What is Mining ?
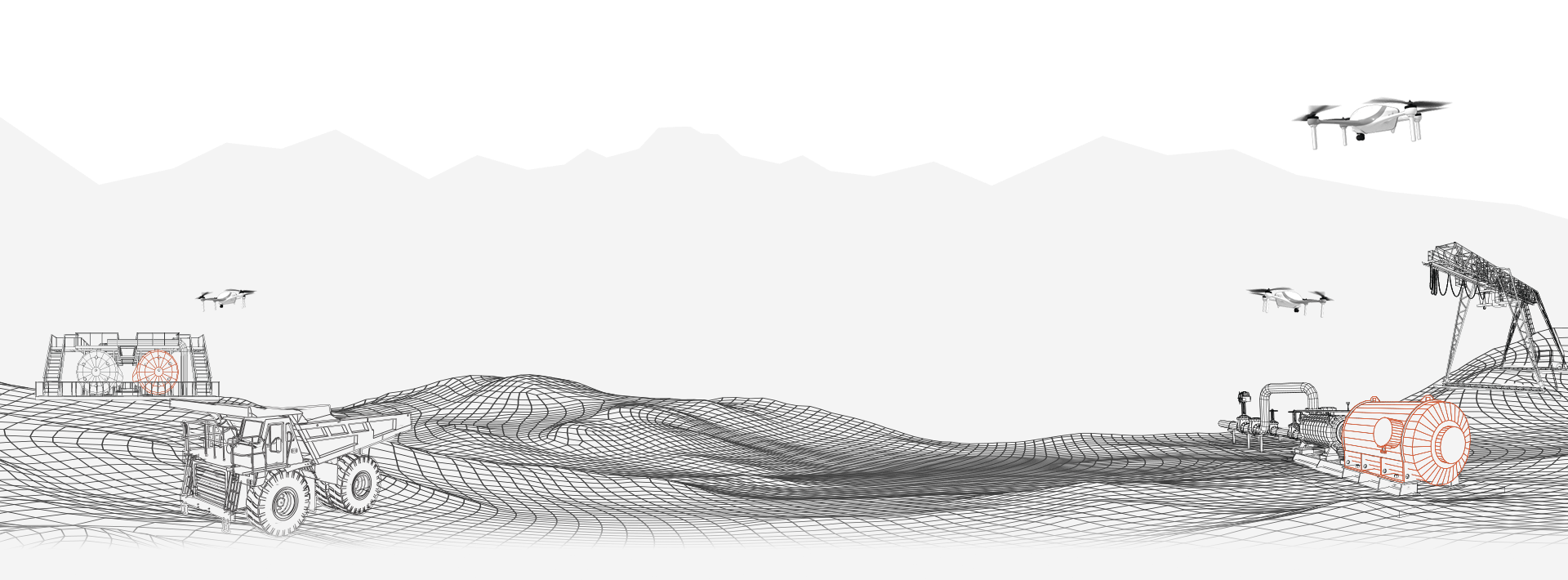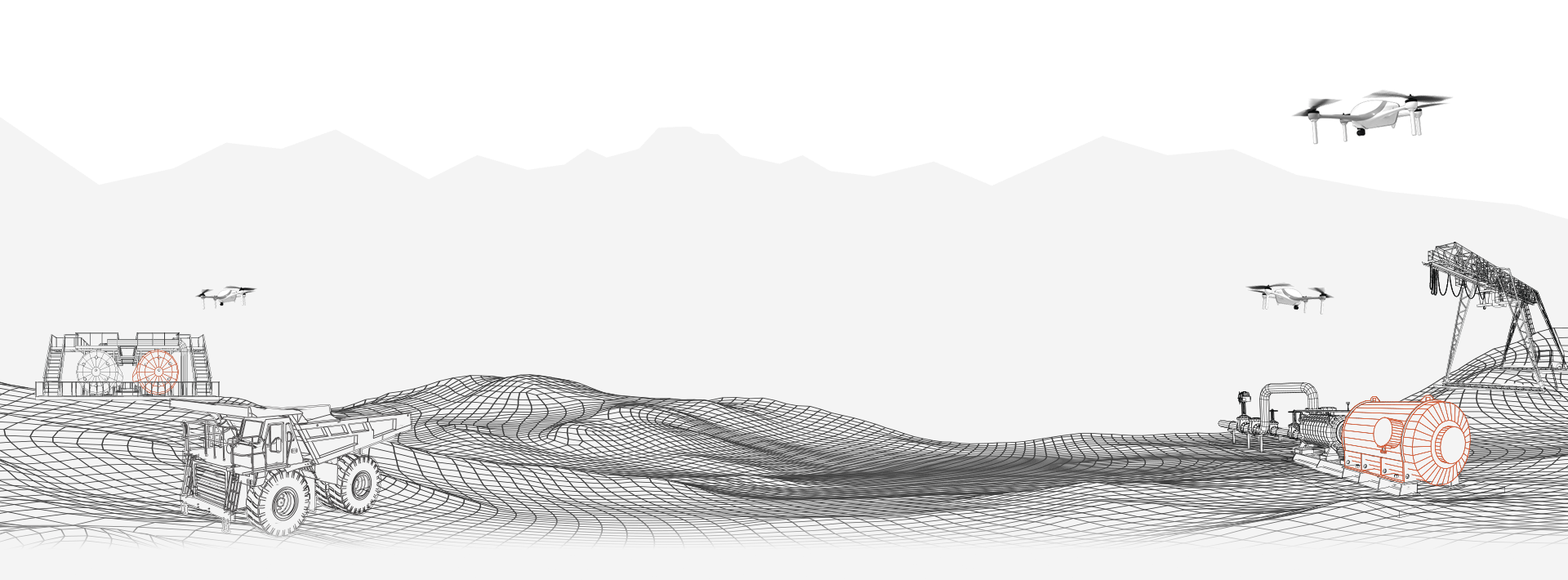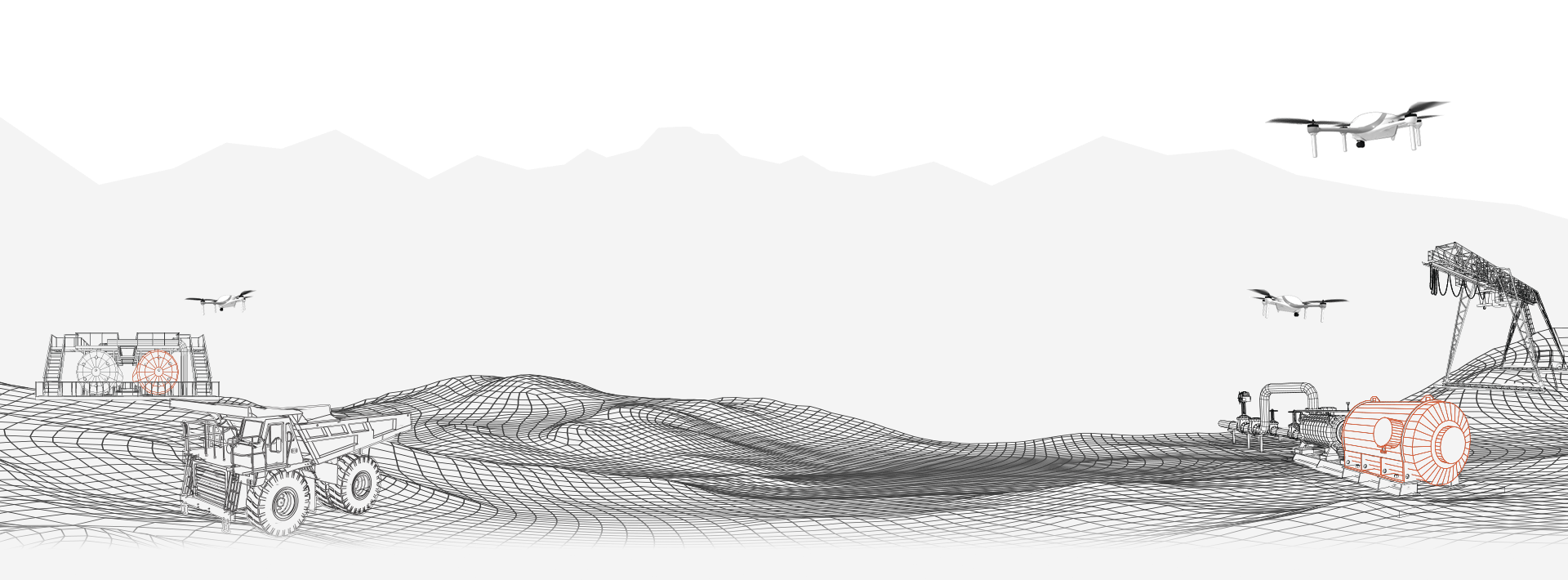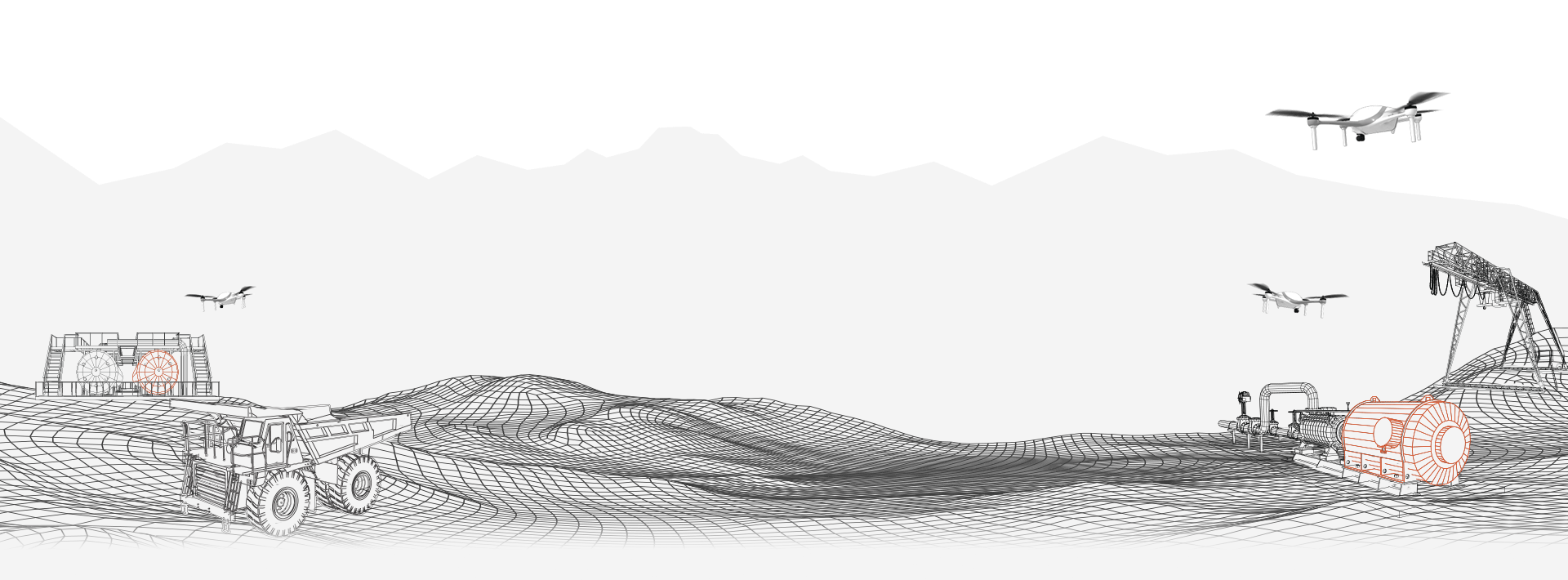
In industry, mining refers to the process of extracting valuable resources from the Earth. These resources can be broadly categorized into two main groups:
Minerals: This includes metals like gold, copper, and iron ore, as well as non-metallic minerals like limestone, clay, and gemstones.
Fossil fuels: Coal, oil shale, and natural gas are all extracted through mining techniques.
Here’s a breakdown of the mining process:
Prospecting and Exploration: Geologists and engineers search for potential deposits of minerals or fossil fuels. This may involve geological surveys, drilling, and other techniques.
Feasibility Study: Once a potential deposit is identified, an economic analysis is done to assess the profitability of mining it. This considers factors like the cost of extraction, the amount of resources present, and the selling price of the materials.
Mine Development: If the feasibility study is positive, the mine is developed. This involves obtaining permits, building infrastructure like access roads and processing plants, and implementing safety measures.
Extraction: There are two main types of extraction methods: surface mining and underground mining. The choice of method depends on the depth and location of the deposit.
Processing and Reclamation: Once extracted, the raw materials may need to be processed to remove impurities or separate valuable components. Finally, after the mine reaches the end of its operational life, reclamation efforts are undertaken to minimize the environmental impact.
Mining is a crucial industry as it provides us with the raw materials needed for a wide range of products, from construction materials and electronics to medicine and fertilizers. However, it’s important to acknowledge that mining can also have negative environmental and social impacts.
Worldwide Mining Industry Evolution ?
| Era | Estimated Time Period | Key Developments |
|---|---|---|
| Early Use | 40,000 – 10,000 years ago | – Early humans extract basic materials like flint for tools and ochre for pigments. – Simple pit digging and gathering techniques used. |
| Rise of Civilizations | 10,000 – 2,000 years ago | – Development of more organized mining activities. – Extraction of copper, gold, silver, and other valuable minerals begins. – Use of fire for processing materials. |
| Large-Scale Techniques | 2,000 years ago – Present | – Romans develop sophisticated mining methods like aqueducts for water transport. – Technological advancements lead to deeper and more complex mining operations. – The Industrial Revolution significantly increases demand for minerals and fuels, driving further development of the industry. |
| Modern Era (Present & Future) | 20th Century – Present | – Focus on automation, mechanization, and efficiency in mining processes. – Growing concerns about environmental impact lead to development of sustainable mining practices. – Increased demand for critical minerals for renewable energy and technology. |
Types of Mining
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Surface Mining | – Removes overburden (waste material) to expose the desired mineral or fossil fuel deposit. – Less expensive than underground mining but can have a larger environmental footprint. |
| Underground Mining | – Involves creating tunnels and shafts to access mineral or fossil fuel deposits located deep underground. – More expensive than surface mining but can be necessary for deep deposits. |
| In-Situ Leaching | – Dissolves minerals underground using a solution, then pumps the solution to the surface for processing. – Less disruptive to the surface but may have environmental concerns related to solution leakage. |
| Placer Mining | – Extracts loose deposits of valuable minerals from riverbeds, streambeds, or beaches. – Often uses techniques like panning or dredging. – Can have environmental impacts on waterways. |
Who When and Why Invented Mining ?
| Era | Estimated Time Period | Key Developments |
|---|---|---|
| Early Use | Prehistoric – 3300 BCE | – Early inhabitants used basic materials like flint for tools. – Limited evidence exists, but some form of rudimentary mining likely occurred. |
| Indus Valley Civilization | 3300-1300 BCE | – Evidence suggests use of copper and bronze tools, indicating some form of metal ore mining. – Fire likely used for processing materials. |
| Historical Period | 1300 BCE – 18th Century | – Increased focus on mining metals like gold, silver, iron, and diamonds. – Development of underground mining techniques. |
| Colonial Era & Modern Times | 18th Century – Present | – Arrival of Europeans led to advancements in mining technology and larger-scale operations. – Focus on coal mining during the Industrial Revolution. – Modernization of mining industry with increased mechanization and regulations. |
History of Mining Industry in India
India has a long and rich history of mining, dating back to prehistoric times. Here’s a breakdown of its key phases:
Early Use (Prehistoric – 3300 BCE):
Evidence suggests early inhabitants of India used basic materials like flint for tools.
There’s limited information on this period, but some form of rudimentary mining likely existed.
Indus Valley Civilization (3300-1300 BCE):
Tools and Ornaments: The Indus Valley Civilization used copper and bronze tools, indicating some form of metal ore mining.
Fire for Processing: Fire was likely used for processing mined materials.
Historical Period (1300 BCE – 18th Century):
Increased Focus on Metals: Mining activities intensified, focusing on metals like gold, silver, iron, and diamonds.
Underground Techniques: Development of underground mining techniques to access deeper deposits.
Colonial Era & Modern Times (18th Century – Present):
European Arrival: The arrival of Europeans like the British East India Company in the 18th century led to advancements in mining technology and larger-scale operations.
Industrial Revolution: The Industrial Revolution fueled a demand for coal mining to power machinery and transportation.
Modernization: The 20th century saw the modernization of the mining industry with increased mechanization, regulations, and establishment of bodies like the Indian Bureau of Mines (1948).
Nationalization: The government nationalized coal mines in phases, leading to the formation of Coal India Limited (CIL) in 1975.
Liberalization: Economic liberalization in the 1990s allowed for greater private sector participation in exploration and mining.
Key Points to Remember:
The mining industry in India has significantly contributed to the nation’s economy by providing essential resources for infrastructure, tools, and industrial development.
However, the industry also faces challenges related to environmental impact, safety regulations, and sustainable practices.
Looking Forward:
The future of mining in India likely involves:
Focus on sustainable practices: Minimizing environmental damage and adopting eco-friendly methods.
Technological advancements: Utilizing automation, robotics, and data analytics for efficiency and safety.
Exploration of new resources: Meeting the growing demand for critical minerals used in renewable energy and technology.
This glimpse into India’s mining history highlights its evolution from early human needs to a modern industry. As the industry navigates future challenges, it will play a crucial role in India’s economic and technological development.
Here are a few interesting facts about the Indian Mining Industry:
Rich in Mineral Resources: India boasts a vast reserve of minerals, ranking among the top producers of coal, iron ore, bauxite, mica, and many more. For instance, it possesses the largest known reserves of barytes in the world.
Ancient Practices, Modern Industry: While mining in India has prehistoric roots, the industry has adopted modern techniques. Today, India is the world’s second-largest producer of cement and coal.
Economic Contributor: The mining sector plays a significant role in the Indian economy, although the GDP contribution directly is around 2-3%. However, it contributes significantly to allied industries and provides employment to a large population.
Focus on Sustainability: The industry is increasingly aware of its environmental impact and is working towards sustainable mining practices. This includes efforts to minimize environmental damage during extraction and implementing reclamation efforts for used mines.
I hope you find these facts interesting!
List of Mines in North East India

Here’s a more detailed list of mines in North East India:
Dilli-Jaintia Coal Mines
Location: East Jaintia Hills District, Meghalaya
Type: Underground Coal Mine
Ownership: Private
Description: The Dilli-Jaintia coal mines are situated in the East Jaintia Hills District of Meghalaya. These mines contribute significantly to the coal production in the region.
Umarsar Coal Mine
Location: South Garo Hills District, Meghalaya
Type: Open-pit Coal Mine
Ownership: Private/Public
Description: Umarsar coal mine is one of the major open-pit coal mines in Meghalaya, extracting coal from the South Garo Hills District.
Ledo Colliery
Location: Tinsukia District, Assam
Type: Underground Coal Mine
Ownership: Public/Private
Description: Ledo Colliery is one of the oldest coal mines in Assam, known for its historical significance in the coal mining industry of Northeast India.
Tirap Colliery
Location: Tirap District, Arunachal Pradesh
Type: Open-pit Coal Mine
Ownership: Public/Private
Description: Tirap Colliery is an open-pit coal mine located in the Tirap District of Arunachal Pradesh, contributing to the coal production in the state.
Namchik-Namphuk Coal Mine
Location: Changlang District, Arunachal Pradesh
Type: Open-pit Coal Mine
Ownership: Public/Private
Description: The Namchik-Namphuk coal mine is one of the major coal mines in Arunachal Pradesh, situated in the Changlang District and known for its coal reserves.
Baragolai Colliery
Location: Dibrugarh District, Assam
Type: Underground Coal Mine
Ownership: Public/Private
Description: Baragolai Colliery is an underground coal mine located in the Dibrugarh District of Assam, playing a significant role in the coal mining industry of the region.
Kopili Opencast Coal Mines
Location: Dima Hasao District, Assam
Type: Open-pit Coal Mine
Ownership: Public/Private
Description: The Kopili Opencast Coal Mines are situated in the Dima Hasao District of Assam, contributing to the coal production in the state through open-pit mining operations.
Chabua Coal Mine
Location: Dibrugarh District, Assam
Type: Underground Coal Mine
Ownership: Public/Private
Description: Chabua Coal Mine is an underground coal mine located in the Dibrugarh District of Assam, playing a crucial role in meeting the coal demand in the region.
These mines represent some of the significant contributors to the mining industry in North East India, extracting various minerals including coal, which is a prominent natural resource in the region.
List of Mines in North India

I can provide you with a general overview of the types of mines and key details you might find for each:
Coal Mines:
Singrauli Coalfield (Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh): Operated by Northern Coalfields Limited (NCL) and others.
Jhilmili Coalfield (Chhattisgarh): Operated by South Eastern Coalfields Limited (SECL) and others.
Sonebhadra Coalfield (Uttar Pradesh): Includes mines operated by Northern Coalfields Limited (NCL).
Copper Mines:
Khetri Copper Mine (Rajasthan): Operated by Hindustan Copper Limited.
Malanjkhand Copper Mine (Madhya Pradesh): Operated by Hindustan Copper Limited.
Zinc Mines:
Rampura Agucha Mine (Rajasthan): Operated by Hindustan Zinc Limited.
Balaria Lead-Zinc Mine (Rajasthan): Operated by Hindustan Zinc Limited.
Kayad Lead-Zinc Mine (Rajasthan): Operated by Hindustan Zinc Limited.
Uranium Mines:
Jaduguda Uranium Mine (Jharkhand): Operated by Uranium Corporation of India Limited (UCIL).
Lignite Mines:
Giral Lignite Mine (Rajasthan): Operated by Rajasthan State Mines and Minerals Limited (RSMML).
For detailed information about each mine, including production capacity, reserves, ownership, and operational status, you would typically need to refer to government publications, mining company reports, or industry databases. These sources provide the most accurate and up-to-date information on mines in India. Additionally, specific details may vary over time due to changes in ownership, regulations, or mining activities.
List of Mines in Western India
Here’s a list of mines in Western India, covering various minerals and resources:
Bauxite Mines:
Gujarat:
Alumina Refinery and Bauxite Mines at Alumina Nagar, Jamnagar.
Bauxite mines in Kutch district.
Limestone Mines:
Gujarat:
Limestone mines in Saurashtra region, including Rajula, Junagadh, and Amreli districts.
Limestone mines in Kutch district.
Coal Mines:
Gujarat:
Coal mines in the Tapi and Surat districts.
Vastan Lignite Mine in Surat district.
Iron Ore Mines:
Goa:
Several iron ore mines in the regions of North Goa and South Goa, although mining operations have been affected by regulatory issues in recent years.
Copper Mines:
Gujarat:
Copper mines near Ambaji in Banaskantha district.
Oil and Gas Fields:
Gujarat:
Ankleshwar Oil and Gas Field.
Cambay Oil and Gas Field.
Kalol Oil and Gas Field.
Salt Mines:
Gujarat:
Salt mines along the coastline in districts such as Kutch and Jamnagar.
Gypsum Mines:
Rajasthan:
Gypsum mines in Bikaner district.
Please note that this list may not be exhaustive, but it covers some significant mines in Western India across different minerals and resources. Additionally, the status and operational details of these mines may vary, and further research would be needed to obtain comprehensive information.
List of Mines in South India

Here’s a list of mines in South India, covering various minerals and resources:
Iron Ore Mines:
Karnataka:
Bellary-Hospet region: Hospet, Sandur, Bellary, Chitradurga districts.
Kudremukh mines in Chikkamagaluru district (Closed since 2006 due to environmental concerns).
Coal Mines:
Telangana:
Singareni Collieries Company Limited (SCCL) operates several coal mines in the Singareni coalfields.
Limestone Mines:
Andhra Pradesh:
Kadapa, Anantapur, Guntur, and Nalgonda districts have limestone mines.
Bauxite Mines:
Andhra Pradesh:
Visakhapatnam district has bauxite mines.
Telangana:
Adilabad district.
Gold Mines:
Karnataka:
Hutti Gold Mines in Raichur district.
Kolar Gold Fields (historic mines, now closed) in Kolar district.
Granite Mines:
Tamil Nadu:
Tamil Nadu is known for its granite reserves, particularly in districts like Madurai, Krishnagiri, Salem, and Dharmapuri.
Mica Mines:
Andhra Pradesh:
Nellore district.
Oil and Gas Fields:
Andhra Pradesh:
Krishna-Godavari Basin.
Please note that this list may not be exhaustive, and the operational status of these mines may vary. Additionally, further research would be needed to obtain detailed information about each mine, including ownership, production, and reserves.
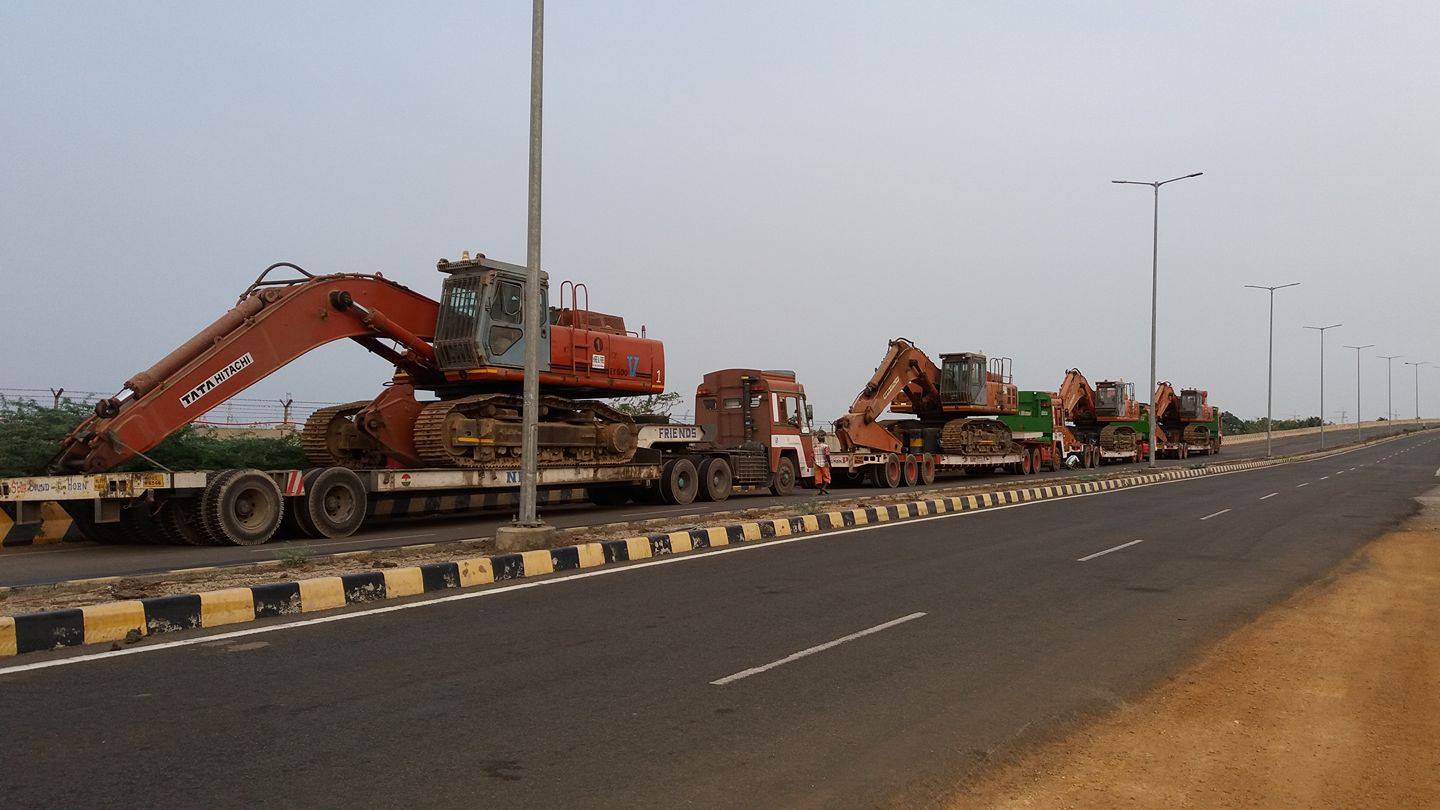
ABCC India Project Cargo Best for Mining Industries Goods Transportation
“ABCC India Project Cargo” indeed stands out as a reliable option for transporting goods, especially for the mining industry. Their specialization in project cargo suggests they have the expertise and equipment to handle large, heavy, and specialized shipments that are typical in the mining sector. Here’s why they might be a good choice:
- Expertise in Project Cargo: Mining equipment and machinery often require specialized handling due to their size, weight, and complexity. ABCC India’s focus on project cargo indicates they have experience in managing such shipments, ensuring they reach their destination safely and on time.
- Customized Solutions: Mining projects often involve transporting equipment to remote and challenging locations. ABCC India likely offers customized transportation solutions tailored to the specific needs of mining companies, including route planning, logistics coordination, and overcoming regulatory hurdles.
- Safety and Compliance: Safety is paramount in the mining industry, and transporting heavy equipment requires strict adherence to safety regulations. ABCC India’s track record in project cargo suggests they prioritize safety and compliance, mitigating risks associated with transporting valuable mining assets.
- Global Network: Many mining projects span across borders or operate in remote regions. ABCC India’s global network and partnerships likely enable them to facilitate transportation across international borders and provide seamless logistics support wherever mining operations may be located.
- Efficiency and Reliability: Timely delivery of equipment is crucial for mining projects to stay on schedule and within budget. ABCC India’s reputation for reliability and efficiency in project cargo transportation suggests they can meet tight deadlines and deliver goods promptly to mining sites.
However, it’s always advisable to conduct thorough research and due diligence before selecting a transportation provider. Evaluating factors such as reputation, past performance, client testimonials, and adherence to industry standards can help ensure you choose the best option for your specific transportation needs in the mining industry.
Basic Raw Material Supplier in Mining Industries
I can provide a framework to help you find suitable raw material suppliers for the mining industry:
| Category | Example Suppliers (India) | Services Offered | Why Consider |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explosives & Detonators | * Indian Explosives Limited (IEL) – Pune* | – Commercial explosives, detonators, and blasting accessories. | – Established player with a wide range of products. |
| Drilling Equipment & Parts | * Sandvik Mining and Rock Technology – Pune* | – Drill rigs, drill bits, and related spare parts. | – Reputed manufacturer offering a complete drilling solution. |
| Grinding Media | * Metso Outotec India Private Limited – Pune* | – Grinding balls, mill liners, and wear protection solutions. | – Global leader in grinding media with a focus on efficiency. |
| Conveyor Systems & Components | * Elecon Engineering Company Limited – Gujarat* | – Design, manufacture, and installation of conveyor systems. | – Indian manufacturer offering customized conveyor solutions. |
| Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) | * Uvex Safety India Private Limited – Pune* | – Wide range of safety equipment for miners. | – Reputable brand offering comprehensive worker protection. |
Mining Industry Contribution in Indian Economy
The Mining Industry’s contribution to the Indian economy is multifaceted, with both direct and indirect impacts. Here’s a breakdown:
Direct Contribution:
GDP: While the direct contribution of mining to India’s GDP is around 2-2.5%, it plays a crucial role in providing essential raw materials for other sectors.
Employment: The industry employs a significant number of people, both directly in mines and indirectly in processing plants and transportation.
Revenue Generation: Mining activities generate revenue for the government through taxes and royalties on extracted minerals.
Indirect Contribution:
Fueling Other Industries: Mining provides raw materials like coal, iron ore, limestone, and bauxite, which are essential for industries like steel, cement, power generation, and construction. A robust mining sector helps these allied industries thrive, contributing significantly to the overall economy.
Infrastructure Development: Minerals are essential for building infrastructure like roads, bridges, and railways. A flourishing mining industry ensures a steady supply of these materials, facilitating infrastructure development across the country.
Export Potential: India exports some minerals like iron ore and mica, generating foreign exchange and boosting the economy.
Challenges and Considerations:
Environmental Impact: Mining activities can have negative environmental consequences like deforestation, air and water pollution, and land degradation. Sustainable mining practices are crucial for mitigating these impacts.
Safety Concerns: Mining can be a hazardous profession, and ensuring worker safety is paramount.
Looking Forward:
The future of the Indian mining industry likely involves:
Focus on Sustainability: Implementing eco-friendly practices to minimize environmental damage.
Technological Advancements: Utilizing automation, robotics, and data analytics for efficiency and safety.
Exploration of New Resources: Meeting the growing demand for critical minerals used in renewable energy and technology.
In conclusion, the mining industry plays a significant role in the Indian economy, providing essential resources and supporting various sectors. However, addressing sustainability concerns and ensuring responsible practices are crucial for the industry’s long-term success.
Transportation Industry Impact Mining Industry
The Transportation Industry and the Mining Industry have a symbiotic relationship. They rely heavily on each other for their success:
Impact of Transportation on Mining:
Delivering Supplies: The transportation industry is crucial for delivering essential supplies to mines. This includes:
Machinery and Equipment: From massive haul trucks and excavators to drill rigs and processing equipment, the transportation industry ensures these reach mining sites.
Fuel and Energy: Mines require a constant supply of fuel for vehicles and machinery, as well as energy for operations. The transportation industry keeps these resources flowing.
Construction Materials: Building and maintaining mine infrastructure like access roads, conveyor systems, and processing plants requires various construction materials. Transportation delivers these materials to the mining location.
Transporting Extracted Materials: Once minerals and fossil fuels are extracted, the transportation industry takes over to move them:
Bulk Transportation: Trains, ships, and large trucks are used for transporting bulk materials like coal, iron ore, and limestone over long distances.
Finished Products: Processed minerals like refined metals or finished products like cement rely on transportation for reaching manufacturers, construction sites, or consumers.
Impact of Mining on Transportation:
Demand for Transportation Services: The mining industry creates a significant demand for transportation services, leading to job creation within the transportation sector.
Development of Transportation Infrastructure: To efficiently transport large quantities of mined materials, the mining industry often plays a role in developing transportation infrastructure. This can involve building dedicated rail lines, upgrading roads, or expanding port facilities.
Specific Transportation Needs: The mining industry sometimes requires specialized transportation solutions. This could involve heavy-duty trucks for hauling massive equipment or pipelines for transporting minerals like slurry.
Challenges and Considerations:
Logistics and Efficiency: Coordinating the transport of large volumes of materials over long distances requires efficient logistics and planning within the transportation industry.
Environmental Impact: The transportation of mined materials can contribute to air and noise pollution. Both industries need to work together to minimize this impact through cleaner technologies and efficient routes.
Future Outlook:
Focus on Sustainability: Both industries are likely to adopt more sustainable practices. This could involve using cleaner-burning fuels for transportation, optimizing routes for reduced emissions, and exploring electric or hydrogen-powered vehicles for mine operations.
Technological Advancements: Advancements in automation, data analytics, and route optimization can further improve efficiency and safety within both sectors.
In conclusion, the Transportation Industry and the Mining Industry are intertwined. Transportation keeps mines operational by delivering supplies and transporting extracted materials, while the mining industry creates a significant demand for these services. As both industries strive for greater sustainability and efficiency, collaboration will be key for their continued success.
Worldwide Top Mining Companies
| Company | Headquarters | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Glencore (GLNCY) | Switzerland | – A global leader in commodity trading and mining. They handle various metals and minerals, including coal, copper, zinc, and nickel. Glencore also operates marketing and distribution arms for these commodities. |
| Jiangxi Copper Co. Ltd. (600362) | China | – China’s largest copper producer, focusing on mining, smelting, and processing of copper products. |
| BHP Group Ltd. (BHP) | Australia | – A diversified mining giant with a presence across iron ore, copper, metallurgical coal, petroleum, and nickel. BHP is known for its large-scale operations and global reach. |
| Rio Tinto PLC (RIO) | United Kingdom | – A multinational mining and metals company dealing in iron ore, copper, aluminum, diamonds, and uranium. Rio Tinto operates large mines across the world. |
| Aluminum Corporation of China Ltd. (ACHHY) | China | – China’s largest producer of aluminum and alumina, with a significant global market share. |
| Vale S.A. (VALE) | Brazil | – A major producer of iron ore, nickel, and other minerals. Vale is known for its extensive operations in Brazil and other countries. |
| Zijin Mining Group Co. Ltd. ( | China | – A diversified mining company with a focus on gold, copper, zinc, and other metals. Zijin Mining has a growing international presence. |
| Anglo American plc (AAUKF) | United Kingdom | – A diversified mining company dealing in diamonds, copper, platinum group metals, iron ore, and coal. Anglo American is known for its focus on innovation and technology in mining. |
| Hindalco Industries Ltd. (HNDNF) | India | – India’s largest aluminum and copper producer, with a significant presence in the metals industry. |
| CMOC Group Ltd. (CMCLF) | China | – A leading producer of molybdenum and other metals, with a growing international presence. |
Where in India is the Largest Favorable Market for Mining industries?
It’s difficult to pinpoint a single “largest favorable market” for mining industries in India due to several factors:
Diversity of Minerals: India has a vast reserve of various minerals spread across different geographical locations.
Market Fluctuations: The demand and favorability for specific minerals can fluctuate based on global market trends.
However, some regions in India are known for their rich mineral deposits and established mining activity:
Eastern India: Particularly Jharkhand, Odisha, and Chhattisgarh, boast rich reserves of coal, iron ore, bauxite, manganese, and chromite. These states have a long history of mining and a well-developed infrastructure supporting these industries.
Central India: Madhya Pradesh is a significant producer of coal and minerals like copper and limestone.
Western India: Rajasthan is a major producer of metals like lead, zinc, and copper, along with sandstone and limestone. Gujarat has reserves of lignite, limestone, and gypsum.
Here are some additional factors that can influence the favorability of a mining market in India:
Mineral Reserves: The quantity and quality of the available mineral deposit play a crucial role.
Government Regulations: Policies and regulations regarding mining permits, environmental considerations, and royalty rates can affect the industry’s viability.
Infrastructure: Easy access to transportation networks like railways and roads is essential for transporting mined materials.
Availability of Skilled Workforce: A skilled workforce experienced in mining operations is necessary for efficient and safe mining practices.
Conclusion:
While some regions like Eastern India have a historical advantage due to their rich deposits, the favorability of a mining market depends on various factors. Considering the specific mineral of interest, along with the factors mentioned above, will help identify promising locations for mining ventures in India.
Dark Time of Mining Industries in India
| Period | Possible Events | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Early 19th Century – Mid 20th Century: | – Lack of Regulations & Safety Standards | – This period likely saw hazardous working conditions, minimal safety protocols, and potential exploitation of workers. |
| 1970s – 1980s: | – Nationalization & Potential Inefficiencies | – Nationalization of some mines might have led to bureaucratic hurdles and inefficiencies in operations. |
| Recent Environmental Concerns: | – Environmental Damage & Social Issues | – Increased awareness of environmental damage from mining and concerns about displacement of communities have led to stricter regulations and project delays. |
Mining Industry: Pros and Cons
| Category | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Benefits | * Creates jobs and supports livelihoods in mining regions. * Contributes to GDP through taxes and royalties. * Provides essential raw materials for various industries. | * Can have a limited direct contribution to GDP compared to other sectors. * Job growth might be concentrated in specific regions. |
| Resource Acquisition | * Provides access to essential minerals and metals for infrastructure, construction, and technology. * Plays a role in energy production (coal mining). | * Finite resources – minerals cannot be replenished. * Reliance on non-renewable resources can hinder development of sustainable alternatives. |
| Environmental Impact | * Land degradation, deforestation, and habitat loss. * Air and water pollution from mining activities. * Disruption of ecosystems and potential endangerment of species. | |
| Social Impact | * Potential for displacement of communities residing near mining areas. * Health risks for miners due to dust, exposure to hazardous materials, and potential accidents. * Ethical concerns regarding working conditions and potential exploitation in some regions. | |
| Technological Advancements | * Advancements can improve safety and efficiency in mining operations. * Automation can reduce risks for miners. * Technologies like data analytics can optimize resource extraction. | * High initial investment costs for implementing new technologies. * Job losses might occur due to automation. |
Overall:
The mining industry presents a complex picture with both advantages and disadvantages. While it provides essential resources and economic benefits, the environmental and social costs cannot be ignored. The industry needs to strive for sustainable practices, community engagement, and technological advancements to ensure responsible resource extraction for the future.
The future of the mining industry in India is likely shaped by several key trends:
Focus on Sustainability:
Minimizing Environmental Impact: Stricter regulations and public pressure will push for practices that minimize land degradation, air and water pollution, and ensure proper mine reclamation.
Renewable Energy and Resource Efficiency: The growing focus on renewable energy and a circular economy might lead to a shift towards mining critical minerals for these technologies, while aiming for efficient resource extraction and utilization.
Technological Advancements:
Automation and Robotics: Automating repetitive and hazardous tasks can improve safety for workers and increase efficiency in mining operations.
Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence: Using data to optimize resource extraction, predict equipment failures, and improve logistics can significantly enhance the industry.
Drone Technology: Drones can be used for surveying mining sites, monitoring environmental impact, and improving security.
Policy and Regulations:
Sustainable Mining Practices: The government is likely to introduce stricter regulations and policies promoting sustainable mining practices to minimize environmental damage and ensure responsible resource extraction.
Community Engagement: Greater emphasis might be placed on involving local communities in decision-making processes and ensuring their concerns regarding displacement and social impact are addressed.
Other Potential Developments:
Exploration of New Resources: Focus on exploring and extracting critical minerals like lithium, cobalt, and rare earth elements crucial for renewable energy technologies and electronics.
Focus on Skill Development: The industry will need a skilled workforce trained in operating new technologies and adhering to sustainable practices.
Challenges and Considerations:
Balancing Economic Growth and Environmental Protection: India needs to find a balance between utilizing its mineral resources for economic development and protecting the environment for future generations.
High Costs of New Technologies: Implementing advanced technologies might come with initial investment costs that smaller mining companies may struggle to afford.
Social Concerns: Addressing concerns related to displacement of communities and ensuring fair compensation will remain crucial for social acceptance of mining projects.
Overall, the future of the Indian mining industry hinges on its ability to embrace sustainability, leverage technology, and operate responsibly. By addressing these challenges and adapting to changing trends, the industry can ensure its long-term viability and contribute to India’s economic and technological development while minimizing its environmental and social footprint.
Indian Mining Industry Impact Environment
The Indian mining industry has a significant impact on the environment, with both positive and negative consequences. Here’s a breakdown of the key areas of impact:
Negative Impacts:
Land Degradation: Mining activities can lead to deforestation, soil erosion, and loss of fertile land. Open-cast mining creates large pits and scars on the landscape, while underground mining can cause subsidence (caving in) of the earth’s surface.
Air and Water Pollution: Dust generated from mining activities pollutes the air, causing respiratory problems for people living nearby. Mining processes can also contaminate water sources with heavy metals, chemicals, and acidic runoff, affecting water quality for human consumption and aquatic life.
Biodiversity Loss: Habitat destruction due to mining disrupts ecosystems and threatens plant and animal species. Mining can also fragment natural habitats, isolating populations and hindering their survival.
Waste Disposal: Mining generates a large amount of waste rock and tailings (finely crushed waste material). Improper disposal of this waste can pollute land and water resources.
Positive Impacts:
Land Reclamation: In recent years, there’s been a growing focus on mine reclamation, where mined land is restored to a usable state after operations cease. This can involve planting trees, regrading land, and creating wetlands.
Economic Benefits: The mining industry can contribute to economic development by creating jobs, generating revenue for the government through taxes and royalties, and providing essential raw materials for various industries. This can lead to improved infrastructure and development in mining regions.
Environmental Monitoring and Regulations: Increased awareness of environmental issues has led to stricter regulations for mining operations. Environmental impact assessments are mandatory for new projects, and ongoing monitoring helps mitigate pollution and promote responsible practices.
Overall Impact:
The overall impact of the Indian mining industry on the environment is negative. However, there’s a growing recognition of the need for sustainable mining practices. Here are some ways the industry can minimize its environmental footprint:
Adopting Cleaner Technologies: Using cleaner technologies for mining and processing minerals can reduce dust emissions and water pollution.
Proper Waste Management: Implementing proper waste disposal practices and utilizing waste materials for other purposes can minimize environmental damage.
Biodiversity Conservation: Minimizing habitat destruction and exploring ways to restore ecosystems around mining sites can help conserve biodiversity.
Community Engagement: Engaging with local communities and addressing their concerns about environmental impact is crucial for social acceptance of mining projects.
The Future:
The future of the Indian mining industry lies in its ability to embrace sustainability. By adopting these measures, the industry can minimize its environmental impact, ensure responsible resource extraction, and contribute to India’s development in an eco-friendly manner.
List Out Mining Scams in India
Illegal mining and scams are a persistent problem in India. Here are some infamous examples of mining scams that have plagued the country:
Bellary Iron Ore Mining Scam (Karnataka): This large-scale scam involved illegal iron ore extraction exceeding permissible limits, causing massive environmental damage and loss of revenue to the state. Politicians, mining companies, and officials were allegedly involved.
Odisha Mining Scam: Reports of rampant illegal mining of iron ore and manganese in Odisha resulted in a Supreme Court-mandated investigation. The investigation revealed large-scale irregularities in issuing mining permits, leading to environmental degradation and loss of revenue.
Granite Scam (Tamil Nadu): This scam involved illegal granite quarrying exceeding permitted limits and environmental violations in Tamil Nadu. Politicians and officials were accused of colluding with mining companies, leading to environmental damage and loss of revenue.
Coal Mining Scams: Allegations of irregularities in coal block allocation for mining have surfaced in several states, including Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh. These scams involved accusations of favoritism towards certain companies and undervaluing of coal blocks, leading to potential loss of revenue for the government.
Sand Mining Mafia: Illegal sand mining from riverbeds is a widespread issue across India. This activity disrupts river ecosystems, affects water flow, and can lead to bridge instability. The sand mafia refers to the network of individuals involved in illegal sand mining and its distribution.
These are just a few examples, and mining scams are unfortunately not uncommon in India. Here are some of the reasons why these scams occur:
Weak Regulatory Framework: Loopholes in mining regulations and lax enforcement create opportunities for illegal activities.
Corruption: Collusion between politicians, officials, and mining companies can facilitate illegal practices.
Lack of Transparency: Opaque processes for granting mining permits and monitoring operations can mask illegal activities.
Demand for Minerals: High demand for minerals, particularly for construction, creates an incentive for illegal mining to meet the demand quickly and cheaply.
Combating these scams requires a multi-pronged approach:
Strengthening Regulations: Implementing stricter regulations, streamlining procedures, and improving enforcement mechanisms are crucial.
Promoting Transparency: Greater transparency in granting permits, monitoring operations, and disclosing financial transactions can deter illegal activities.
Enhancing Accountability: Stricter penalties for corruption and holding officials and companies accountable for violations can act as a deterrent.
Community Involvement: Empowering local communities to monitor mining activities and report irregularities can be a valuable tool.
By addressing these issues, India can work towards a more sustainable and legal mining industry that benefits the economy and environment.
It’s important to note that these are complex issues, and the information provided here is a general overview. Further research on specific scams can provide a more detailed understanding.
Mining Industry Conclusion
The Mining Industry in India presents a complex picture with both significant contributions and challenges. Here’s a concluding summary:
Economic Importance:
The mining industry plays a crucial role in India’s economy by:
Providing essential raw materials for various sectors like steel, cement, power generation, and construction.
Generating revenue through taxes and royalties on extracted minerals.
Creating jobs and supporting livelihoods in mining regions.
Environmental Impact:
Mining activities can have a significant negative impact on the environment, including:
Land degradation, deforestation, and loss of biodiversity.
Air and water pollution from dust, chemicals, and acidic runoff.
Disruption of ecosystems and potential endangerment of species.
Social Impact:
The social impact of mining can be positive and negative:
Positive impacts include job creation and economic development in mining regions.
Negative impacts include potential displacement of communities, health risks for miners, and ethical concerns regarding working conditions.
The Future:
The future of the Indian mining industry hinges on its ability to:
Embrace Sustainability: Minimize environmental impact through cleaner technologies, proper waste management, and mine reclamation practices.
Leverage Technology: Utilize automation, robotics, data analytics, and drone technology for efficiency, safety, and resource optimization.
Operate Responsibly: Address social concerns, engage with communities, and ensure fair compensation for those affected by mining activities.
Adhere to Regulations: Comply with stricter environmental and safety regulations for sustainable resource extraction.
Overall, the Indian mining industry can play a crucial role in the country’s development, but it must do so responsibly. By focusing on sustainability, innovation, and social responsibility, the industry can ensure its long-term viability and contribute to a greener and more equitable future for India.
Click and follow for regular warehousing Upgraded Updated news report :- Please Click
Merger and Acquisition Group for efficiently Cost Optimisation :- Join (Investing Budget Min 10 Crore INR)
Warehousing Development and Regulatory Authority :- www.wdra.gov.in
India Logistics & Supply Chain Association (ILSCA) :- www.aplf.net
Federation of Cold Storage Associations of India FCAOI :- www.fcaoi.org
Central Warehousing Corporation :- www.cewacor.nic.in
Agricultural Machinery Manufacturers Association (AMMA – India) :- www.aiamma.org
Indian Construction Equipment Manufactures’ Association: ICEMA :- www.i-cema.in
Department of Heavy Industry :- www.dhi.nic.in
Ministry of coal :- www.coal.nic.in
NOTE :- From our point of view, the biggest problem today is that due to mistrust, disagreement, insecurity, today the price of our business and daily essential commodities and raw materials is increasing infinitely unnecessary.We have a small effort which is expected that every good buyer should get a good seller without a middleman and a good seller gets a good buyer.We always provide advanced information on our behalf to our customers. If you are interested in public interest by the presentation and renewal of your business, then share with us by people what revolutionary changes you have made to your business that have benefited the people.So that our good business community and you also benefit forever. And people should benefit so that a good business environment is created.
Advantage Our Pro Membership :-We provide advanced support to our pro membership clients in Transportation, Logistics, Warehousing, Finance etc….
Recommended :-
- Please click and See Our Endless Journey – Please Click
- Manufacturer association in India – AIAI India ( www.aiaiindia.com )
- Merchants manufacturer industries manufacturing companies
- Difference between sales and marketing
- Fraud Cases and Examples in Business
- Business Problems and Solutions
Public frequently asked questions (FAQs) :-
Who is the largest producer of iron ore in India?What does mining industry mean?
The branch of manufacture and trade based on the extraction of ores, fossil fuels, minerals, stone, clay, gravel, and similar commodities. This does not include the refinement of these commodities (see manufacturing)
Which type of industry is mining?
The mining industry is like any other manufacturing industry in that it utilises sophisticated and productive machinery, along with digitisation, so that it can prosper by increasing productivity while decreasing costs. Development in mining technology is ongoing throughout the world, notwithstanding India.
What are three benefits of mining?
These benefits include low-cost, reliable electricity and the materials necessary to build our homes, schools, hospitals, roads, highways, bridges and airports.
Can we live without mining?
Mineral products are essential components for cell phones, cars, energy towers, solar panels, wind turbines, fertilizers, machinery and all kinds of construction.
How many mining companies are there in India?
784 mining companies listed in India .
Which is the largest mining company in India?
Coal India Limited (CIL) is a state-owned coal mining corporation which came into existence in November 1975. It has been awarded the status of Maharatna company. With its normal production of 79 million tonnes (MT) in the year of its establishment, Coal India Limited is today the world’s largest coal producer.
Who owns mines in India?
Under the Constitution of India, the states have the power to regulate mines and mineral development. However, this power is subject to the federal laws and regulations on mining. Minerals are classified into two types – major and minor.
Who is the largest producer of iron ore in India?
In the financial year 2019, the eastern state of Odisha was the leading producer of iron ore in India. Iron ore is abundantly available in the districts of Mayurbhanj, Sundargarh, Keonjhar, and Jajpur.
How do I start a mining company?
Once you purchase advance machineries tools, you need to hire skilled employees to work for your mining company. You will need to hire a lot of people due to the nature of the work that you have to do. A lot of employees will be working for a manual labor job, who can assist you mine materials.
Which is the first mine in India?
In India first coal mine began in 1774 with John Sumner and Suetonius Grant Heatly of the East India Company in the Raniganj Coalfield along the Western bank of Damodar river.
Which mineral is rich in India?
India’s major mineral resources include Coal (4th largest reserves in the world), Iron ore, Manganese ore (7th largest reserve in the world as in 2013), Mica, Bauxite (5th largest reserve in the world as in 2013), Chromite, Natural gas, Diamonds, Limestone and Thorium.
Which is the deepest mine in India?
The Kolar Gold fields are about 100 kilometres from Bangalore. Operated by the Bharat Gold Mines Limited (BGML), a public sector undertaking, the KGF was the world’s second deepest gold mine at a depth of 3,000 metres.
Can I mine in India?
Even mining done on small scale contributes 6% to the entire cost of mineral production. Indian mining industry provides job opportunities to around 700,000 individuals. As of 2012, India is the largest producer of sheet mica, 2015 the fourth largest producer of iron ore, alumina, chromite, and bauxite in the world.
Who is the largest producer of diamond in India?
Madhya Pradesh is the only diamond producing state and is leading producer of copper conc., pyrophyllite and diaspore. State hosts country’s 68% diaspore, 41% molybdenum ore, 46% pyrophyllite, 32% diamond, 29% copper ore, 17% rock phosphate, 16% each of manganese ore and fireclay and 11% ochre resources.
What are the bad effects of mining?
Environmental issues can include erosion, formation of sinkholes, loss of biodiversity, and contamination of soil, groundwater and surface water by chemicals from mining processes.
What is advantage of mining industry india ?
Even mining done on small scale contributes 6% to the entire cost of mineral production. Indian mining industry provides job opportunities to around 700,000 individuals. As of 2012, India is the largest producer of sheet mica, 2015 the fourth largest producer of iron ore, alumina, chromite, and bauxite in the world.
What is disadvantage of mining industry india ?
The miners also face health hazards arising out of on site pollution due to dust, gases, noise, and polluted water. Health related issues are increasingly coming into focus. One of the major environmental challenges facing the mining industry is due to the mine sites which are no longer in use.
Disadvantages of Mining
Mining can lead to soil pollution.
Groundwater pollution.
Deforestation.
Depletion of natural resources.
Mining implies the destruction of habitats.
Endangerment of species.
Loss of biodiversity.
Landslides become more likely.