What is Aviation ?
Imagine birds! Aviation is basically about humans copying birds and other creatures to fly. Here’s the simple version:
Flying machines: It’s all about airplanes, helicopters, and anything else we build to fly in the air.
Making flying happen: This includes learning to fly these machines safely, designing and building them, and keeping them in tip-top shape.
Air travel: This is the big one! Taking airplanes on trips, from vacations to carrying packages, is a huge part of aviation.
So, next time you see a plane soar by, you know it’s all thanks to aviation!
What is Aviation Industry ?
The aviation industry is like a giant orchestra, with many different parts working together to keep airplanes flying. Here’s a breakdown:
The airplanes themselves: This includes companies that design and build all sorts of aircraft, from passenger jets to cargo planes and even helicopters.
Airlines: These are the companies that operate the airplanes, transporting passengers and cargo around the world.
Airports: They provide a home for airplanes to take off and land, with runways, air traffic control towers, and terminals for passengers.
Air traffic control: These are the people who make sure airplanes fly safely in the sky, keeping them separated and ensuring a smooth flow of air traffic.
Maintenance: Keeping airplanes in top condition is crucial, and there’s a whole industry dedicated to mechanics, inspectors, and specialists who make sure everything is flying fit.
Other players: There are many more behind-the-scenes roles in aviation. This includes companies that make airplane parts, caterers who stock food for flights, security personnel who keep everyone safe, and even travel agents who help people book their flights.
All these parts work together to make the aviation industry a massive global network that keeps people, goods, and even dreams flying!
Types Of Aviation
Two main types of aviation: civil aviation and military aviation.
Civil Aviation
This is the non-military use of aircraft and encompasses a wide range of activities:
Commercial Aviation: This is the transportation of passengers and cargo on scheduled flights by airlines. Airlines can be further categorized into full-service carriers, low-cost carriers, and cargo airlines.
General Aviation: This is a broad category that includes all non-commercial flying. It can be for business or pleasure, such as private flying, air taxis, air ambulances, flight training, aerial photography, crop dusting, and recreational flying like gliders and hot air balloons.
Military Aviation
Military aviation refers to the use of aircraft by the armed forces of a country for military operations and national defense. Here are some of the core functions of military aviation:
Air Combat: Fighter jets and bombers are used for aerial warfare to establish air superiority and attack ground targets.
Transport: Military transport aircraft carry troops, equipment, and supplies to support operations around the world.
Reconnaissance: Military aircraft are used for gathering intelligence by collecting information and imagery of enemy positions and activities.
Training: Training aircraft are used to train future military pilots and other aviation personnel.
Worldwide Aviation Industry Evolution
| Year | Event | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Early 1900s | First powered flights by Wright Brothers | Paved the way for heavier-than-air flight technology |
| 1910s | First commercial airmail service | Pioneered the use of airplanes for transportation |
| 1920s-1930s | Development of metal monoplanes | Increased aircraft range, speed, and capacity |
| 1940s | World War II | Technological advancements in aircraft design and production |
| 1950s | Introduction of jet airliners | Revolutionized air travel with faster and more efficient flights (e.g., Boeing 707) |
| 1960s-1970s | Rise of mass air travel | Growth of tourism and business travel due to affordability and accessibility |
| 1970s | Deregulation of airlines in some countries (e.g., USA) | Increased competition and lower fares, leading to passenger growth |
| 1990s | Globalization and rise of low-cost carriers | Made air travel more accessible to a wider range of people |
| 2001 | 9/11 terrorist attacks | Significant impact on passenger confidence and air travel safety measures |
| 2000s-present | Technological advancements (e.g., composite materials, avionics) | Improved fuel efficiency, safety, and comfort |
| 2020s | Focus on sustainability | Development of alternative fuels and electric aircraft to reduce environmental impact |
Challenges in Aviation Industry
The aviation industry soars high, but it also faces some bumpy turbulence. Here are some of the key challenges it navigates:
Fuel Costs and Efficiency: Keeping planes fueled is a major expense, and fluctuations in oil prices can significantly impact airlines’ profitability. The industry is constantly seeking ways to improve fuel efficiency through new technologies and aircraft designs.
Economic Fluctuations: A weak global economy can lead to decreased travel demand, hurting airlines’ bottom lines.
Workforce Shortages: From pilots and mechanics to air traffic controllers, the industry faces shortages of skilled personnel, impacting operations and potentially delaying flights.
Infrastructure Constraints: Busy airports and congested airspace can lead to delays and cancellations. Upgrading infrastructure and air traffic control systems is crucial for smooth operations.
Global Geopolitical Issues: Political instability, pandemics like COVID-19, and airspace closures due to conflicts can disrupt travel patterns and cause economic losses.
Customer Experience: Balancing affordability with passenger comfort and amenities is an ongoing challenge. Airlines strive to provide a seamless travel experience while keeping costs in check.
Cybersecurity Threats: The aviation industry is increasingly reliant on technology, making it vulnerable to cyberattacks that could disrupt operations. Robust cybersecurity measures are essential.
Environmental Impact: Aviation is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. The industry is under pressure to develop sustainable practices and alternative fuels to reduce its environmental footprint.
These are just some of the challenges the aviation industry faces. Overcoming them will require innovation, collaboration, and investment in new technologies and infrastructure.
Aviation Industry Advantage
The aviation industry brings a whole lot of benefits to our world, not just for travelers but for the global economy and society as a whole. Here are some key advantages:
Speed and Efficiency: Air travel is the fastest mode of transportation, shrinking distances and saving time. This facilitates global business, tourism, and the movement of time-sensitive goods.
Economic Growth: Aviation is a major economic driver. It creates jobs in airlines, airports, manufacturing, tourism, and many other sectors. It also fosters international trade by enabling the efficient movement of goods.
Global Connectivity: The aviation industry connects people and cultures across vast distances. This promotes cultural exchange, tourism, and international collaboration.
Humanitarian Aid and Disaster Relief: Fast and reliable air transport plays a vital role in delivering aid and personnel to areas affected by natural disasters or emergencies.
Medical Services: Air ambulances transport critically ill or injured patients to specialized medical facilities, saving lives and improving access to healthcare.
Technological Innovation: The constant push for efficiency, safety, and sustainability in aviation drives innovation in aerospace technology, benefiting other sectors as well.
Career Opportunities: The industry offers a wide range of exciting and well-paying careers in various fields, from pilots and engineers to air traffic controllers and logistics specialists.
Overall, the aviation industry plays a critical role in our interconnected world, bringing people, goods, and ideas closer together. While it faces challenges, its advantages contribute significantly to economic prosperity, social development, and technological advancements.
Aviation Industry Disadvantage
The aviation industry takes us to new heights, but it also has some downsides that need addressing. Here are some of the key disadvantages:
Environmental Impact: Air travel is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. Aircraft burn a lot of fuel, releasing pollutants like carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere.
Noise Pollution: Airplanes generate significant noise pollution, particularly during takeoff and landing, which can disrupt communities near airports and impact wildlife.
Safety Concerns: While statistically very safe, air travel accidents can have devastating consequences. Continuous improvement in safety measures is crucial.
Accessibility and Cost: Air travel can be expensive compared to other modes of transportation, making it less accessible for everyone. This can limit social and economic opportunities for some.
Dependence on Oil: The industry relies heavily on fossil fuels, making it vulnerable to price fluctuations and contributing to reliance on non-renewable resources.
Risk of Disease Transmission: Air travel can facilitate the spread of infectious diseases as large numbers of people gather in close quarters. Measures to control the spread of illnesses are essential.
Infrastructure Limitations: Airport capacity and airspace congestion can lead to delays and cancellations, frustrating passengers and impacting efficiency.
Security Concerns: Aviation is a target for terrorism and other security threats. Robust security measures are necessary to ensure passenger safety.
These disadvantages highlight the need for the aviation industry to find sustainable solutions. Focusing on cleaner fuels, developing quieter aircraft, and improving efficiency are crucial steps towards a more eco-friendly future for air travel.
Dark Time of Aviation Industry
The aviation industry has faced several periods of turbulence throughout its history, but a few particularly dark times stand out:
Early Days of Flight (1900s): While a pioneering era, the early days of aviation were marked by frequent accidents due to limited technology, pilot inexperience, and poor weather understanding. This period saw many fatalities and setbacks before safety regulations and advancements improved air travel significantly.
World Wars (1914-1945): While war often drives technological innovation, it also has a devastating impact on the aviation industry. During both World Wars, civilian air travel was severely curtailed as resources and aircraft were directed towards military operations. The industry faced a long recovery period after each war.
9/11 Terrorist Attacks (2001): This dark day in history significantly impacted the aviation industry. The attacks led to stricter security measures, flight cancellations, and a decrease in passenger confidence. The industry took a long time to recover from the economic and psychological impact of this event.
COVID-19 Pandemic (2020-Present): The global pandemic brought air travel to a near standstill. Travel restrictions, lockdowns, and health concerns caused a dramatic drop in passenger demand. Many airlines faced financial difficulties, grounded fleets, and job losses. While recovery is underway, the pandemic’s long-term effects on the industry are still unfolding.
These are some of the darkest times the aviation industry has faced. However, it’s important to remember that the industry has a history of resilience and innovation. After each period of crisis, advancements in technology, safety, and regulation have paved the way for a more robust and sustainable future for air travel.
Why Do You Want to Join Aviation Industry
I can analyze it and tell you why someone might want to be a part of it, considering carrier features and the future:
Carrier Features:
Specific Airline: Different airlines offer unique experiences for their employees. Some might be known for their pilot training programs, international reach, focus on innovation, or strong company culture. Researching the specific carrier’s offerings would be key.
Career Path: The aviation industry offers a wide range of exciting careers. Pilots, engineers, air traffic controllers, cabin crew, and logistics specialists are just a few examples. You’d need to consider the specific role you’re interested in and the opportunities the carrier provides for growth and development.
Benefits and Compensation: Airlines offer competitive salaries, benefits packages (including travel perks!), and the chance to work in a dynamic and fast-paced environment.
Future of Aviation:
Innovation: The aviation industry is constantly evolving. Being part of it means being at the forefront of technological advancements in areas like sustainable fuels, electric aircraft, and autonomous flight.
Global Impact: Aviation plays a critical role in connecting the world. You could be part of an industry that facilitates global trade, tourism, and cultural exchange.
Problem-Solving: The industry faces challenges like environmental impact and infrastructure limitations. Being a part of finding solutions and creating a more sustainable future for air travel could be incredibly rewarding.
Overall, a career in aviation can be incredibly fulfilling. Consider what excites you most – the specific airline, the chosen field within aviation, or the industry’s future – and tailor your approach to highlight your passion when pursuing opportunities.
EV Industry Impact Aviation Industry
The EV (Electric Vehicle) industry has the potential to significantly impact the aviation industry, but it’s still early days. Here’s a breakdown of the potential influence:
Potential Benefits:
Reduced Emissions: Electric airplanes, if they become viable for commercial use, could drastically cut down on greenhouse gas emissions from aviation. This would be a major step towards a more sustainable future for air travel.
Quieter Operation: Electric motors are much quieter than jet engines, potentially leading to less noise pollution around airports and for communities on flight paths.
Lower Operating Costs: Electric airplanes could have lower operating costs due to potentially cheaper electricity compared to jet fuel. This could lead to more affordable airfare in the long run.
Challenges and Limitations:
Battery Technology: Current battery technology doesn’t offer the energy density needed for long-haul flights. Significant advancements are required to make electric airplanes practical for most commercial routes.
Infrastructure Needs: Charging infrastructure for electric airplanes at airports would need to be developed.
Range Limitations: Even with advancements, electric airplanes might initially be limited to shorter regional flights, with longer routes still relying on traditional jet engines (potentially using sustainable biofuels).
Overall Impact:
The EV industry is likely to influence the aviation industry in the long term, but the exact timeline and how dramatic the impact will be depends on technological breakthroughs. Here are some possibilities:
Hybrid Solutions: Hybrid airplanes that combine electric motors with traditional jet engines could be a stepping stone, offering a balance between range and emissions reduction.
Short-haul Revolution: Electric airplanes could become the dominant mode of transport for shorter regional flights, while traditional jet engines remain crucial for long-haul travel.
Focus on Sustainability: The push for electric vehicles will likely pressure the aviation industry to find ways to become more sustainable, even if full electrification isn’t immediately achievable. This could involve increased use of biofuels or hydrogen technologies.
The EV industry is acting as a catalyst for change in aviation, pushing for cleaner and quieter skies. While there are significant challenges, the potential benefits for the environment and the future of air travel are undeniable.
Top Airlines by Region: Charting the Skies
| Region | Airline | Country | Why Best | Major Routes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| North America | American Airlines | USA | Largest airline in the world by fleet size and passengers carried | North American hubs to major destinations worldwide |
| North America | United Airlines | USA | Extensive route network and strong partnerships with other airlines | North American hubs to major destinations worldwide |
| North America | Delta Air Lines | USA | High on-time performance and customer satisfaction ratings | North American hubs to major destinations worldwide |
| Europe | Lufthansa Group (Lufthansa, SWISS, Austrian Airlines) | Germany | Extensive network within Europe and major hubs for connecting flights | Major European hubs to destinations worldwide |
| Europe | Air France-KLM | France & Netherlands | Large combined network with strong presence in former colonies | European hubs to destinations worldwide, particularly Africa |
| Europe | Turkish Airlines | Turkey | Strategic location for connecting flights and competitive fares | Istanbul hub as a major connecting point between Europe, Asia, and Africa |
| Asia | Emirates Airline | United Arab Emirates | Modern fleet, award-winning service, and focus on innovation | Dubai hub as a major connecting point for East-West travel |
| Asia | Qatar Airways | Qatar | Highly rated for service and comfort, particularly in Business and First Class | Doha hub as a major connecting point between Europe, Asia, and Africa |
| Asia | Singapore Airlines | Singapore | Top-ranked airlines for customer service and in-flight experience | Singapore Changi Airport hub as a major connecting point in Southeast Asia |
| Latin America | LATAM Airlines Group (LATAM Airlines Chile, LATAM Airlines Brazil) | Chile & Brazil | Strong presence and comprehensive network within Latin America | Major South American hubs to destinations worldwide |
| Latin America | Avianca Holdings (Avianca & Avianca Costa Rica) | Colombia & Costa Rica | Largest airline in Colombia and significant presence in Central and South America | Bogotá hub as a major connecting point for travel within the region |
| Africa | Ethiopian Airlines | Ethiopia | Largest airline in Africa and significant growth in international destinations | Addis Ababa hub as a major connecting point for travel within Africa and beyond |
Top Most Used Passenger Aircraft Models
| Aircraft Model | Manufacturer | Engine Type | Passenger Capacity (Typical) | Range (km) | Average Working Age (Years) | Fuel Efficiency (Liters per Passenger-km) | Major Accidents (Since 2000) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boeing 737-800 | Boeing | Turbofan | 162-189 | 5425 | 13+ | 5.0 | 11 (hull loss accidents) |
| Airbus A320-200 | Airbus | Turbofan | 150-180 | 5410 | 12+ | 4.8 | 10 (hull loss accidents) |
| Boeing 737 MAX 8 (Grounded as of March 2024) | Boeing | Turbofan | 162-200 | 6570 | 5 (average before grounding) | Not currently flying | 3 (hull loss accidents) |
| Airbus A321neo | Airbus | Turbofan | 190-240 | 8400 | 7+ | 4.0 | 1 (hull loss accident) |
| Boeing 777-300ER | Boeing | Turbofan | 350-400 | 10,680 | 18+ | 3.4 | 5 (hull loss accidents) |
| Airbus A350-900 | Airbus | Turbofan | 300-350 | 15,000 | 8+ | 3.0 | 0 (hull loss accidents) |
Top Cargo Airlines by Region
| Region | Airline | Country | Capability | Why Best | Major Routes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North America | FedEx Express | USA | Extensive global network, freighter fleet variety | Largest cargo airline by freight tonnage | Global network including major trade lanes (e.g., US-Asia, US-Europe) |
| North America | UPS Airlines | USA | Large freighter fleet, strong ground infrastructure | Integrated logistics network with reliable delivery times | Global network with focus on major trade hubs |
| Europe | Lufthansa Cargo | Germany | Extensive European network, freighter and passenger belly cargo | Strong European reach and connections within Lufthansa Group | Europe, North America, Asia (extensive network within Lufthansa Group) |
| Europe | Emirates SkyCargo | UAE | Modern freighter fleet, focus on perishables | Modern fleet with efficient hubs in Dubai for perishables | Global network with focus on Middle East, Africa, and Asia |
| Asia | Cathay Pacific Cargo | Hong Kong | Strong Asia-Pacific network, freighter and passenger belly cargo | Extensive network within Asia and connections with Cathay Pacific passenger flights | Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe |
| Asia | Korean Air Cargo | South Korea | Focus on innovation and technology, freighter and passenger belly cargo | Investment in automation and cool chain solutions | Asia, North America, Europe, strong network within Asia |
| Latin America | LATAM Cargo | Chile | Extensive Latin American network, freighter and passenger belly cargo | Dominant player in Latin American cargo market | Latin America, North America, Europe, Miami hub for regional distribution |
| Middle East | Qatar Cargo | Qatar | Rapid growth, modern freighter fleet | One of the fastest-growing cargo airlines, efficient Doha hub | Global network with focus on Middle East, Africa, and Asia |
Top Cargo Aircraft by Usage
| Aircraft Model | Manufacturer | Engine Type | Max Payload Capacity (tonnes) | Typical Range (km) | Average Working Age (Years) | Fuel Efficiency (Liters/Ton-km) | Major Accidents (Since 2000) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boeing 747-400F | Boeing | Turbofan | 127 | 8,643 | 25+ | 3.9 | 5 (hull loss) |
| Boeing 777F | Boeing | Turbofan | 103 | 9,070 | 18+ | 3.4 | 2 (hull loss) |
| Boeing 767-300F | Boeing | Turbofan | 52.7 | 6,010 | 30+ | 4.2 | 3 (hull loss) |
| McDonnell Douglas MD-11F | McDonnell Douglas (Boeing) | Turbofan | 97.7 | 7,170 | 28+ | 4.0 | 3 (hull loss) |
| Airbus A330-200F | Airbus | Turbofan | 70 | 7,400 | 15+ | 3.3 | 0 (hull loss) |
Worldwide Regions | Major Aircraft Manufacturers
| Region | Major Aircraft Manufacturers | Notable Aircraft Models (Passenger / Cargo) |
|---|---|---|
| North America | Boeing (USA) | *Passenger: 737, 747, 777, 787 Dreamliner *Cargo: 747-400F, 767-300F |
| North America | Bombardier (Canada) | *Passenger: Q Series, CRJ Series *Business Jets: Challenger, Global |
| Europe | Airbus (France & Germany) | *Passenger: A220, A320 family, A330, A350 XWB *Cargo: A330-200F |
| Europe | ATR (France & Italy) | *Turboprop: ATR 42, ATR 72 |
| Brazil | Embraer (Brazil) | *Passenger: E-Jet family, E-Jet E2 family *Business Jets: Phenom, Praetor |
| Russia | United Aircraft Corporation (UAC) (Russia) | *Passenger: Sukhoi Superjet 100 *Cargo: IL-76 |
| China | COMAC (China) | *Passenger: ARJ21 (regional jet), C919 (narrowbody) |
Fact About Aviation Industry
Here are a few interesting facts about the aviation industry:
First Official Airmail: The very first commercial aviation flight actually carried mail, not passengers! It flew across the Yamuna River in India on February 18, 1911.
High Flyers: Commercial airplanes typically cruise at altitudes between 30,000 and 40,000 feet, which is why the sky appears much darker from a window seat.
Cold Comfort: At cruising altitude, the outside air temperature can be as low as -70°C (-94°F)! Thankfully, the cabin air is heated and regulated for passenger comfort.
Weighty Matters: The weight of all the passengers and cargo on a large airplane is only a fraction of the total weight at takeoff. Most of the weight is fuel!
Clear Skies for Safety: Lightning strikes are actually not uncommon for airplanes, but they are usually harmless due to the metal skin acting as a cage that conducts the electricity around the airplane.
Language in the Air: Pilots and air traffic controllers around the world communicate in a standardized language called ICAO English to ensure clear and concise communication.
Tiny Tracks, Big Impact: The contrails, or condensation trails, left behind by airplanes can actually contribute to cloud formation and potentially have a small impact on climate.
Bird Brain Avoidance: Airports employ various methods to deter birds from the vicinity of runways to prevent bird strikes, which can be dangerous.
Pillow Power: The air pressure changes during flight can affect your hearing and make you feel slightly swollen. That’s why airlines provide those fluffy pillows – not just for comfort, but also to help equalize pressure in your ears.
A Global Network: The aviation industry connects thousands of destinations around the world, making it possible to travel vast distances in a relatively short amount of time.
Aviation Industry: Pros and Cons
| Aspect | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Speed and Efficiency | * Fastest mode of transportation * Shrinks distances, saves time | * Limited point-to-point options compared to ground transportation |
| Economic Growth | * Creates jobs in airlines, airports, manufacturing, tourism * Facilitates global trade | * Contributes to global economic vulnerability during crises (e.g., pandemics) |
| Global Connectivity | * Connects people and cultures across vast distances * Promotes tourism, cultural exchange, international collaboration | * Can contribute to homogenization of cultures |
| Humanitarian Aid & Disaster Relief | * Delivers aid and personnel to disaster zones quickly | * Reliance on infrastructure and weather conditions can limit accessibility in emergencies |
| Medical Services | * Transports critically ill or injured patients for specialized care | * High costs can limit accessibility for some |
| Technological Innovation | * Drives innovation in aerospace technology * Benefits other sectors like materials science and engineering | * High research and development costs |
| Career Opportunities | * Offers exciting, well-paying careers in various fields | * Some jobs require specialized skills and training |
Environmental Impact
| Aspect | Concerns | Potential Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Greenhouse Gas Emissions | * Major contributor to climate change | * Development of sustainable biofuels and electric aircraft |
| Noise Pollution | * Disrupts communities near airports | * Quieter aircraft designs, stricter noise regulations around airports |
Safety
| Aspect | Strengths | Areas for Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| Safety Regulations | * Stringent regulations and high safety standards | * Continuous improvement in areas like pilot training and maintenance procedures |
| Accident Rates | * Statistically very safe mode of transportation | * Addressing human error and mechanical failures through advanced technology |
Conclusion
The aviation industry soars high, but navigating its future requires addressing both headwinds and tailwinds. Here’s a concluding summary:
Strengths:
Speed and connectivity: Aviation shrinks distances and connects the world, fostering global trade, tourism, and cultural exchange.
Economic engine: It creates jobs, drives innovation, and facilitates the movement of goods and people, impacting economies worldwide.
Lifeline services: Air travel plays a vital role in delivering aid, medical services, and personnel to those in need.
Technological advancements: The industry constantly pushes boundaries, developing more efficient, safer, and quieter aircraft.
Challenges:
Environmental impact: Emissions and noise pollution are major concerns. Sustainable solutions like biofuels and electric aircraft are crucial.
Infrastructure limitations: Airport congestion and airspace constraints can lead to delays. Upgrading infrastructure is essential.
Security threats: Robust security measures are necessary to ensure passenger safety in the face of evolving threats.
Accessibility and affordability: Air travel can be expensive compared to other modes of transport, limiting access for some.
The Future:
The aviation industry is at a crossroads. Sustainability is paramount. Technological advancements in electric and hybrid propulsion, quieter engines, and cleaner fuels offer hope for a greener future. Additionally, improving efficiency, infrastructure, and affordability will be key to making air travel accessible to a wider range of people.
Overall, the aviation industry plays a significant role in our world. By addressing its challenges and embracing innovation, it can continue to connect people, cultures, and economies while minimizing its environmental footprint. The future of aviation is likely to be shaped by a focus on sustainability, efficiency, and inclusivity, ensuring that the skies remain open for generations to come.
Click and follow for regular warehousing Upgraded Updated news report :- Please Click
Merger and Acquisition Group for efficiently Cost Optimisation :- Join (Investing Budget Min 10 Crore INR)
Warehousing Development and Regulatory Authority :- www.wdra.gov.in
India Logistics & Supply Chain Association (ILSCA) :- www.aplf.net
Federation of Cold Storage Associations of India FCAOI :- www.fcaoi.org
Central Warehousing Corporation :- www.cewacor.nic.in
AirSewa :- www.airsewa.gov.in
Ministry of Civil Aviation :- www.civilaviation.gov.in
Directorate General of Civil Aviation :- www.dgca.gov.in
Airports Authority of India :- www.aai.aero
NOTE :- From our point of view, the biggest problem today is that due to mistrust, disagreement, insecurity, today the price of our business and daily essential commodities and raw materials is increasing infinitely unnecessary.We have a small effort which is expected that every good buyer should get a good seller without a middleman and a good seller gets a good buyer.We always provide advanced information on our behalf to our customers. If you are interested in public interest by the presentation and renewal of your business, then share with us by people what revolutionary changes you have made to your business that have benefited the people.So that our good business community and you also benefit forever. And people should benefit so that a good business environment is created.
Advantage Our Pro Membership :-We provide advanced support to our pro membership clients in Transportation, Logistics, Warehousing, Finance etc….
Recommended :-
- Please click and See Our Endless Journey – Please Click
- Manufacturer association in India – AIAI India ( www.aiaiindia.com )
- Merchants manufacturer industries manufacturing companies
- Difference between sales and marketing
- Fraud Cases and Examples in Business
- Business Problems and Solutions
Frequently Asked Questions FAQ :-


How is the situation of airlines and aviation companies in India?
Air travel, even after 70 years of independence, is considered a luxury service in India.Due to which no metros cities were left untouched except for some big cities
What and how much does aviation and air transport contribute to India’s development?
The real progress of any country is determined by its improved transportation . India did not have the expected progress in the last decades, but can be said to be more satisfactory than the neighboring countries.Today, foreign airlines and air transport contribute 50% to the growth of India’s business environment.
Why are aviation and air transport companies sunk or sold in India?
The whole world should learn from the national love of Japan. Japan is at the pinnacle of success today, considering only nationalist nationalism and national interest as paramount. Today, due to the greed of our small discounts, we are giving untapped benefits to the foreign web portal companies in the interest of the country, which they will only use in our harm and destruction.The result of our betrayal is that today India’s topmost means of communication and transport is to sell at a price of a bunch. Is it a matter of respect and dignity for Indian business? Or the slap on our characterization whose pain will also shatter our future breeds.Today the character of the Indian business has become such that the big businessmen who are selling dirty liquor and the small shopkeepers who sell goods of worship are called thugs. Will India’s trade survive at the cost of this origin?
What is the importance of aviation and air transport companies in India?
India has a total of 36 states, 686 districts, and about 6.5 lakh small and large villages.There are not even 100 airports in India and what is there is limited. Which is also contrary to normal achievement.There is a need for an advanced air transport system to connect India with an advanced chain. But in the present environment its possibilities are not seen very far.
What is the history of aviation and air transport companies in India?
Air transport in India has advanced since the era of Satyuga, Treta and Dwapar, but the over-ambition of some opportunists led to its destruction. The Tata group has made the largest and most respected contribution to the development of India’s air transport system.
How can the plight of aviation and air transport companies in India be rectified or changed?
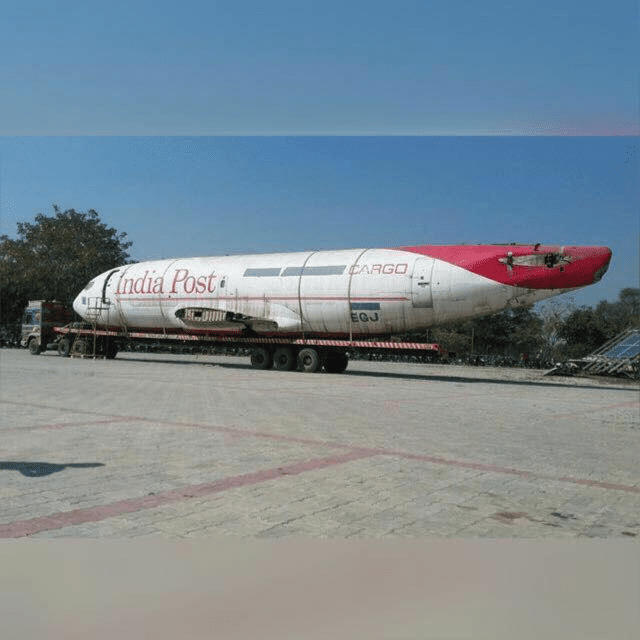
Air India and India Post running in shabby condition should be combined. Perhaps there are no more profitable companies left in India.
What is the future of jobs in aviation and air transport companies in India safe?.
Seeing the current situation, the youth of the country should consider the cost of studying in this field. It is not prudent to ignore the threat of unemployment and employment after fairly large study expenses.
What is the work of aviation?
Pilots are those who fly and navigate aircraft and helicopters. Airline pilots fly aircraft for airlines which transport people and cargo on a fixed schedule. They are responsible for transporting passengers who are usually going on holiday or travelling for business, and generally work for commercial airlines.
Who is father of aviation?
Sir George Cayley Bt He was a pioneer of aeronautical engineering and is sometimes referred to as “the father of aviation.” He discovered and identified the four forces which act on a heavier-than-air flying vehicle: weight, lift, drag and thrust.
Why aviation is important?
Aviation provides the only rapid worldwide transportation network, which makes it essential for global business. It generates economic growth, creates jobs, and facilitates international trade and tourism.
What is the difference between aviation and airline?
As stated, the airline industry refers to companies that offer air transport services to paying customers, whereas the aviation industry includes all aviation-related businesses. With this in mind, the airline industry can be classed as just one sector of the wider aviation industry.
What is aviation industry in general?
The aviation industry encompasses almost all aspects of air travel and the activities that help to facilitate it. This means it includes the entire airline industry, aircraft manufacturing, research companies, military aviation, and much more.
Which is the oldest airline in the world?
KLM is the world’s oldest airline and celebrated its 100th anniversary in 2019
Which is the richest airline in India?
IndiGo is an Indian low-cost airline headquartered in Gurugram, Haryana, India. It is the largest airline in India by passengers carried and fleet size, with a 59.24% domestic market share as of August 2020.
Which is No 1 airport in world?
Singapore Changi Airport . Singapore Changi Airport once again earned the top prize again this year as the world’s best airport for the eighth consecutive year.


