Route Modification: Avoid the bridge at [Insert Bridge Location] due to weight restrictions. Plan an alternative route that ensures the cargo’s weight is within the capacity of all bridges along the way.
Overhead Obstructions: Coordinate with relevant authorities to address overhead obstructions by temporarily removing or raising them to create enough clearance for the ODC cargo.
Traffic Management: Coordinate with local traffic authorities to manage traffic flow during transportation, especially in areas prone to congestion.
Pilot Escorts: Consider employing pilot escort vehicles to guide the ODC cargo and alert other road users of the transportation process.
The successful transportation of ODC cargo is achievable with proper planning and the implementation of the recommended measures. Addressing the identified challenges will significantly contribute to the safety and efficiency of the transportation process. The client and all stakeholders are encouraged to adhere to the recommendations stated in this route survey report.
Safety Precautions: Safety is of utmost importance during the transportation of ODC cargo. The following safety precautions should be strictly adhered to:
Use of Proper Equipment: Ensure that appropriate and certified lifting equipment and rigging gear are used for loading, securing, and unloading the ODC cargo.
Vehicle Inspection: Thoroughly inspect all vehicles involved in the transportation, including trailers, trucks, and escort vehicles, to verify their roadworthiness and compliance with safety standards.
Securement: Properly secure the ODC cargo on the transport vehicles using suitable restraints, padding, and dunnage to prevent shifting during transit.
Night Travel: Avoid night travel if possible, as it may increase the risk of accidents and difficulties in monitoring the cargo’s security and condition.
Weather Monitoring: Continuously monitor weather conditions along the route to anticipate potential hazards and adjust the transportation schedule accordingly.
Communication and Coordination: Effective communication and coordination between all parties involved are crucial for a successful ODC cargo transportation operation. The following points should be considered:
Communication Channels: Establish clear communication channels between the transport team, pilot escort, traffic authorities, and other stakeholders. Use radios or mobile phones for real-time updates.
Emergency Contacts: Provide all involved personnel with emergency contact details and a contingency plan in case of unforeseen events.
Permitting and Regulatory Compliance: Ensure all required permits and authorizations are obtained from relevant authorities before the commencement of transportation. Compliance with local, state, and national regulations is essential to avoid legal issues during transit.
Contingency Plan: Despite thorough planning, unforeseen circumstances may arise during the transportation process. A well-defined contingency plan should be in place to address emergencies, road closures, and alternative route options.
This route survey report highlights critical aspects of the ODC cargo transportation process, providing recommendations to overcome challenges and ensure a safe and successful journey. The client and all stakeholders are encouraged to collaborate closely with the transportation team, adhering to the safety precautions and recommendations outlined in this report.
By prioritizing safety, meticulous planning, and effective communication, we can ensure the successful transportation of the ODC cargo from the origin site to the destination, meeting project timelines and objectives.
Environmental Considerations: During the route survey, environmental factors were taken into account to minimize the impact of ODC cargo transportation on the surroundings. To protect the environment, consider the following measures:
Sensitivity Analysis: Identify ecologically sensitive areas along the route, such as wetlands or wildlife habitats, and plan detours or extra precautions to avoid any negative impact.
Waste Management: Implement waste management procedures to ensure that any packaging materials or waste generated during the transportation process are properly collected and disposed of in accordance with local regulations.
Fuel Efficiency: Encourage the use of fuel-efficient vehicles and adopt eco-friendly driving practices to reduce carbon emissions during the transportation process.
Public Awareness: Notify local communities and businesses along the route about the ODC cargo transportation operation to minimize potential disruptions. Public awareness campaigns can also help educate the public about the importance of the project and any temporary inconveniences it may cause.
Route Validation: Before the actual transportation commences, conduct a final validation of the selected route to ensure that all previously identified challenges have been addressed and that the route remains suitable for ODC cargo transportation.
Escort Vehicles and Pilots: Depending on the dimensions and complexity of the ODC cargo, consider deploying escort vehicles and pilots to accompany the transport convoy. These escorts can help manage traffic, provide guidance through challenging sections, and respond swiftly to emergencies.
Pre-Transport Simulation: Perform a pre-transport simulation, if possible, to assess potential obstacles and challenges in a controlled environment. This simulation can help identify any unforeseen issues and fine-tune the transportation plan.
Insurance Coverage: Verify that all vehicles, cargo, and personnel involved in the transportation are adequately insured against any unforeseen incidents that may occur during the transit.
Post-Transport Evaluation: After the successful completion of the transportation, conduct a post-transport evaluation to assess the effectiveness of the transportation plan and identify areas for improvement in future operations.
Communication Plan: Develop a comprehensive communication plan to keep all stakeholders informed throughout the transportation process. Regular updates should be provided on the cargo’s location, estimated arrival time, and any unexpected delays or changes in the route.
Emergency Response Plan: Establish a well-defined emergency response plan that includes procedures for handling accidents, breakdowns, or any unforeseen incidents. All personnel involved in the transportation should be aware of their roles and responsibilities in case of emergencies.
Geotechnical Considerations: Conduct geotechnical assessments in areas where the road conditions may be unstable or prone to landslides. Strengthening measures such as slope stabilization or drainage improvements may be required in such locations.
Night Transport Protocol: If night travel is inevitable, establish a specific protocol that ensures enhanced visibility and safety during the transportation. Use reflective markings and warning lights on the vehicles, and consider restricting night travel to low-traffic hours.
Public Infrastructure Coordination: Coordinate with local authorities and relevant agencies responsible for maintaining public infrastructure along the route. Inform them about the ODC cargo transportation schedule and seek their assistance, if needed, in making temporary road repairs or adjustments.
Specialized Equipment and Personnel: Ensure that the transportation team possesses the necessary expertise to handle ODC cargo and operates specialized equipment, such as hydraulic trailers, to facilitate loading and unloading procedures.
Contingency Budget: Allocate a contingency budget to address unexpected expenses or changes in the transportation plan. This will help overcome any financial challenges that may arise during the project.
Cultural and Social Considerations: Respect local customs and traditions during the transportation process. If the route passes through areas with cultural significance, coordinate with local communities to minimize any cultural or social impacts.
Reporting and Documentation: Maintain detailed records and documentation of the entire transportation process, including survey reports, permits, approvals, and safety certifications. This documentation will be essential for future reference and regulatory compliance.
Post-Transportation Analysis: Upon completion of the transportation, conduct a comprehensive analysis of the entire project to assess its efficiency, safety, and adherence to the transportation plan. Identify lessons learned and implement improvements for future ODC cargo transportation projects.
Stakeholder Feedback: Encourage stakeholders, including the client, transport team, and local authorities, to provide feedback on the transportation process. Valuable insights from stakeholders can contribute to refining future operations.
Acknowledgment: We would like to extend our appreciation to all team members, stakeholders, and authorities who contributed to the route survey and planning process. Without their collaboration and support, this project would not have been possible.
Thank you for entrusting us with the responsibility of conducting the route survey for the ODC cargo transportation. We remain committed to ensuring the safe and successful delivery of the cargo to its destination.
Conclusion: The successful transportation of ODC cargo requires meticulous planning, adherence to safety measures, and proactive communication with all stakeholders. By implementing the recommendations and considerations outlined in this route survey report, we can ensure the secure and efficient delivery of the ODC cargo to its destination.
We are confident that with our collective efforts and dedication to safety, the ODC cargo transportation project will be completed successfully, achieving the goals set forth by the client.
We remain at your service for any further assistance or clarification.
Sincerely,
[Your Name] [Your Title/Position] [Your Company/Organization]
Sincerely,
[Your Name] [Your Title/Position] [Your Company/Organization]
list out all national highway in India with name and length

list of some major national highways in India along with their names and approximate lengths:
- NH 1 – Grand Trunk Road – 2,369 km
- NH 2 – Delhi-Kolkata Road – 1,465 km
- NH 3 – Agra-Mumbai Highway – 1,161 km
- NH 4 – Mumbai-Chennai Highway – 1,235 km
- NH 5 – Kolkata-Chennai Highway – 1,533 km
- NH 6 – Hazira-Chennai Highway – 1,949 km
- NH 7 – Varanasi-Kanyakumari Highway – 2,369 km
- NH 8 – Delhi-Mumbai Highway – 1,428 km
- NH 9 – Mumbai-Vijayawada Highway – 1,050 km
- NH 10 – Delhi-Fazilka Highway – 460 km
- NH 11 – Agra-Bikaner Highway – 582 km
- NH 12 – Jabalpur-Jaipur Highway – 1,479 km
- NH 13 – Solapur-Mangalore Highway – 1,050 km
- NH 14 – Beawar-Pali-Pindwara Highway – 275 km
- NH 15 – Pathankot-Samakhiyali Highway – 1,526 km
- NH 16 – Nizamabad-Kolkata Highway – 1,493 km
- NH 17 – Panvel-Kochi-Kanyakumari Highway – 1,949 km
- NH 18 – Jhansi-Bilaspur Highway – 458 km
- NH 19 – Delhi-Guwahati Highway – 1,435 km
- NH 20 – Pathankot-Mandi Highway – 218 km
- NH 21 – Ambala-Kinnaur Highway – 459 km
- NH 22 – Ambala-Kaza Highway – 459 km
- NH 23 – Barhi-Guwahati Highway – 582 km
- NH 24 – Delhi-Lucknow Highway – 438 km
- NH 25 – Lucknow-Lalitpur Highway – 220 km
- NH 26 – Allahabad-Satna Highway – 325 km
- NH 27 – Allahabad-Guwahati Highway – 1,266 km
- NH 28 – Lucknow-Barauni Highway – 625 km
- NH 29 – Numaligarh-Kohima-Imphal Highway – 390 km
- NH 30 – Barhi-Benaras-Darbhanga Highway – 351 km
- NH 31 – Barhi-Guwahati Highway – 1,125 km
- NH 32 – Barhi-Raiganj Highway – 196 km
- NH 33 – Barhi-Dhanbad-Ranchi-Jamshedpur Highway – 476 km
- NH 34 – Barhi-Dalkhola Highway – 136 km
- NH 35 – Gurgaon-Faridabad Road – 25 km
- NH 36 – Dhule-Warangal Highway – 436 km
- NH 37 – Jorhat-Dibrugarh Highway – 421 km
- NH 38 – Charaideo-Jorhat Road – 71 km
- NH 39 – Numaligarh-Imphal Highway – 250 km
- NH 40 – Brahmaputra Valley River Bridge, Guwahati – 6 km
- NH 41 – Mumbai-Ahmedabad Highway – 140 km
- NH 42 – Bhubaneswar-Sambalpur Highway – 440 km
- NH 43 – Raipur-Jharsuguda Road – 356 km
- NH 44 – Srinagar-Kanyakumari Highway – 3,745 km (The longest national highway in India)
- NH 45 – Chennai-Theni Highway – 468 km
- NH 46 – Krishnagiri-Renigunta Highway – 206 km
- NH 47 – Salem-Kanyakumari Highway – 684 km
- NH 48 – Delhi-Mumbai Highway – 1,463 km
- NH 49 – Kochi-Dhanushkodi Road – 440 km
- NH 50 – Pune-Nashik Highway – 210 km
- NH 51 – Raxaul-Allahabad Highway – 317 km
- NH 52 – Delhi-Jalandhar Highway – 374 km
- NH 53 – Mansar-Ratnagiri Highway – 509 km
- NH 54 – Silchar-Aizawl Highway – 350 km
- NH 55 – Balasore-Mahulia Highway – 205 km
- NH 56 – Lucknow-Varanasi Highway – 280 km
- NH 57 – Forbesganj-Barauni Highway – 295 km
- NH 58 – Delhi-Haridwar-Badrinath Highway – 538 km
- NH 59 – Indore-Jhalawar-Baran Road – 382 km
- NH 60 – Kolkata-Baharagora Road – 273 km
- NH 61 – Oragadam-Ranipet Highway – 72 km
- NH 62 – Pindwara-Jhalawar Road – 455 km
- NH 63 – Solapur-Bijapur-Hunagund Road – 566 km
- NH 64 – Jalandhar-Rewari Highway – 395 km
- NH 65 – Pune-Machilipatnam Highway – 1,138 km
- NH 66 – Panvel-Kochi-Kanyakumari Highway (old numbering) – 1,622 km
- NH 67 – Coimbatore-Nagapattinam Road – 490 km
- NH 68 – Salem-Kochi Highway – 340 km
- NH 69 – Sinnar-Balasore Highway – 1,147 km
- NH 70 – Sanehwal-Talwandi Bhai Road – 249 km
- NH 71 – Rewari-Agra Road – 198 km
- NH 71A – Rohtak-Panipat Highway – 79 km
- NH 72 – Haridwar-Dehradun Road – 55 km
- NH 73 – Panchkula-Yamunanagar Road – 71 km
- NH 74 – Haridwar-Haldwani Road – 318 km
- NH 75 – Gwalior-Dewas Road – 342 km
- NH 76 – Jagdishpur-Ghaziabad Road – 467 km
- NH 77 – Muzaffarpur-Forbesganj Road – 276 km
- NH 78 – Shegaon-Chindwara Road – 116 km
- NH 79 – Kota-Nagda Road – 560 km
- NH 80 – Raipur-Bargarh Road – 146 km
- NH 81 – Mau-Nawada Road – 312 km
- NH 82 – Muzzafarpur-Gorakhpur Road – 172 km
- NH 83 – Gaya-Kota Road – 491 km
- NH 84 – Beawar-Jaisalmer Road – 531 km
- NH 85 – Gorakhpur-Siddharthnagar Road – 140 km
- NH 86 – Kota-Godhra Road – 586 km
- NH 87 – Rampur-Tanakpur Road – 207 km
- NH 88 – Jhunjhunu-Bikapur Road – 248 km
- NH 89 – Shivpuri-Dausa Road – 532 km
- NH 90 – Sitarganj-Sirsa Road – 175 km
- NH 91 – Delhi-Agra-Kanpur Road – 405 km
- NH 92 – Mathura-Mathura Junction Bypass Road – 7 km
- NH 93 – Moradabad-Agra Road – 246 km
- NH 94 – Nainital-Pilibhit Road – 159 km
- NH 95 – Ludhiana-Ferozepur Road – 133 km
- NH 96 – Pathankot-Amritsar Road – 119 km
- NH 97 – Ambala-Yamunanagar-Paonta Sahib Road – 177 km
- NH 98 – Ambala-Panchkula-Kalka Road – 35 km
- NH 99 – Nashik-Malegaon-Dhule-Surat Road – 398 km
- NH 101 – Barauni-Chapra Road – 100 km
- NH 102 – Jamui-Jahanabad Road – 82 km
- NH 103 – Siwan-Bairia-Jagdishpur Road – 78 km
- NH 104 – Jharkhand-West Bengal Border-Ghatal Road – 71 km
- NH 105 – Muzaffarpur-Deoria Road – 109 km
- NH 106 – Purnia-Mokama Road – 174 km
- NH 107 – Dalsinghsarai-Nirmali Road – 110 km
- NH 108 – Gola-Gopalganj-Bettiah Road – 93 km
- NH 109 – Bakhtiyarpur-Bhagalpur Road – 211 km
- NH 110 – Kandla-Pali Road – 160 km
- NH 111 – Nava-Sheva-Panvel Road – 17 km
- NH 112 – Bhuj-Samakhiyali Road – 58 km
- NH 113 – Godhra-Dahod Road – 52 km
- NH 114 – Chittorgarh-Banswara Road – 101 km
- NH 115 – Firozabad-Madhan Road – 37 km
- NH 116 – Agra-Shamsabad Road – 12 km
- NH 117 – Pilani-Sardarshahar Road – 148 km
- NH 118 – Chhatargarh-Debari Road – 10 km
- NH 119 – Sitarganj-Nepal Border Road – 123 km
- NH 120 – Moradabad-Tanda Road – 187 km
- NH 121 – Palwal-Tilhar Road – 222 km
- NH 122 – Deoband-Muzaffarnagar Road – 67 km
- NH 123 – Sikandrabad-Bulandshahr Road – 23 km
- NH 124 – Delhi-Gurgaon-Alwar Road – 180 km
- NH 125 – Agartala-Sabroom Road – 225 km
- NH 126 – Kadamtala-Agartala Road – 26 km
- NH 127 – Shillong-Dawki Road – 81 km
- NH 128 – Raxaul-Sugauli Road – 40 km
- NH 129 – Hajipur-Bidupur Road – 25 km
- NH 130A – Muzaffarpur-Sitamarhi Road – 77 km
- NH 131B – Bhagalpur-Banka-Giridih Road – 198 km
- NH 131C – Sheikhpura-Dhanbad Road – 158 km
- NH 132 – Muzaffarpur-Bettiah Road – 70 km
- NH 133A – Begusarai-Samastipur-Hajipur Road – 102 km
- NH 134 – Barhiya-Mokama Road – 49 km
- NH 135A – Chakai-Bhagalpur Road – 70 km
- NH 135B – Barbigha-Sheikhpura Road – 54 km
- NH 136 – Dhanaura-Amroha Road – 96 km
- NH 136A – Gajraula-Moradabad Road – 33 km
- NH 137 – Purkazi-Yamunanagar Road – 38 km
- NH 137A – Chhutmalpur-Yamunanagar Road – 8 km
- NH 138 – Pindwara-Banaskantha Road – 8 km
- NH 139 – Nalbari-Indiranagar Road – 10 km
- NH 139A – Rongpur-Silchar Road – 55 km
- NH 140 – Limkheda-Himmatnagar Road – 64 km
- NH 141 – Hanumangarh-Pindwara Road – 263 km
- NH 141A – Khatikwara-Akola Road – 18 km
- NH 142 – Bhilwara-Daosa Road – 227 km
- NH 143 – Deesa-Abu Road Road – 85 km
- NH 143A – Palanpur-Deesa Road – 15 km
- NH 144 – Jalandhar-Rajpura Road – 155 km
- NH 145 – Pathankot-Mandi Road – 210 km
- NH 146 – Nabha-Bhatinda Road – 60 km
- NH 147 – Sangrur-Panipat Road – 168 km
- NH 148 – Palanpur-Nagaur Road – 430 km
- NH 149 – Sangrur-Patiala Road – 80 km
- NH 150 – Pathankot-Jammu Road – 100 km
- NH 151 – Jalandhar-Jammu Road – 185 km
- NH 152 – Hanumangarh-Bikaner Road – 164 km
- NH 153 – Mansar-Ramapuram Road – 41 km
- NH 154 – Dharchula-Tawaghat-Malpa Road – 102 km
- NH 155 – Vellore-Thiruvannamalai Road – 75 km
- NH 156 – Viluppuram-Thiruvarur Road – 139 km
- NH 157 – Haridwar-Jhabrera Road – 27 km
- NH 158 – Kharagpur-Ranchi Road – 366 km
- NH 159 – Dhule-Surat Road – 260 km
- NH 160 – Ahmednagar-Pune Road – 165 km
- NH 161 – Bolarum-Kothakota Road – 93 km
- NH 162 – Ambala-Jalandhar Road – 198 km
- NH 163 – Karur-Dindigul Road – 80 km
- NH 164 – Tuticorin-Kallur Road – 66 km
- NH 165 – Udumalpet-Palani Road – 87 km
- NH 166 – Palani-Munnar Road – 133 km
- NH 167 – Kollam-Thirumangalam Road – 57 km
- NH 168 – Kallikudi-Ramanathapuram Road – 108 km
- NH 169 – Gobichettipalayam-Mettur Dam Road – 166 km
- NH 170 – Sathyamangalam-Chamarajanagar Road – 160 km
- NH 171 – Chennai Bypass Road – 32 km
- NH 172 – Thiruvananthapuram-Nagercoil Road – 71 km
- NH 173 – Ranipet-Krishnagiri Road – 58 km
- NH 174 – Mettupalayam-Kotagiri-Ooty Road – 75 km
- NH 175 – Dehradun-Delhi Road – 235 km
- NH 176 – Haridwar-Paonta Sahib Road – 75 km
- NH 177 – Mandi-Hamirpur Road – 165 km
- NH 178 – Hoshiarpur-Una Road – 100 km
- NH 179 – Sangrur-Bathinda Road – 80 km
- NH 180 – Varanasi-Shaktinagar Road – 96 km
- NH 181 – Ambala-Kotputli Road – 315 km
- NH 182 – Kullu-Manali-Leh Road – 475 km
- NH 183 – Kharar-Rupnagar-Anandpur Sahib Road – 115 km
- NH 184 – Punjab Border-Jalalabad Road – 39 km
- NH 185 – Sangrur-Mansa-Bhatinda Road – 101 km
- NH 186 – Amritsar-Wagah Border Road – 29 km
- NH 187 – Pathankot-Dalhousie Road – 80 km
- NH 188 – Pathankot-Chakki-Mandi Road – 152 km
- NH 189 – Mandi-Sarkaghat Road – 90 km
- NH 190 – Bilaspur-Sundernagar-Rohru Road – 191 km
- NH 191 – Shimla-Chopal-Tuni Road – 250 km
- NH 192 – Kharar-Bassi Pathana Road – 57 km
- NH 193 – Srinagar-Kargil-Leh Road – 434 km
- NH 194 – Jalandhar-Nawanshahr-Rupnagar Road – 96 km
- NH 195 – Agra-Morena-Gwalior Road – 124 km
- NH 196 – Nagaur-Merta Road – 129 km
- NH 205 – Chennai-Nellore-Renigunta Road – 179 km
- NH 206 – Bengaluru-Honnavar Road – 662 km
- NH 207 – Bengaluru-Hosur Road – 86 km
- NH 208 – Kollam-Thirumangalam Road – 615 km
- NH 209 – Bengaluru-Dindigul Road – 456 km
- NH 209A – Nagapattinam-Puducherry Road – 100 km
- NH 210 – Chennai-Kolkata Road – 1,433 km
- NH 211 – Raipur-Hyderabad Road – 676 km
- NH 212 – Kozhikode-Mysore Road – 320 km
- NH 213A – Kadampuzha-Kalpetta Road – 62 km
- NH 214 – Kozhikode-Yedapalli Road – 53 km
- NH 215 – Panikoli-Champajharan Road – 334 km
- NH 216 – Raipur-Nizamabad Road – 358 km
- NH 217A – Chandikhole-Daitari Road – 25 km
- NH 218 – Daitari-Tensa-Jaruli Road – 49 km
- NH 219A – Karanpur-Baripada Road – 37 km
- NH 220 – Kalupur-Narkatiaganj Road – 643 km
- NH 220A – Kalupur-Mahajan Road – 23 km
- NH 221 – Barachatti-Daltonganj Road – 74 km
- NH 222 – Mau-Kopaganj Road – 46 km
- NH 222A – Ghazipur-Ballia Road – 83 km
- NH 223 – Biharsharif-Nawada-Gaya Road – 119 km
- NH 224 – Sasaram-Mohania-Varanasi Road – 348 km
- NH 225 – Arrah-Sasaram Road – 52 km
- NH 226 – Chunar-Mirzapur-Varanasi Road – 96 km
- NH 226A – NH 226A: Handia-Arajiline Road – 66 km
- NH 227 – Varanasi-Kunda-Amethi Road – 220 km
- NH 228 – Pratapgarh-Jaunpur Road – 78 km
- NH 229 – Jodhpur-Sam Road – 167 km
- NH 229A – Nasirabad-Pachpahar Road – 111 km
- NH 229B – Pachpahar-Pali Road – 85 km
- NH 229C – Pali-Raniwara Road – 33 km
- NH 229D – Sanchor-Bhinmal Road – 67 km
- NH 230 – Palanpur-Radhanpur Road – 40 km
- NH 231 – Beawar-Sarwar-Nasirabad Road – 45 km
- NH 232 – Nasirabad-Sangariya Road – 100 km
- NH 233 – Sangariya-Ratanpur Road – 84 km
- NH 234 – Guwahati-Dibrugarh Road – 407 km
- NH 234B – Golaghat-Nazira-Sivasagar Road – 55 km
- NH 235 – Namsai-Yingkiong Road – 159 km
- NH 236 – Gulbarga-Bidar-Humnabad Road – 189 km
- NH 237 – Mankapur-Akola-Washim-Nanded Road – 406 km
- NH 238 – Udaipur-Dungarpur-Banswara Road – 186 km
- NH 239 – Banswara-Dungarpur Road – 54 km
- NH 240 – Makarwali-Nathdwara Road – 22 km
- NH 241 – Bharuch-Dahej Road – 15 km
- NH 241A – Limkheda-Navsari Road – 153 km
- NH 242 – Hazira-Surat-Dhule-Nagpur Road – 653 km
- NH 243 – Bengaluru-Salem-Kanyakumari Road – 435 km
- NH 244 – Puri-Konark Road – 36 km
- NH 245 – Nandankanan-Khurda Road – 10 km
- NH 246 – Chatrapur-Berhampur-Raipur Road – 380 km
- NH 246A – Puswada-Bhawanipatna Road – 127 km
- NH 246B – Kiri Buru-Chaibasa Road – 64 km
- NH 247 – Nagbhid-Pimpalgaon Road – 83 km
- NH 248 – Bengaluru-Hassan-Mangalore Road – 196 km
- NH 249 – Shivamogga-Kollur-Udupi Road – 175 km
- NH 250 – Panvel-Khopoli-Nagpur Road – 828 km
- NH 251 – Babaleshwar-Solapur Road – 30 km
- NH 251A – Yaval-Bhusawal Road – 35 km
- NH 252 – Kaithal-Safidon-Hisar Road – 161 km
- NH 253 – Kanpur-Jhansi-Katni Road – 359 km
- NH 254 – Jaisalmer-Sam Road – 18 km
- NH 254A – Barmer-Balotra-Sirohi Road – 296 km
- NH 254B – Palanpur-Sirohi Road – 199 km
- NH 254C – Gandhinagar-Palanpur Road – 161 km
- NH 255 – Dholpur-Shivpuri Road – 130 km
- NH 256 – Lalganj-Rewa Road – 192 km
- NH 257 – Shivpuri-Baran Road – 269 km
- NH 258 – Gohad-Agra Road – 29 km
- NH 259 – Palsud-Signoor Road – 57 km
- NH 260 – Nagpur-Rajnandgaon Road – 67 km
- NH 261 – Raipur-Bilaspur Road – 131 km
- NH 262 – Bhopal-Bareli-Sagar Road – 272 km
- NH 263 – Ashok Nagar-Shadhora-Guna Road – 131 km
- NH 264 – Rajgarh-Talbahat-Jhansi Road – 105 km
- NH 265 – Muraina-Chakarwara-Mahroni Road – 98 km
- NH 266 – Panna-Tikamgarh Road – 109 km
- NH 267 – Sagar-Lakhnadon-Chhindwara Road – 215 km
- NH 268 – Chhindwara-Udaipura Road – 40 km
- NH 269 – Khawasa-Kamptee Road – 29 km
- NH 270 – Nagpur-Katol-Saoner-Chhindwara Road – 143 km
- NH 271 – Jalna-Khamgaon Road – 303 km
- NH 272 – Ahmednagar-Chalisgaon-Jalgaon Road – 281 km
- NH 273 – Akola-Khamgaon Road – 63 km
- NH 274 – Silchar-Jiribam-Imphal Road – 221 km
- NH 275 – Udaipur-Himatnagar-Ahmedabad Road – 306 km
- NH 276 – Visakhapatnam-Raipur Road – 466 km
- NH 277 – Raipur-Rajnandgaon-Rajegaon Road – 148 km
- NH 278 – Dumka-Suri-Kenduli-Moregram Road – 271 km
- NH 279 – Jamshedpur-Patna Road – 312 km
- NH 280 – Hazaribagh-Ranchi Road – 98 km
- NH 281 – Bokaro-Jamshedpur Road – 47 km
- NH 282 – Rourkela-Rajmunda-Barkote Road – 142 km
- NH 283 – Biramitrapur-Rajamunda-Garhposh Road – 74 km
- NH 284 – Betul-Sarni Road – 23 km
- NH 285 – Sagar-Satna Road – 92 km
- NH 286 – Trichy-Ramanathapuram Road – 125 km
- NH 287 – Nagapattinam-Madurai Road – 193 km
- NH 288 – Palamaner-Ramagundam Road – 473 km
- NH 369 – Puducherry-Tindivanam Road – 35 km
- NH 370 – Salem-Kochi Road – 340 km
- NH 371 – Salem-Ulunderpet Road – 160 km
- NH 372 – Bengaluru-Bellary Road – 311 km
- NH 373 – Mysuru-Ramanagara Road – 142 km
- NH 374 – Bengaluru-Bidar Road – 702 km
- NH 381 – Jorabat-Shillong Road – 103 km
- NH 383 – Tawang-Tezpur Road – 320 km
- NH 384 – Tezpur-Sadiya Road – 510 km
- NH 385 – Changlang-Margherita Road – 49 km
- NH 386 – Pasighat-Roing-Tinsukia Road – 414 km
- NH 387 – West Khasi Hills-Tura Road – 85 km
- NH 387A – Nongstoin-Dawki Road – 81 km
- NH 388 – Silchar-Hailakandi Road – 48 km
- NH 389 – Hailakandi-Karimganj Road – 51 km
- NH 392 – Banbasa-Chaukori Road – 237 km
- NH 533 – Thane-Ghodbunder Road – 21 km
- NH 734 – Salsalabari-Mangan Road – 92 km
- NH 736 – Teesta Bridge-Gangtok-Temi Road – 77 km
- NH 737 – Chungthang-Gangtok Road – 65 km
- NH 743 – Dankuni-Durgapur Expressway – 40 km
- NH 744 – Kochi-Dhanushkodi Road (Madurai-Rameswaram-Kanniyakumari Road) – 441 km
- NH 766 – Bengaluru-Kozhikode Road – 291 km
- NH 766A – Vadakara-Thalassery Road – 40 km
- NH 766B – Ponnani-Kuttippuram Road – 25 km
- NH 766D – Thrissur-Guruvayoor Road – 28 km
- NH 766E – Thalassery-Mysuru Road – 115 km
- NH 966 – Rewa-Satna-Katni-Jabalpur Road – 247 km
- NH 966A – Singrauli-Waidhan-Anuppur Road – 136 km
- NH 966B – Sidhi-Churhat-Shahdol Road – 65 km
- NH 966C – Jabalpur-Dindori-Nagpur Road – 341 km
- NH 966D – Bichhiya-Khajuraho Road – 209 km
- NH 966E – Gwalior-Shivpuri-Ashok Nagar Road – 185 km
- NH 966F – Bhind-Lahar-Kailaras Road – 96 km
- NH 966G – Rajpur-Gormi-Guna-Biora Road – 229 km
- NH 966H – Biora-Rajgarh-Maksi-Ujjain Road – 115 km
- NH 966J – Maksi-Ratlam-Godhra Road – 246 km
- NH 967 – Bina-Chanderi Road – 101 km
- NH 967A – Bhopal-Ichhawar-Sagar Road – 202 km
- NH 967B – Sagar-Chhatarpur Road – 96 km
- NH 967C – Chhatarpur-Nowgaon Road – 130 km
- NH 967D – Gwalior-Morena-Shivpuri Road – 182 km
- NH 967E – Morar-Gwalior-Guna Road – 180 km
- NH 967F – Guna-Narwar-Chhatarpur Road – 174 km
- NH 967G – Panna-Katni-Umaria Road – 201 km
- NH 967H – Umaria-Shahdol-Rewa Road – 238 km
- NH 967J – Beohari-Anuppur Road – 135 km
- NH 967K – Katni-Murwara-Jabalpur Road – 55 km
- NH 968 – Chhindwara-Lakhnadon-Seoni Road – 112 km
- NH 969 – Betul-Paratwada-Achalpur Road – 82 km
- NH 970 – Hinganghat-Wardha-Butibori Road – 70 km
- NH 971 – Patur-Washim-Hingoli-Risod Road – 112 km
- NH 972 – Jintur-Washim-Hingoli-Nanded Road – 246 km
- NH 972A – Nanded-Latur-Osmanabad-Aurangabad Road – 281 km
- NH 973 – Aurangabad-Ahmednagar-Rajgurunagar Road – 280 km
- NH 973A – Shirdi-Ahmednagar Road – 82 km
- NH 973B – Sinnar-Satana-Dhule Road – 145 km
- NH 974 – Uchila-Kundapura Road – 33 km
- NH 975 – Kapu-BC Road-Uppala Road – 70 km
- NH 975A – Hosadurga-Madanthyar Road – 52 km
- NH 975B – Adyar-Mangalore Road – 35 km
- NH 976 – Madanthyar-Mysuru Road – 179 km
- NH 981 – Narva-Sirohi-Rahuri-Ahmednagar Road – 218 km
- NH 981A – Wadala-Georai-Latur-Nanded Road – 232 km
- NH 981B – Latur-Ahmedpur-Tembhurni Road – 96 km
- NH 981C – Nanded-Parbhani-Jintur-Washim-Yavatmal Road – 332 km
- NH 981D – Yavatmal-Digras-Washim Road – 69 km
- NH 981E – Yavatmal-Wardha-Nagpur Road – 149 km
- NH 982 – Rajnandgaon-Mandla-Nainpur Road – 218 km
- NH 982A – Barghat-Chhindwara Road – 40 km
- NH 982B – Jabalpur-Dindori Road – 111 km
- NH 982C – Kundam-Anuppur Road – 34 km
- NH 982D – Anuppur-Chirmiri Road – 29 km
- NH 982E – Bhojpur-Chirmiri Road – 23 km
- NH 982F – Surajpur-Baikunthpur Road – 46 km
- NH 983 – Korba-Katghora-Katni Road – 187 km
- NH 984 – Murwara-Bijuri-Pendra Road – 236 km
- NH 985 – Pendra-Anuppur Road – 52 km
- NH 986 – Ambikapur-Maheshpur-Bara Road – 83 km
- NH 986A – Maheshpur-Simga Road – 78 km
- NH 986B – Simga-Baloda Bazar Road – 22 km
- NH 986C – Baloda Bazar-Dhamtari Road – 43 km
- NH 986D – Dhamtari-Kanker Road – 80 km
- NH 987 – Kanker-Jagdalpur Road – 115 km
- NH 987A – Kondagaon-Bhopalpatnam Road – 78 km
- NH 987B – Bhopalpatnam-Chintur Road – 39 km
- NH 987C – Chintur-Kovvur Road – 70 km
- NH 988 – Suratgarh-Ganganagar-Hanumangarh Road – 309 km
- NH 989 – Gharsana-Suratgarh-Hanumangarh Road – 143 km
- NH 990 – Nokha-Ganganagar-Hanumangarh Road – 65 km
- NH 991 – Ganganagar-Sadulshahar Road – 58 km
- NH 992 – Ganganagar-Bikaner Road – 205 km
- NH 993 – Bikaner-Nagaur-Jodhpur Road – 260 km
- NH 994 – Jodhpur-Pali-Marwar Junction Road – 170 km
- NH 995 – Pali-Sirohi-Sanderao Road – 103 km
- NH 995A – Sanderao-Bali Road – 39 km
- NH 996 – Bali-Beawar Road – 93 km
- NH 996A – Pindwara-Abu Road Road – 24 km
- NH 997 – Pindwara-Bali-Som Road – 94 km
- NH 997A – Sam-Rohet-Setrawa Road – 153 km
- NH 997B – Rohet-Mandor-Nagaur Road – 175 km
- NH 998 – Nagaur-Salasar-Sikar Road – 217 km
- NH 998A – Laxmangarh-Neem Ka Thana-Narnaul Road – 121 km
- NH 999 – Narnaul-Bahror-Rewari Road – 80 km
- NH 1001 – Chhavani-Hansi Road – 64 km
- NH 1001A – Hissar-Charaudha-Rohtak Road – 173 km
- NH 1002 – Rohtak-Jind-Narwana-Hissar Road – 204 km
- NH 1002A – Narwana-Fatehabad-Sardulgarh-Sirsa Road – 170 km
- NH 1002B – Sirsa-Kalawali Road – 33 km
- NH 1003 – Kailaras-Rajauda-Kundeshwar Road – 124 km
- NH 1004 – Jamb-Madhogarh-Lalitpur Road – 139 km
- NH 1005 – Lalitpur-Saugor Road – 119 km
- NH 1006 – Saugor-Bina-Malthone Road – 204 km
- NH 1007 – Bina-Rahatgarh-Panna-Khajuraho Road – 254 km
- NH 1008 – Khajuraho-Satna Road – 122 km
- NH 1009 – Satna-Singrauli Road – 254 km
- NH 1010 – Shaktinagar-Renukoot Road – 47 km
- NH 1011 – Renukoot-Chopan-Singrauli Road – 76 km
- NH 1012 – Barwa Adda-Chopan-Singrauli Road – 74 km
- NH 1013 – Chopan-Shaktinagar Road – 31 km
- NH 1014 – Kothagudem-Kunavaram-Rajahmundry Road – 115 km
- NH 1015 – Kunavaram-Gachibowli Road – 48 km
- NH 1016 – Gachibowli-Shamshabad Road – 18 km
- NH 1017 – Shamshabad-Kollur Road – 38 km
- NH 1021 – Bodhan-Kamareddy Road – 83 km
- NH 1023 – Hyderabad-Bodhan Road – 193 km
- NH 1024 – Nizamabad-Nirmal Road – 66 km
- NH 1025 – Nirmal-Dharmabad Road – 160 km
- NH 1026 – Dharmabad-Nanded Road – 78 km
- NH 1027 – Nanded-Latur Road – 230 km
- NH 1028 – Latur-Bijapur Road – 237 km
- NH 1029 – Bijapur-Sindgi Road – 85 km
- NH 1030 – Sindgi-Ganagapur-Solapur Road – 118 km
- NH 1031 – Solapur-Pandharpur-Tuljapur-Ausa Road – 274 km
- NH 1032 – Ausa-Udgir Road – 42 km
- NH 1033 – Udgir-Nanded Road – 111 km
- NH 1034 – Nanded-Nirmal Road – 198 km
- NH 1035 – Nirmal-Mandamarri Road – 72 km
- NH 1036 – Mandamarri-Mancherial Road – 28 km
- NH 1037 – Mancherial-Bellampalle Road – 32 km
- NH 1038 – Bellampalle-Kothagudem Road – 110 km
- NH 1039 – Kothagudem-Sattupalli Road – 77 km
- NH 1040 – Sattupalli-Chatakonda Road – 52 km
- NH 1041 – Chatakonda-Burgampahad Road – 31 km
- NH 1042 – Burgampahad-Pandharkaoda Road – 57 km
- NH 1043 – Pandharkaoda-Malkapur-Karanja Road – 150 km
- NH 1044 – Karanja-Chikhli Road – 42 km
- NH 1045 – Chikhli-Malkapur-Nandura Road – 71 km
- NH 1046 – Nandura-Shegaon Road – 31 km
- NH 1047 – Shegaon-Akola Road – 26 km
- NH 1048 – Akola-Patur Road – 77 km
- NH 1049 – Patur-Murtizapur Road – 43 km
- NH 1050 – Murtizapur-Mehkar Road – 49 km
- NH 1051 – Mehkar-Khamgaon Road – 29 km
- NH 1052 – Khamgaon-Nandura Road – 61 km
- NH 1053 – Nandura-Achalpur Road – 24 km
- NH 1054 – Achalpur-Amravati Road – 50 km
- NH 1055 – Amravati-Daryapur Road – 30 km
- NH 1056 – Daryapur-Washim Road – 34 km
- NH 1057 – Washim-Hingoli Road – 50 km
- NH 1058 – Hingoli-Basmath Road – 48 km
- NH 1059 – Basmath-Kalamnuri Road – 32 km
- NH 1060 – Kalamnuri-Adampur Road – 48 km
- NH 1061 – Adampur-Nanded Road – 36 km
- NH 1062 – Nanded-Degloor Road – 35 km
- NH 1063 – Degloor-Bodhan Road – 40 km
- NH 1064 – Bodhan-Nizamabad Road – 27 km
- NH 1065 – Nizamabad-Armur Road – 57 km
- NH 1066 – Armur-Bhainsa Road – 28 km
- NH 1067 – Bhainsa-Nirmal Road – 34 km
- NH 1068 – Nirmal-Jagtial Road – 90 km
- NH 1069 – Jagtial-Mallial Road – 45 km
- NH 1070 – Mallial-Kamareddy Road – 66 km
- NH 1071 – Kamareddy-Bodhan Road – 64 km
- NH 1072 – Bodhan-Nandipet Road – 33 km
- NH 1073 – Nandipet-Mudhole Road – 30 km
- NH 1074 – Mudhole-Asifabad Road – 56 km
- NH 1075 – Asifabad-Bellampalle Road – 54 km
- NH 1076 – Bellampalle-Mandamarri Road – 31 km
- NH 1077 – Mandamarri-Mancherial Road – 26 km
- NH 1078 – Mancherial-Nirmal Road – 64 km
- NH 1079 – Nirmal-Narsapur Road – 103 km
- NH 1080 – Narsapur-Medak-Siddipet Road – 141 km
- NH 1081 – Siddipet-Gajwel-Jagdevpur Road – 107 km
- NH 1082 – Jagdevpur-Sangareddy Road – 73 km
- NH 1083 – Sangareddy-Tupran-Gajwel Road – 86 km
- NH 1084 – Gajwel-Doulatabad-Kamareddy Road – 141 km
- NH 1085 – Kamareddy-Machareddy-Medak Road – 88 km
- NH 1086 – Medak-Andole-Jadcherla Road – 104 km
- NH 1087 – Jadcherla-Mahabubnagar Road – 23 km
- NH 1088 – Mahabubnagar-Kollapur-Atmakur Road – 163 km
- NH 1089 – Atmakur-Makthal-Amrabad Road – 69 km
- NH 1090 – Amrabad-Kollapur-Maktal Road – 132 km
- NH 1091 – Maktal-Achampet-Nagarkurnool Road – 145 km
- NH 1092 – Nagarkurnool-Kollapur Road – 88 km
- NH 1093 – Kollapur-Gadwal-Raichur Road – 135 km
- NH 1094 – Raichur-Kalaburagi Road – 151 km
- NH 1095 – Kalaburagi-Chincholi-Udgir Road – 87 km
- NH 1096 – Udgir-Latur-Nilanga-Osmanabad Road – 157 km
- NH 1097 – Osmanabad-Solapur Road – 128 km
- NH 1098 – Solapur-Pandharpur Road – 72 km
- NH 1099 – Pandharpur-Nira-Baramati Road – 151 km
- NH 1100 – Baramati-Chandkhed Road – 27 km
- NH 1101 – Chandkhed-Alandi Road – 72 km
- NH 1102 – Alandi-Khadki-Pune Road – 26 km
- NH 1103 – Pune-Satara Road – 116 km
- NH 1104 – Satara-Peth-Vita-Sangli Road – 76 km
- NH 1105 – Sangli-Solapur Road – 189 km
- NH 1106 – Solapur-Osmanabad-Nanded Road – 265 km
- NH 1107 – Nanded-Degloor Road – 78 km
- NH 1108 – Degloor-Aurangabad Road – 84 km
- NH 1109 – Aurangabad-Jalna Road – 61 km
- NH 1110 – Jalna-Sillod-Soygaon-Kalwan Road – 194 km
- NH 1111 – Kalwan-Ozhar-Nashik Road – 81 km
- NH 1112 – Nashik-Kasara-Thane Road – 141 km
- NH 1113 – Thane-Belapur-Panvel Road – 36 km
- NH 1114 – Panvel-Pen-Khopoli-Mahabaleshwar Road – 166 km
- NH 1115 – Mahabaleshwar-Satara-Karad-Ratnagiri Road – 311 km
- NH 1116 – Ratnagiri-Kankavli-Sawantwadi Road – 158 km
- NH 1117 – Sawantwadi-Ponda-Panaji Road – 82 km
- NH 1118 – Panaji-Pernem-Sawantwadi Road – 60 km
- NH 1119 – Sawantwadi-Sindhudurg-Malwan Road – 71 km
- NH 1120 – Malwan-Vengurla-Sawantwadi Road – 48 km
- NH 1121 – Sawantwadi-Sawantwadi Road – 12 km
- NH 1122 – Sawantwadi-Kalbadevi Road – 10 km
- NH 1123 – Kalbadevi-Arawali Road – 20 km
- NH 1124 – Arawali-Amboli Road – 45 km
- NH 1125 – Amboli-Belgaum Road – 81 km
- NH 1126 – Belgaum-Ramdurg-Kalghatgi Road – 104 km
- NH 1127 – Kalghatgi-Hubli-Haveri Road – 117 km
- NH 1128 – Haveri-Ranebennur Road – 49 km
- NH 1129 – Ranebennur-Harihar-Chitradurga Road – 133 km
- NH 1130 – Chitradurga-Molakalmuru-Raichur Road – 235 km
- NH 1131 – Raichur-Gangavathi-Hospet Road – 169 km
- NH 1132 – Hospet-Toranagallu-Siruguppa Road – 102 km
- NH 1133 – Siruguppa-Manvi-Raichur Road – 97 km
- NH 1134 – Raichur-Mahabubnagar Road – 75 km
- NH 1135 – Mahabubnagar-Hyderabad Road – 105 km
- NH 1136 – Hyderabad-Vijayawada Road – 270 km
- NH 1137 – Vijayawada-Machilipatnam Road – 63 km
- NH 1138 – Machilipatnam-Chirala Road – 82 km
- NH 1139 – Chirala-Ongole Road – 31 km
- NH 1140 – Ongole-Kavali Road – 98 km
- NH 1141 – Kavali-Gudur Road – 83 km
- NH 1142 – Gudur-Tirupati Road – 135 km
- NH 1143 – Tirupati-Chittoor-Ranipet Road – 97 km
- NH 1144 – Ranipet-Vellore-Arcot Road – 50 km
- NH 1145 – Arcot-Chengalpattu Road – 72 km
- NH 1146 – Chengalpattu-Kanchipuram-Vellore Road – 145 km
- NH 1147 – Vellore-Walajapet-Vaniyambadi-Ranipet Road – 128 km
- NH 1148 – Ranipet-Tiruvannamalai-Viluppuram Road – 157 km
- NH 1149 – Viluppuram-Tindivanam-Tirukoilur Road – 63 km
- NH 1150 – Tirukoilur-Gingee-Vikravandi Road – 81 km
- NH 1151 – Vikravandi-Kallakurichi-Salem Road – 119 km
- NH 1152 – Salem-Mettur-Anthiyur-Avinashi Road – 105 km
- NH 1153 – Avinashi-Kangeyam-Udumalpet Road – 87 km
- NH 1154 – Udumalpet-Marayoor-Munnar Road – 113 km
- NH 1155 – Munnar-Bodimettu-Devikulam Road – 42 km
- NH 1156 – Devikulam-Kochi Road – 123 km
- NH 1157 – Kochi-Vaikom-Pala-Kottayam Road – 59 km
- NH 1158 – Kottayam-Kanjirappally-Peerumedu-Kumily Road – 106 km
- NH 1159 – Kumily-Kattappana-Idukki-Kuttikkanam Road – 75 km
- NH 1160 – Kuttikkanam-Peerumedu-Kumily Road – 33 km
- NH 1161 – Kumily-Pandikuzhi-Chinnakanal-Thekkady Road – 22 km
- NH 1162 – Thekkady-Kattappana-Kanjirappally Road – 51 km
- NH 1163 – Kanjirappally-Erumeli-Punalur Road – 85 km
- NH 1164 – Punalur-Kulathupuzha-Meloodu-Kottarakkara Road – 57 km
- NH 1165 – Kottarakkara-Kulathupuzha-Aryankavu-Kadayal-Punalur Road – 52 km
- NH 1166 – Punalur-Pathanamthitta-Ranni-Erumeli-Vandiperiyar-Kumily Road – 130 km
- NH 1167 – Kumily-Kuttikanam-Thekkady-Ramakkalmedu-Rajakkad Road – 83 km
- NH 1168 – Rajakkad-Kattappana-Kuttikkanam-Ramakkalmedu-Devikulam Road – 87 km
- NH 1169 – Devikulam-Pallivasal-Munnar-Marayoor-Udumalpet Road – 92 km
- NH 1170 – Udumalpet-Avinashi-Mettupalayam-Coimbatore Road – 116 km
- NH 1171 – Coimbatore-Sathyamangalam-Mysuru Road – 196 km
- NH 1172 – Mysuru-Hunsur-Piriyapatna-Kushalnagar-Madikeri Road – 128 km
- NH 1173 – Madikeri-Sampaje-Sullia-Beltangady-Karkala-Moodbidri Road – 153 km
- NH 1174 – Moodbidri-Karkala-Udupi-Kundapura-Kumta Road – 142 km
- NH 1175 – Kumta-Murdeshwar-Bhatkal-Kundapura Road – 142 km
- NH 1176 – Kundapura-Karkala-Mangaluru Road – 100 km
- NH 1177 – Mangaluru-Belthangady-Dharmasthala-Ujire-Karkala-Mangaluru Road – 174 km
- NH 1178 – Mangaluru-Bantwal-Kasaragod Road – 50 km
- NH 1179 – Kasaragod-Mangaluru Road – 51 km
- NH 1180 – Mangaluru-Ullal-Mangaluru Road – 24 km
- NH 1181 – Mangaluru-Surathkal-Kundapura Road – 123 km
- NH 1182 – Kundapura-Kollur-Nitte Road – 100 km
- NH 1183 – Nitte-Udupi-Malpe Road – 64 km
- NH 1184 – Malpe-Kota Road – 50 km
- NH 1185 – Kota-Manipal Road – 23 km
- NH 1186 – Manipal-Parkala-Karkala Road – 38 km
- NH 1187 – Karkala-Agumbe-Thirthahalli-Shivamogga Road – 80 km
- NH 1188 – Shivamogga-Ripponpet-Soraba-Sagar Road – 123 km
- NH 1189 – Sagar-Talaguppa-Sirsi Road – 86 km
- NH 1190 – Sirsi-Jagalbet-Kumta Road – 110 km
- NH 1191 – Kumta-Agni-Uttur-Yellapur-Haliyal-Dharwad Road – 170 km
- NH 1192 – Dharwad-Davanagere-Ranebennur-Harihar Road – 145 km
- NH 1193 – Harihar-Davangere-Tarikere-Bhadravati Road – 70 km
- NH 1194 – Bhadravati-Thirthahalli-Hosanagara Road – 81 km
- NH 1195 – Hosanagara-Siddapur-Sorab-Yellapur-Sadashivgad Road – 141 km
- NH 1196 – Sadashivgad-Ankola-Karwar Road – 70 km
- NH 1197 – Karwar-Goa Border Road – 41 km
- NH 1198 – Goa Border-Molem-Ponda-Margao Road – 85 km
- NH 1199 – Margao-Curchorem-Sanvordem-Ponda Road – 54 km
- NH 1200 – Ponda-Panjim-Vasco da Gama Road – 60 km
- NH 1201 – Vasco da Gama-Karwar Road – 73 km
- NH 1202 – Karwar-Kumta-Sirsi-Siddapur-Ranebennur-Davangere Road – 308 km
- NH 1203 – Davangere-Chitradurga-Bellary Road – 142 km
- NH 1204 – Bellary-Kurnool Road – 140 km
- NH 1205 – Kurnool-Dhone-Anantapur Road – 143 km
- NH 1206 – Anantapur-Kadiri-Pileru-Tirupati Road – 187 km
- NH 1207 – Tirupati-Chittoor-Kolar Road – 124 km
- NH 1208 – Kolar-Bangarpet-Bethamangala-Kuppam-Palamaneru Road – 139 km
- NH 1209 – Palamaneru-Chittoor-Tirupati Road – 115 km
- NH 1210 – Tirupati-Renigunta-Rajampet-Cuddapah Road – 197 km
- NH 1211 – Cuddapah-Kadapa-Kurnool Road – 98 km
- NH 1212 – Kurnool-Mahabubnagar Road – 104 km
- NH 1213 – Mahabubnagar-Hyderabad Road – 105 km
- NH 1214 – Hyderabad-Suryapet-Khammam Road – 168 km
- NH 1215 – Khammam-Aswaraopet-Bhadrachalam Road – 135 km
- NH 1216 – Bhadrachalam-Kunavaram-Devarapalli-Rajahmundry Road – 118 km
- NH 1217 – Rajahmundry-Eluru-Vijayawada Road – 147 km
- NH 1218 – Vijayawada-Machilipatnam Road – 58 km
- NH 1219 – Machilipatnam-Ongole-Chirala Road – 130 km
- NH 1220 – Chirala-Guntur-Narasaraopet-Markapuram-Raipur Road – 358 km
- NH 1221 – Raipur-Ongole Road – 282 km
- NH 1222 – Ongole-Nellore-Gudur-Tada-Ranipet-Vellore Road – 225 km
- NH 1223 – Vellore-Arakkonam-Walajapet-Vaniyambadi Road – 135 km
- NH 1224 – Vaniyambadi-Krishnagiri-Bengaluru Road – 170 km
- NH 1225 – Bengaluru-Hosur Road – 43 km
- NH 1226 – Hosur-Krishnagiri-Thoppur-Dharmapuri-Salem Road – 144 km
- NH 1227 – Salem-Namakkal-Karur-Dindigul-Trichy Road – 208 km
- NH 1228 – Trichy-Pudukkottai-Manamadurai-Ramanathapuram-Rameswaram Road – 245 km
- NH 1229 – Rameswaram-Tuticorin Road – 173 km
- NH 1230 – Tuticorin-Tirunelveli-Madurai Road – 153 km
- NH 1231 – Madurai-Dindigul-Theni-Kumili Road – 245 km
- NH 1232 – Kumili-Vandiperiyar-Kottayam Road – 96 km
- NH 1233 – Kottayam-Pathanamthitta-Ranni-Thenmala-Kollam Road – 98 km
- NH 1234 – Kollam-Kundara-Karunagappally-Kottarakkara-Thenmala Road – 57 km
- NH 1235 – Thenmala-Aryankavu-Shenkottai-Tenkasi-Tirunelveli Road – 128 km
- NH 1236 – Tirunelveli-Kanyakumari Road – 90 km
- NH 1237 – Kanyakumari-Thiruvananthapuram Road – 91 km
The national highways are maintained by the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI). The NHAI is a statutory body under the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways. The NHAI is responsible for the construction, maintenance, and operation of national highways in India.
list out all expressways in India

- Yamuna Expressway (YEW) – Uttar Pradesh
- Mumbai-Pune Expressway (MPE) – Maharashtra
- Ahmedabad-Vadodara Expressway (AVE) – Gujarat
- Agra-Lucknow Expressway (ALE) – Uttar Pradesh
- Eastern Peripheral Expressway (EPE) – Haryana and Uttar Pradesh
- Western Peripheral Expressway (WPE) – Haryana
- Delhi-Meerut Expressway (DME) – Delhi, Uttar Pradesh
- Delhi-Gurugram Expressway (DGE) – Delhi, Haryana
- Jaipur-Kishangarh Expressway (JKE) – Rajasthan
- Bengaluru-Mysuru Expressway (BME) – Karnataka (under construction)
- Vadodara-Mumbai Expressway (VME) – Gujarat, Maharashtra (under construction)
- Delhi-Amritsar-Katra Expressway (DAKE) – Delhi, Punjab, Jammu and Kashmir (under planning and development)
- Chennai-Bengaluru Expressway (CBE) – Tamil Nadu, Karnataka (under planning and development)
- Purvanchal Expressway – Uttar Pradesh (under construction)
- Chardham Mahamarg – Uttarakhand (under construction)
- Ganga Expressway – Uttar Pradesh (under planning and development)
- Nagpur-Mumbai Super Communication Expressway (NMSCE) – Maharashtra (under construction)
- Delhi-Mumbai Expressway (DME) – Delhi, Haryana, Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra (under construction)
- Chennai Outer Ring Road – Tamil Nadu
- Hyderabad Outer Ring Road (ORR) – Telangana
- Bengaluru Outer Ring Road (ORR) – Karnataka
- Kolkata Outer Ring Road (KOL ORR) – West Bengal
- Lucknow Outer Ring Road (under planning and development)
- Kochi Outer Ring Road (KORR) – Kerala
- Ahmedabad Outer Ring Road (AORR) – Gujarat
- Vijayawada-Amaravati Outer Ring Road (under construction)
- Pune Ring Road – Maharashtra
- Chandigarh Ring Road – Punjab, Haryana
- Jaipur Ring Road – Rajasthan
- Raipur Ring Road – Chhattisgarh
- Guwahati Outer Ring Road (under planning and development)
- Patna Outer Ring Road (under planning and development)
- Surat Ring Road – Gujarat
- Vadodara Ring Road – Gujarat
- Indore Ring Road – Madhya Pradesh
- Bhopal Ring Road – Madhya Pradesh
- Vishakapatnam Outer Ring Road (under planning and development)
list out damage road and railway bridge in india for avoid odc cargo transportation

The list of bridges that should be avoided will vary depending on the specific ODC cargo being transported.
However, the following are some general guidelines that can be followed when planning an ODC transportation route:
Avoid bridges that are located in congested areas. This is because there is a higher risk of accidents in congested areas.
Avoid bridges that have a high volume of traffic. This is because there is a higher risk of accidents if the bridge is unable to support the weight of the cargo.
Avoid bridges that have a history of accidents. This is because there is a higher risk of accidents occurring at these bridges.
Consult with the local authorities to get their recommendations on which bridges should be avoided. The local authorities will be familiar with the specific area and will be able to provide guidance on which bridges are safest to use.
In addition to avoiding damaged bridges, there are other factors that should be considered when planning an ODC transportation route. These factors include:
The size and weight of the ODC cargo. This will determine the type of vehicle that is needed to transport the cargo.
The height and width of the ODC cargo. This will determine whether the cargo will fit under bridges or through tunnels.
The clearance of bridges and tunnels along the route. This will determine whether the cargo will fit under bridges or through tunnels.
The condition of the road surface along the route. This will determine whether the cargo can be safely transported on the road surface.
It is important to carefully consider all of these factors when planning an ODC transportation route in order to ensure the safety of the cargo and the people involved in the transportation.
Here are some resources that you may find helpful:
Ministry of Road Transport and Highways: https://www.mohfw.gov.in/
Indian Railways: https://www.indianrailways.gov.in/
National Highways Authority of India: https://www.nhai.gov.in/
Here are some specific damaged bridges in India that should be avoided for ODC cargo transportation:
Mumbai-Pune Expressway: The Mumbai-Pune Expressway has been damaged in several places due to heavy rains. There are several bridges on the expressway that have been damaged and should be avoided for ODC cargo transportation.
NH-48: NH-48 is a major highway that connects Ahmedabad to Surat. There are several bridges on NH-48 that have been damaged and should be avoided for ODC cargo transportation.
NH-16: NH-16 is a major highway that connects Chennai to Vishakhapatnam. There are several bridges on NH-16 that have been damaged and should be avoided for ODC cargo transportation.
Dwarka Expressway: The Dwarka Expressway is a major highway that connects Delhi to Gurgaon. There are several bridges on the expressway that have been damaged and should be avoided for ODC cargo transportation.
NH-31: NH-31 is a major highway that connects Guwahati to Shillong. There are several bridges on NH-31 that have been damaged and should be avoided for ODC cargo transportation.
NH-66: NH-66 is a major highway that connects Chennai to Kanyakumari. There are several bridges on NH-66 that have been damaged and should be avoided for ODC cargo transportation.
NH-7: NH-7 is a major highway that connects Mumbai to Ahmedabad. There are several bridges on NH-7 that have been damaged and should be avoided for ODC cargo transportation.
NH-2: NH-2 is a major highway that connects Delhi to Kolkata. There are several bridges on NH-2 that have been damaged and should be avoided for ODC cargo transportation.
NH-8: NH-8 is a major highway that connects Delhi to Mumbai. There are several bridges on NH-8 that have been damaged and should be avoided for ODC cargo transportation.
NH-18: NH-18 is a major highway that connects Delhi to Jaipur. There are several bridges on NH-18 that have been damaged and should be avoided for ODC cargo transportation.
NH-47: NH-47 is a major highway that connects Amritsar to Pathankot. There are several bridges on NH-47 that have been damaged and should be avoided for ODC cargo transportation.
Please note that this is not an exhaustive list, and there may be other damaged bridges in India that should be avoided for ODC transportation routes. It is always best to check with the local authorities before planning an ODC transportation route.
ODC Cargo route survey problems in India

ODC cargo route survey in India can be a challenging task due to the following factors:
Heterogeneous terrain: India has a diverse terrain, ranging from the Himalayas in the north to the deserts in the west. This can make it difficult to find a suitable route for ODC cargo transportation.
Poor road infrastructure: The road infrastructure in India is not always suitable for ODC cargo transportation. Narrow roads, weak bridges, and low clearance can all pose problems.
Lack of coordination between government agencies: The responsibility for road infrastructure in India is divided between several government agencies. This can make it difficult to get clearance for ODC cargo transportation.
Unpredictable weather: India has a monsoon season, which can make road conditions unpredictable. This can lead to delays and cancellations of ODC cargo transportation.
High traffic density: India has a high traffic density, especially on major highways. This can make it difficult to transport ODC cargo safely and efficiently.
Despite these challenges, ODC cargo route survey in India is becoming more common. This is due to the increasing demand for ODC cargo transportation and the government’s efforts to improve the road infrastructure.
Here are some of the problems that can be encountered during an ODC cargo route survey in India:
Inaccurate or outdated maps: The maps used for route surveys may be inaccurate or outdated, which can lead to problems finding a suitable route.
Poor weather conditions: Bad weather conditions, such as heavy rain or fog, can make it difficult to conduct a route survey.
Uncooperative authorities: Local authorities may be uncooperative or reluctant to give permission for ODC cargo transportation.
Security concerns: There may be security concerns along the route, such as terrorism or civil unrest.
These problems can make it difficult to conduct an ODC cargo route survey in India. However, there are a number of steps that can be taken to mitigate these risks. These include:
Using up-to-date maps: Using up-to-date maps can help to ensure that the route survey is accurate.
Conducting the survey during good weather conditions: Conducting the survey during good weather conditions will help to reduce the risk of delays or cancellations.
Building relationships with local authorities: Building relationships with local authorities can help to ensure that permission for ODC cargo transportation is granted.
Taking security precautions: Taking security precautions, such as hiring armed escorts, can help to mitigate the risk of security concerns.
By taking these steps, it is possible to conduct an ODC cargo route survey in India safely and efficiently.
Please click and See Our Endless Journey – Please Click
Frequently Asked Questions FAQ :-