🚛 Transport in India: The Story of a Nation on the Move
In the heart of a bustling Indian morning, as the first rays of sunlight strike the highways, the country begins to hum with motion. Trucks roar to life carrying fresh produce from distant farms; buses groan under the weight of early commuters; trains thunder across the plains, while aircraft slice through dawn skies. From the smallest village road to the largest metro station, one pulse runs through India — transportation.
Transport in India isn’t just about movement; it’s a story of connection, culture, and courage. It’s about how a billion dreams find direction through roads, rails, rivers, and runways. It’s the invisible thread that binds the farmer in Punjab to the factory in Gujarat, the IT professional in Bengaluru to the exporter in Chennai, and the student in Delhi to the teacher in Kolkata.
🚦 From Bullock Carts to Bullet Trains: The Journey of Evolution
A few centuries ago, India’s transport landscape was humble but vibrant. Bullock carts, horse-drawn tongas, and wooden boats served as the lifelines of trade and travel. Goods took days to reach nearby towns; travelers measured journeys not in miles, but in months. Yet, even in this simplicity, the rhythm of trade flourished. Salt, spices, silk — everything moved slowly, but purposefully.
Then came the industrial revolution and the British Empire’s iron rails. The first passenger train, launched in 1853 from Bombay to Thane, marked the beginning of India’s modern transport story. Railways became the nation’s backbone, connecting provinces and accelerating economic exchange. Over the decades, India’s railway tracks grew into one of the largest rail networks in the world, symbolizing unity through motion.
🛣️ Roads: The Nerves of a New India
After independence, India faced a new challenge — to knit a fragmented nation into one seamless entity. Roads became the answer. The government began laying down asphalt ribbons across states, linking villages to cities and markets to minds.
From the dusty lanes of Rajasthan to the expressways of Maharashtra, India built one of the world’s longest road networks, now spanning over 66 lakh kilometers. Every highway became a story — of truck drivers battling sleepless nights, of buses carrying families toward better opportunities, and of logistics companies like ABCC INDIA PROJECT CARGO CORPORATION ensuring that even the heaviest cargo reached the remotest corner safely.
In many ways, the road network didn’t just connect cities; it connected destinies.
🚆 Railways: The Steel Backbone of Dreams
If roads connected villages, railways united hearts. The Indian Railways became the heartbeat of the nation — carrying over 23 million passengers and millions of tons of goods daily.
For the common man, the train is more than transport; it’s emotion. It’s the sound of childhood vacations, the scent of tea at platform stalls, the comfort of a window seat watching fields glide by. For businesses, it’s the guarantee of reliability.
From coal and steel to cement and agricultural produce, freight trains ensure India’s industries never stop running. The new Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFC) are transforming speed and efficiency — a silent revolution in how India moves goods from one coast to another.
✈️ Air Transport: Wings of Modern India
While trains and roads built the base, air transport gave India its wings. What once took days on land now takes hours in the air.
The sky became India’s new highway — carrying not only people but also perishable goods, pharmaceuticals, and express cargo. Domestic airlines connected smaller towns under the UDAN Scheme, turning previously remote areas into economic hubs.
For logistics companies, air freight became a symbol of precision — time-bound, high-value, and crucial. It transformed India’s delivery systems, helping businesses promise “next-day delivery” even across states.
🚢 Waterways: The Ancient Artery Reborn
Long before airplanes and expressways, India’s rivers carried the soul of commerce. The Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Godavari served as ancient trade routes. Today, under the Sagarmala Project and National Waterways Act, those rivers are being revived as modern logistics highways.
Cargo ships and barges now move over 145 million tonnes annually, offering an eco-friendly and cost-effective transport mode. Ports like Chennai, Kochi, and Mumbai are transforming into multimodal hubs — combining sea, road, and rail for seamless logistics.
🏭 The Goods Transport Revolution
Behind every industrial milestone lies the unsung hero — the goods transport sector. From agricultural produce to heavy machinery, India’s goods transport system keeps the economy breathing.
Modern logistics players like ABCC INDIA PROJECT CARGO CORPORATION have elevated this sector with technology-driven operations, heavy-haul trucking, and all-India ODC transportation. Their trailers, ranging from 10 to 65 feet, ensure that even massive industrial components reach their destination safely and efficiently.
In today’s India, transporting a turbine or a transformer is not just about power — it’s about precision, professionalism, and trust.
⚙️ Government Initiatives and Infrastructure Growth
India’s transport success is powered by policy vision. Projects like:
- Bharatmala (for highway development),
- Sagarmala (for coastal port connectivity),
- National Logistics Policy (to reduce logistics costs),
- Metro Rail Expansion, and
- Electric Vehicle Promotion Schemes
are shaping a new era of sustainable, integrated, and multimodal mobility.
These initiatives don’t just build roads or tracks — they build opportunities.
🌱 Towards a Greener and Smarter Future
India’s transport is now turning digital and green. Electric buses hum silently on city streets. GPS-tracked trucks optimize routes. Smart logistics parks connect warehouses with highways and ports.
The future lies in Electric Mobility (EV), AI-driven route planning, and multimodal logistics, where one digital platform connects road, rail, air, and sea seamlessly.
💡 The Human Side of Transport
Beyond infrastructure, there’s emotion. The driver who covers 1,000 km to deliver food grains, the train operator ensuring millions reach safely, the logistics manager tracking every shipment — together, they represent India’s unstoppable spirit of movement.
Every journey — whether a daily bus ride or a cross-country shipment — adds to the symphony of a moving nation.
🏁 The Road Ahead
The story of Transport in India is a story of resilience, reinvention, and reach. It’s about how roads, rails, rivers, and runways merge into one mission — to move a nation forward.
From bullock carts to bullet trains, from wooden boats to container ships, from hand-pulled rickshaws to electric trucks — India has not just built transport; it has built transformation.
And leading this transformation are companies like ABCC INDIA PROJECT CARGO CORPORATION, ensuring that India’s goods, industries, and ambitions never stand still.
🚦 Types of Transport in India (Public & Goods)
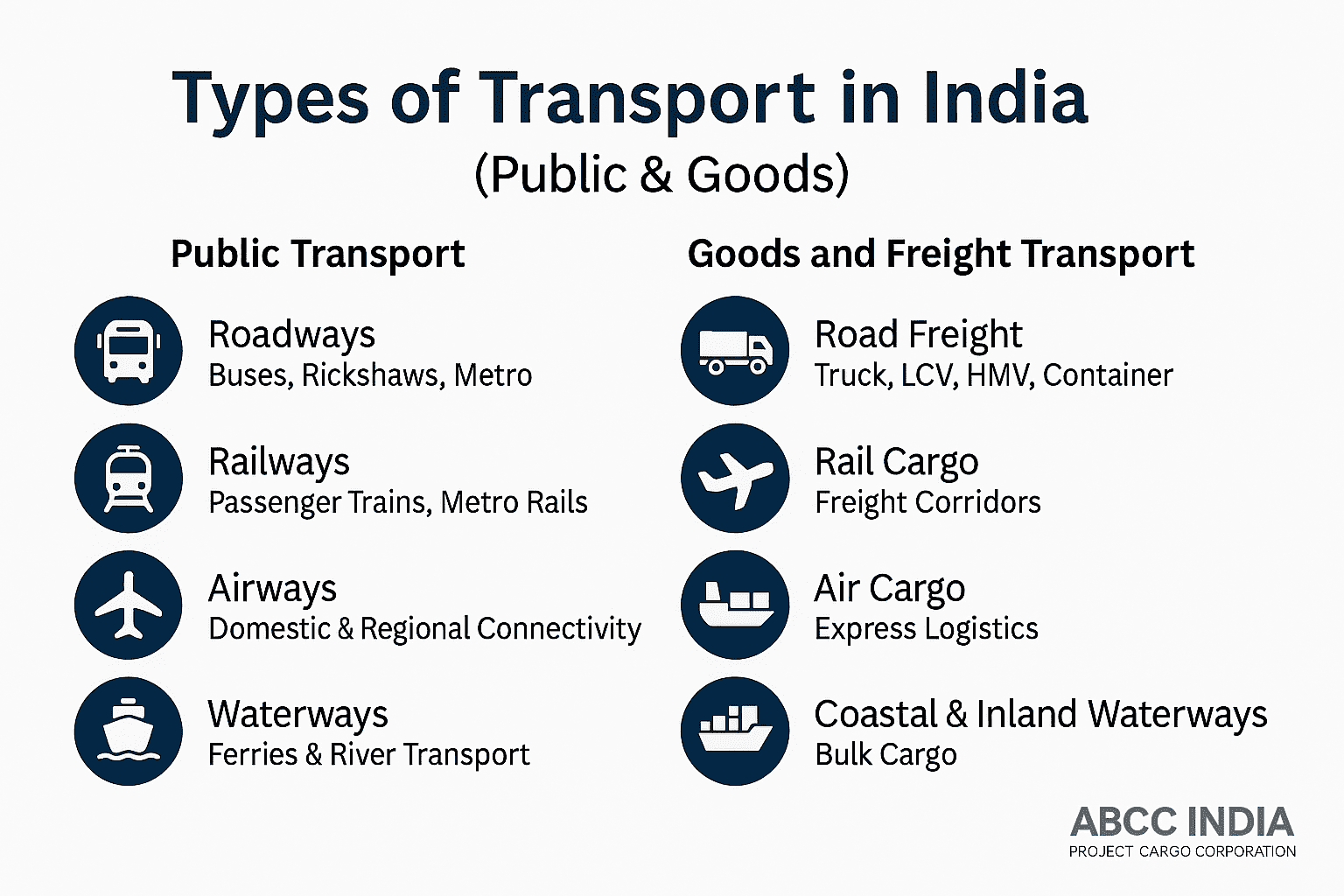
The Journey That Moves a Nation Forward
Transport in India is not merely a network of roads, rails, skies, or rivers — it’s a living, breathing system that keeps 1.4 billion people connected. From school buses to shipping vessels, every mode of transport tells a story — of ambition, adaptation, and advancement.
Let’s travel through the lanes, tracks, skies, and waterways that make India’s transport system one of the most dynamic in the world.
🚍 1. Road Transport: The Artery of Everyday Life

Every dawn in India begins with the hum of engines — trucks, buses, and scooters lining up for their daily journeys. Road transport is the most vital and accessible mode, covering over 66 lakh kilometers of highways, rural roads, and expressways.
🚗 Public Road Transport
For millions, the road is life itself. City dwellers depend on buses, cabs, and autorickshaws, while rural commuters rely on shared jeeps and state-run transport. From the jam-packed Delhi Metro feeder buses to the scenic mountain drives of Himachal, roads bring rhythm to daily living.
🚛 Goods Road Transport
But beneath this public flow runs the lifeline of commerce — goods transport. Thousands of trucks, containers, and trailers traverse the nation daily, carrying everything from fresh fruits to construction equipment.
Companies like ABCC INDIA PROJECT CARGO CORPORATION have transformed this sector, offering:
- Trailer Trucks (10–65 feet) for ODC cargo
- Containerized Fleet for sensitive shipments
- Multi-axle Trucks for heavy machinery
- Specialized Vehicles for car carriers and industrial freight
Every mile covered by these vehicles contributes to the nation’s GDP, ensuring that goods move seamlessly from Madurai to Mumbai and Chennai to Chandigarh.
🚆 2. Rail Transport: The Steel Symphony of India

If roads are the veins of India, then railways are its beating heart. Since the first train steamed out of Bombay in 1853, India’s rail system has grown into one of the largest in the world — spanning over 68,000 kilometers.
🚋 Public Passenger Railways
For the average Indian, trains are not just a mode of travel; they are memories. From chai at stations to window seats in sleeper coaches, the railway is a journey through India’s soul. It connects metros to remote villages, carrying over 23 million passengers daily.
🚂 Goods Railways
On parallel tracks runs another story — one of industry and logistics. India’s freight trains carry bulk commodities like coal, steel, fertilizers, and cement across the country.
The Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFC), a flagship project, have revolutionized the logistics landscape by enabling faster, more efficient cargo movement.
For companies like ABCC INDIA PROJECT CARGO CORPORATION, rail freight offers an eco-friendly alternative for long-haul, heavy, and containerized cargo — merging cost-efficiency with reliability.
✈️ 3. Air Transport: India’s Wings of Progress

High above the chaos of roads and rails, India’s air transport is rewriting the rules of speed and efficiency.
🛫 Public Air Transport
Air travel once meant luxury, but today it’s a symbol of accessibility. Under the UDAN Scheme (Ude Desh ka Aam Nagrik), even small towns like Jharsuguda and Belgaum have regular air connectivity. Airlines like IndiGo, Air India, and Vistara link business hubs, tourist cities, and border regions.
Air transport now carries millions of passengers annually, shrinking time and distance across the vast subcontinent.
📦 Air Cargo Transport
Beyond passengers, India’s skies also carry precision cargo — medical equipment, electronics, and express parcels. Logistics players use air routes for high-value, time-sensitive deliveries.
ABCC INDIA PROJECT CARGO CORPORATION leverages air-cargo integration for clients needing rapid transit for critical materials, balancing time and reliability with advanced route planning.
🚢 4. Water Transport: The Ancient Artery Reimagined
Before rails and roads, India’s rivers and coasts powered trade and travel. Today, water transport is making a powerful comeback as an eco-friendly, low-cost mode of logistics.
⛴️ Public Water Transport
In states like Kerala, Goa, and Assam, ferries and boats continue to serve passengers daily. Urban water metros, like in Kochi, bring sustainable public commuting back to life.
⚓ Goods and Cargo Waterways
Under the Sagarmala Project and National Waterways Act, India has revitalized its maritime network. Over 145 million tonnes of cargo now move through inland and coastal routes annually.
Major ports like Mumbai, Chennai, and Kochi act as logistics gateways for both domestic and international trade. For bulk goods such as coal, steel, and food grains, waterways remain a cost-effective alternative to road or rail.
🚜 5. Pipeline Transport: The Hidden Flow Beneath
Unseen but powerful, pipeline transport silently carries India’s lifeblood — crude oil, natural gas, and petroleum products. Stretching thousands of kilometers underground, pipelines connect refineries, ports, and industries without traffic or pollution.
This system ensures constant energy supply while reducing dependence on road and rail tankers, contributing to national energy security.
🛰️ 6. Emerging Digital and Electric Transport
India is witnessing a futuristic transition — from diesel to digital, and from mechanical to electrical.
Electric buses glide across cities, and EV trucks are reshaping goods logistics.
ABCC INDIA PROJECT CARGO CORPORATION has begun adapting to this change with hybrid fleets and sustainable logistics solutions — making Indian transport cleaner, smarter, and more efficient.
🏁 One Nation, Many Modes, One Mission

Transport in India is not just infrastructure — it’s identity. Whether it’s a villager boarding a bus to the nearest town or a trailer truck hauling turbines across states, every journey adds to India’s movement story.
From bullock carts to bullet trains, from ferries to freight corridors — India moves, and the world takes note.
And at the heart of this motion, companies like ABCC INDIA PROJECT CARGO CORPORATION ensure that goods, people, and progress never stop rolling forward.
graphic for this section — showing all types of transport (Public & Goods) with icons and ABCC logo watermark in white background?
🚦 INDIA’S TRANSPORT ECOSYSTEM AT A GLANCE
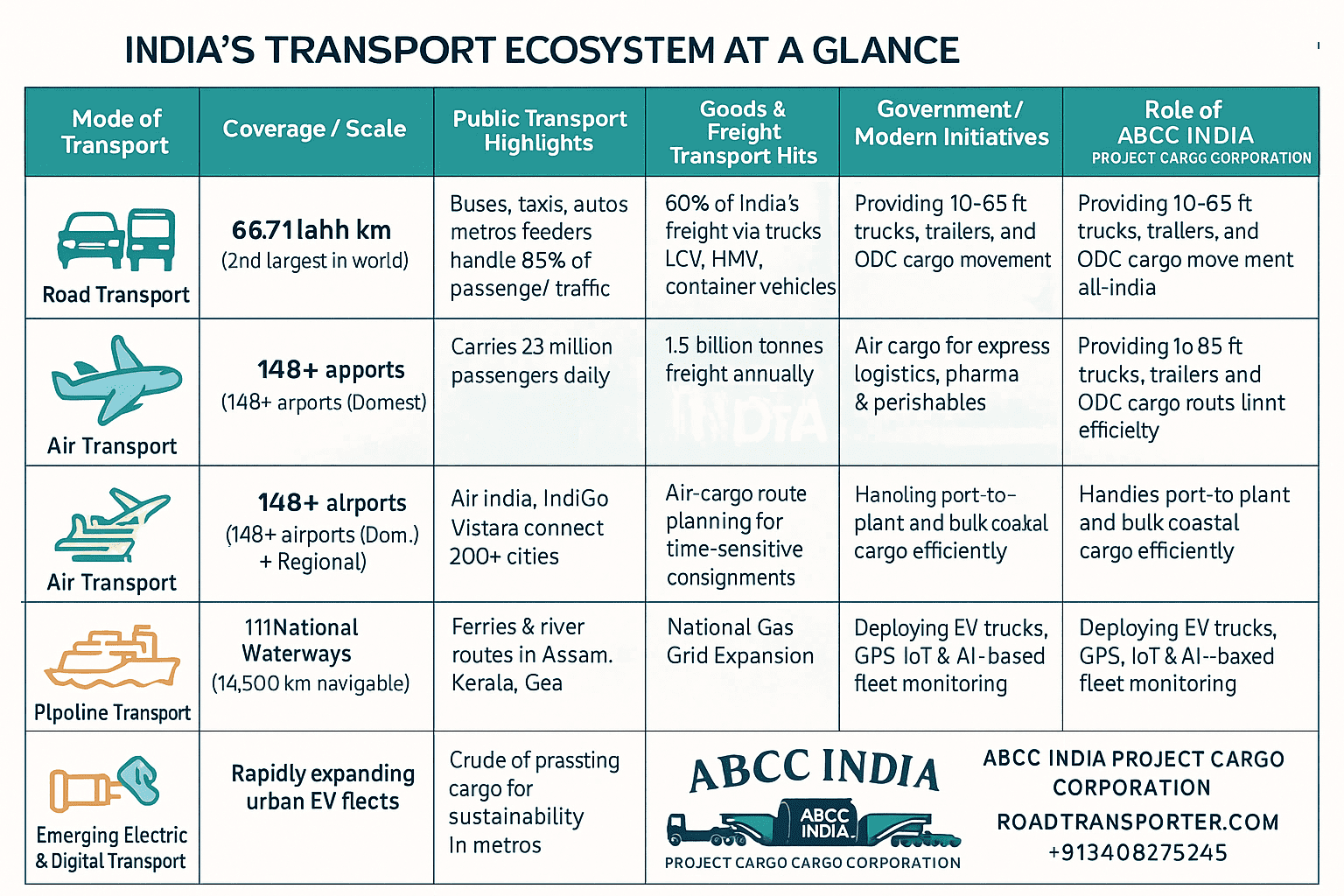
| 🚗 Mode of Transport | 🧭 Coverage / Scale | 🚍 Public Transport Highlights | 🚛 Goods & Freight Transport Highlights | ⚙️ Government / Modern Initiatives | 🏢 Role of ABCC INDIA PROJECT CARGO CORPORATION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Road Transport | 66.71 lakh km (2nd largest in world) | Buses, taxis, autos, metro feeders handle 85% of passenger traffic | 60% of India’s freight via trucks, LCV, HMV, container vehicles | Bharatmala Project, Expressway Development | Provides 10–65 ft trucks, trailers, and ODC cargo movement all-India |
| Rail Transport | 68,000+ km | Carries 23 million passengers daily | 1.5 billion tonnes freight annually | Dedicated Freight Corridors, Vande Bharat Trains | Offers multimodal coordination with rail logistics for heavy loads |
| Air Transport | 148+ airports (Domestic + Regional) | Air India, IndiGo, Vistara connect 200+ cities | Air cargo for express logistics, pharma & perishables | UDAN Scheme, Airport Modernization | Air-cargo route planning for time-sensitive consignments |
| Water Transport | 111 National Waterways, 14,500 km navigable | Ferries and river routes in Assam, Kerala, Goa | 145 million tonnes cargo (inland + coastal) | Sagarmala Project, Inland Water Terminals | Handles port-to-plant and bulk coastal cargo efficiently |
| Pipeline Transport | 32,000+ km | Not applicable | Crude oil, gas & petroleum movement | National Gas Grid Expansion | Supports combined energy-logistics coordination with bulk partners |
| Emerging Electric & Digital Transport | Rapidly expanding urban EV fleets | Electric buses and shared mobility in metros | Hybrid & EV trucks for sustainable freight | National EV Policy, Digital Logistics Mission | Deploying EV trucks, GPS, IoT & AI-based fleet monitoring |
🚛 Road Transport in India for Public and Goods: The Artery of a Moving Nation
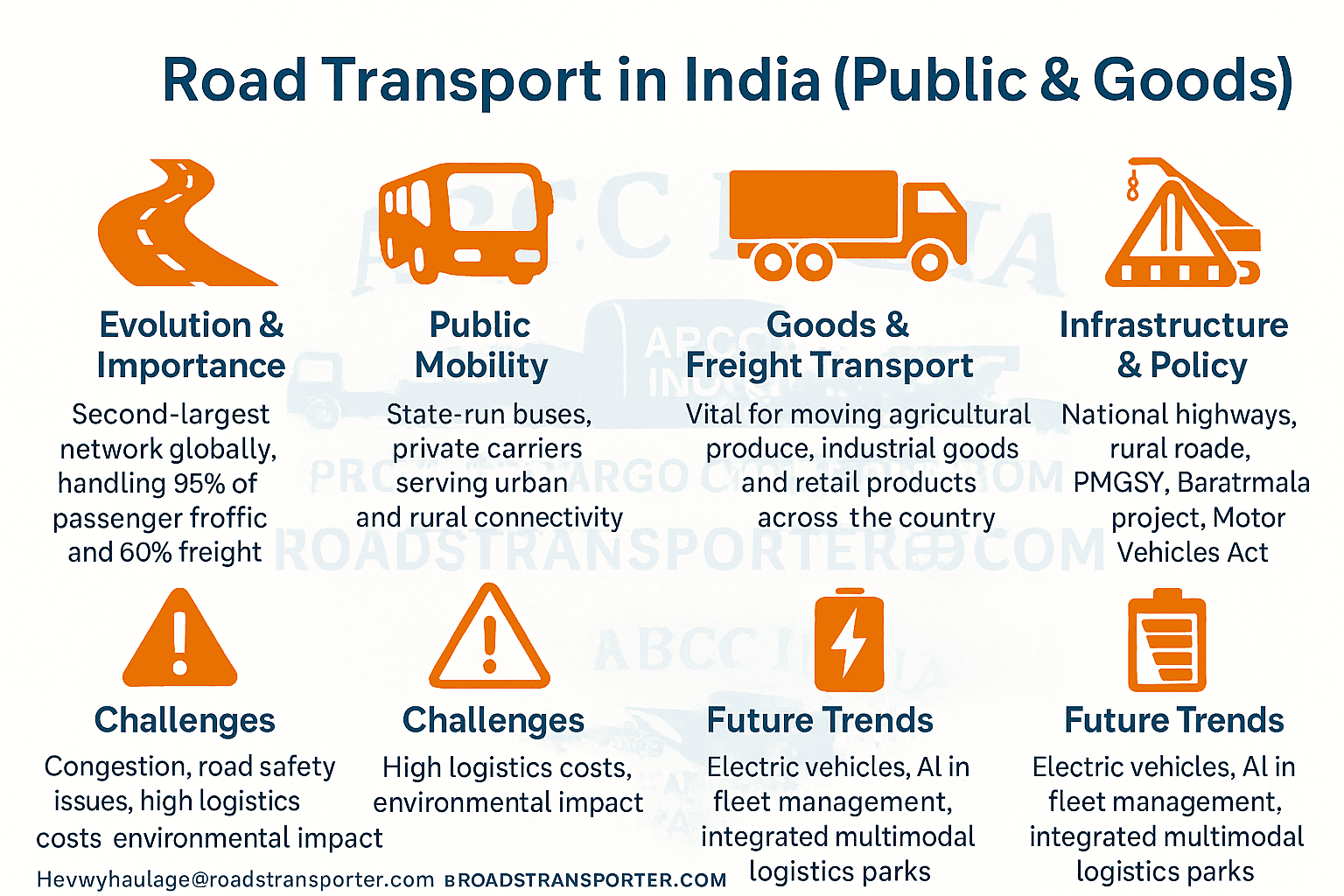
Road transport in India is not merely a mode of travel; it is the lifeline of the nation’s economy and society. Every dawn witnesses a vibrant spectacle — buses loaded with passengers, trucks carrying goods across states, and highways humming with motion. The Indian road network binds together over 1.4 billion people, linking the remotest villages to metropolitan hubs, and farmers to markets.
It is both the heart of public mobility and the backbone of commercial logistics.
🛣️ 1. Evolution and Importance of Road Transport in India
The history of road transport in India traces back centuries — from ancient trade routes like the Grand Trunk Road connecting Kabul to Kolkata, to modern expressways linking Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, and Bengaluru. After independence, the Indian government prioritized roads as the most flexible and accessible mode of connectivity.
With time, roadways have grown into the second-largest road network in the world, spanning more than 66.7 lakh kilometers. Roads today handle 85% of passenger traffic and over 60% of freight movement, playing a central role in both rural and urban development.
Unlike railways or airways, road transport offers door-to-door convenience, allowing direct accessibility to homes, factories, and marketplaces — a crucial factor for a geographically diverse country like India.
🚍 2. Road Transport for Public Mobility
2.1. Backbone of Daily Commuting
Public road transport serves as the primary mode of travel for millions of Indians every day. From urban metro buses and ride-sharing cabs to rural jeeps and auto-rickshaws, the road network caters to every socioeconomic layer.
The system includes:
- State Transport Undertakings (STUs) operating intercity and interdistrict buses.
- Private operators running local and long-distance services.
- Metro feeder buses and shared mobility services improving last-mile connectivity.
In cities like Mumbai, Bengaluru, and Delhi, buses remain the most affordable and accessible option for daily commuting, particularly for the working class.
2.2. Rural Connectivity
For rural India, road transport is synonymous with opportunity. Projects like the Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) have connected thousands of villages to nearby markets, schools, and hospitals.
These rural roads are not just travel paths; they are economic corridors that enable farmers to sell produce, students to access education, and patients to reach healthcare facilities.
2.3. Modernization and Challenges
The government has introduced digital ticketing, GPS tracking, and electric bus programs to modernize public transport. However, challenges remain — such as congestion, pollution, and inadequate infrastructure in smaller towns. The transition to Electric Vehicles (EVs) and integrated multimodal systems is now redefining how Indian roads support sustainable public movement.
🚚 3. Road Transport for Goods and Freight
3.1. The Economic Engine
Goods transport by road forms the spine of India’s logistics industry. It connects production centers, warehouses, ports, and consumers across states. The trucking industry alone handles nearly two-thirds of the nation’s freight — moving agricultural products, construction materials, manufacturing goods, and retail supplies.
The rise of e-commerce, industrial corridors, and fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) has further strengthened the demand for efficient goods road transport. Highways serve as arteries through which the economy’s pulse flows.
3.2. Types of Goods Vehicles
India’s freight vehicles range from mini trucks and light commercial vehicles (LCVs) for local deliveries to heavy motor vehicles (HMVs) and multi-axle trailers for long-haul cargo. Specialized carriers are also used for:
- Containerized goods
- Over-Dimensional Cargo (ODC)
- Hazardous materials
- Cold chain logistics
Each category serves a unique purpose within the logistics framework, enabling transport across terrains — from hilly regions to coastal zones.
3.3. Role in Industrial and Agricultural Supply Chains
Road freight ensures that India’s industries — steel, cement, textiles, and chemicals — function smoothly. It bridges the gap between production zones and consumption markets. Similarly, it allows perishable goods like fruits, dairy, and grains to reach cities from rural regions in minimal time.
Without road transport, India’s farm-to-market and port-to-factory linkages would break down.
🏗️ 4. Infrastructure and Policy Framework
4.1. National Highways and Expressways
India’s National Highways Authority (NHAI) oversees major routes that connect cities and states. With projects like Bharatmala Pariyojana, India is developing economic corridors, expressways, and logistics hubs to minimize travel time and freight cost.
Key corridors include:
- Delhi–Mumbai Expressway
- Chennai–Bengaluru Industrial Corridor
- Eastern and Western Dedicated Freight Corridors (integrating rail and road systems)
4.2. State and Rural Roads
State highways and district roads ensure last-mile access. They may not always match the capacity of national highways but play a vital role in regional commerce and mobility. Rural connectivity projects continue to expand, empowering local economies and reducing migration pressures on cities.
4.3. Policy and Regulation
The Motor Vehicles Act, Goods and Services Tax (GST), and E-Way Bill system have streamlined interstate transportation.
Technological adoption, including FASTag tolling and real-time vehicle tracking, has improved transparency and reduced delays in freight movement.
⚙️ 5. Challenges in Road Transport
Despite its massive scale, India’s road transport sector faces structural and operational challenges:
- Congestion: Urban areas experience severe traffic due to population density and rising vehicle ownership.
- Road Safety: India records high accident rates due to inadequate enforcement and driver fatigue.
- Environmental Impact: Heavy reliance on diesel contributes to pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Logistics Costs: India’s logistics cost (~13% of GDP) is higher than developed economies (8–9%), primarily due to inefficiencies in multimodal integration.
Efforts to address these include the promotion of electric mobility, green logistics, and digitized transport infrastructure.
🌱 6. Future Trends: Toward Smart and Sustainable Roads
The future of road transport in India is defined by technology, sustainability, and connectivity.
Key trends shaping the sector include:
- Electric and Hydrogen Vehicles: Reducing dependency on fossil fuels.
- AI and IoT in Fleet Management: Real-time monitoring for cost optimization.
- Integrated Multimodal Logistics Parks: Seamless connection between road, rail, and ports.
- Public Transport Electrification: Eco-friendly buses and smart city transport solutions.
- Highway Digitalization: Intelligent Traffic Management Systems (ITMS) for safer travel.
Together, these initiatives aim to make India’s road network faster, cleaner, and smarter — turning infrastructure into innovation.
🏁 Road transport in India embodies mobility, economic growth, and social transformation. For the public, it represents access — to education, work, and healthcare. For industries, it ensures the circulation of goods and wealth.
Every highway, from the bustling Mumbai–Pune Expressway to the quiet rural lanes of Odisha, contributes to a collective national rhythm — the movement that defines India.
As the country embraces technological innovation and sustainable practices, road transport will continue to evolve — not just as a means of travel, but as a symbol of progress and resilience.
🛣️ EVOLUTION OF ROAD TRANSPORT IN INDIA
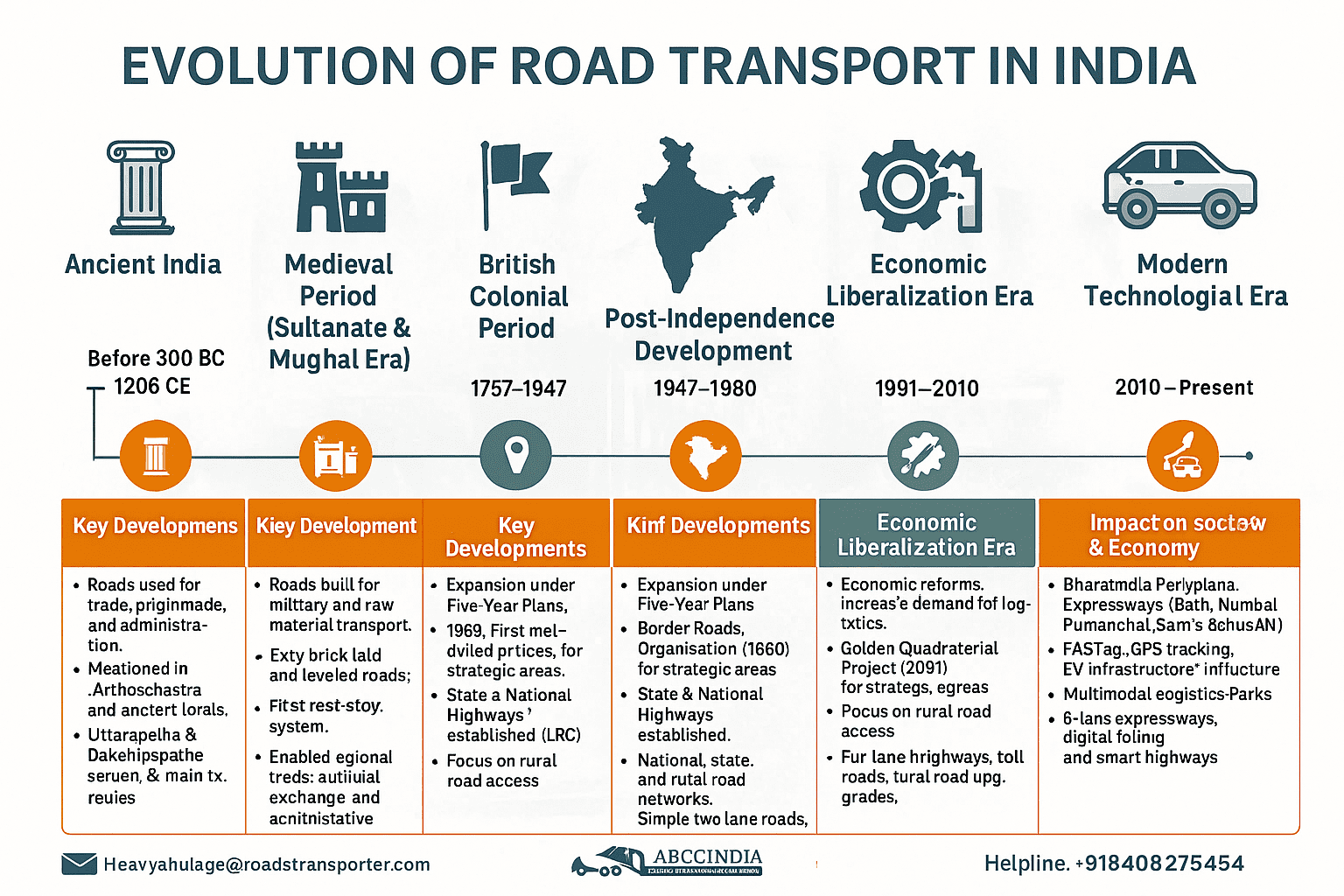
| 🏺 Era / Period | 🕰️ Timeline | 🚗 Key Developments | 🏗️ Infrastructure Features | 🌏 Impact on Society & Economy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ancient India | Before 300 BCE – 1200 CE | – Roads used for trade, pilgrimage, and administration.- Mentioned in Arthashastra and ancient texts.- Uttarapatha & Dakshinapatha served as main routes. | Dirt tracks and stone pathways; maintained by local kingdoms. | Enabled regional trade, cultural exchange, and administrative connectivity. |
| Medieval Period (Sultanate & Mughal Era) | 1200 – 1757 | – Sher Shah Suri built the Grand Trunk Road connecting Kabul to Bengal.- Establishment of Sarai (rest houses) and milestones. | Early brick-laid and leveled roads; first rest-stop system. | Strengthened trade across empires; improved postal and military movement. |
| British Colonial Period | 1757 – 1947 | – Roads built for military and raw material transport.- 1839: First metalled road (Calcutta–Diamond Harbour).- 1920: Formation of Indian Roads Congress (IRC).- 1943: Nagpur Road Plan proposed national framework. | Paved roads linking ports and cantonments; early highways. | Boosted exports, urban growth near ports, and military logistics. |
| Post-Independence Development | 1947 – 1990 | – Expansion under Five-Year Plans.- Border Roads Organisation (1960) for strategic areas.- State & National Highways established.- Focus on rural road access. | National, state, and rural road networks.Simple two-lane roads. | Enhanced internal trade, unity, and rural mobility. |
| Economic Liberalization Era | 1991 – 2010 | – Economic reforms increased demand for logistics.- Golden Quadrilateral Project (2001).- Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (2000) for village roads.- PPP model and NHAI modernization. | Four-lane highways, toll roads, and rural road upgrades. | Improved freight efficiency and intercity transport connectivity. |
| Modern Technological Era | 2010 – Present | – Bharatmala Pariyojana, Expressways (Delhi–Mumbai, Purvanchal, Samruddhi).- FASTag, GPS tracking, and EV infrastructure.- Development of Multimodal Logistics Parks. | 6-lane expressways, digital tolling, and smart highways. | Reduced logistics cost, faster travel, sustainable transport vision. |
India’s road transport evolved from mud pathways to digital expressways, integrating technology, sustainability, and inclusivity.
It now covers 66.71 lakh km, carrying 85% of passenger traffic and 60% of freight, serving as the backbone of India’s economy.
🚗 ROAD TRANSPORT EXPANSION IN INDIA
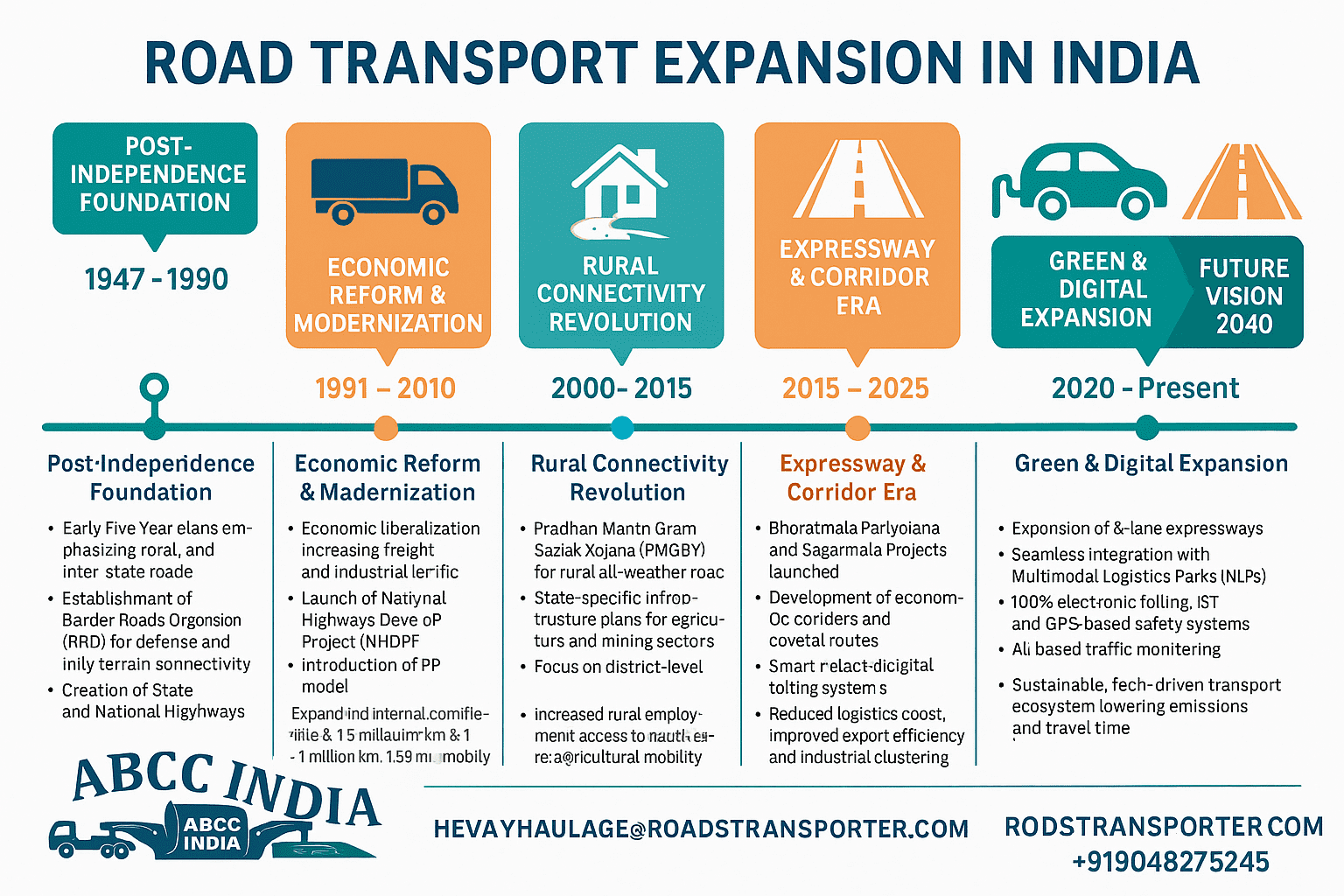
| 🏗️ Phase / Period | 🕰️ Timeline | 🚦 Major Developments & Programs | 🌉 Infrastructure Highlights | 📈 Impact on Connectivity & Economy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Post-Independence Foundation | 1947 – 1990 | – Early Five-Year Plans emphasized rural and inter-state roads.- Establishment of Border Roads Organisation (BRO) for defense and hilly terrain connectivity.- Creation of State and National Highways. | 0.4 million km of mixed-surface roads expanded to 1.5 million km.First National and State Highway grids. | Improved internal connectivity, rural market access, and defense mobility. |
| Economic Reform & Modernization | 1991 – 2010 | – Economic liberalization increased freight and industrial traffic.- Launch of National Highways Development Project (NHDP).- Golden Quadrilateral and North–South / East–West Corridors initiated.- Introduction of PPP model. | Upgraded 4-lane highways connecting Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata.Widening of key national routes. | Boosted national trade routes, improved freight speed, and supported industrial logistics. |
| Rural Connectivity Revolution | 2000 – 2015 | – Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) for rural all-weather roads.- State-specific infrastructure plans for agriculture and mining sectors.- Focus on district-level roads. | 1.8 lakh+ villages connected.Upgraded rural infrastructure with concrete and bitumen roads. | Increased rural employment, access to healthcare, and agricultural mobility. |
| Expressway & Corridor Era | 2015 – 2025 | – Bharatmala Pariyojana and Sagarmala Projects launched.- Development of economic corridors and coastal routes.- Smart traffic and digital tolling systems (FASTag). | Construction of 6-lane expressways (Delhi–Mumbai, Samruddhi, Purvanchal).Expansion to 1,40,000+ km National Highways. | Reduced logistics cost, improved export efficiency, and industrial clustering. |
| Green & Digital Expansion | 2020 – Present | – PM Gati Shakti integrated planning for roads, ports, and rails.- National Logistics Policy (NLP 2022).- Use of recycled materials, solar lighting, EV charging networks.- AI-based traffic monitoring. | Digital highway management, green corridors, and electric mobility routes. | Sustainable, tech-driven transport ecosystem lowering emissions and travel time. |
| Future Vision 2040 | 2025 – 2040 (Projection) | – Expansion of 8-lane expressways.- Seamless integration with Multimodal Logistics Parks (MMLPs).- 100% electronic tolling, IoT and GPS-based safety systems. | Advanced expressways, AI-integrated logistics zones, and EV transport highways. | India as a global logistics hub with reduced transit cost and enhanced global competitiveness. |
🧭 Summary Insight
- India’s road network has expanded from 0.4 million km in 1947 to 66.7 lakh km in 2025, making it the second-largest globally.
- Roads handle 85% of passenger transport and 60% of goods transport, playing a vital role in employment, industry, and logistics efficiency.
- Expansion continues toward sustainable, multimodal, and digital connectivity under projects like Bharatmala, PM Gati Shakti, and Green Highway initiatives.
🚛 ROAD TRANSPORT CONTRIBUTION IN MULTIMODAL LOGISTICS (INDIA)
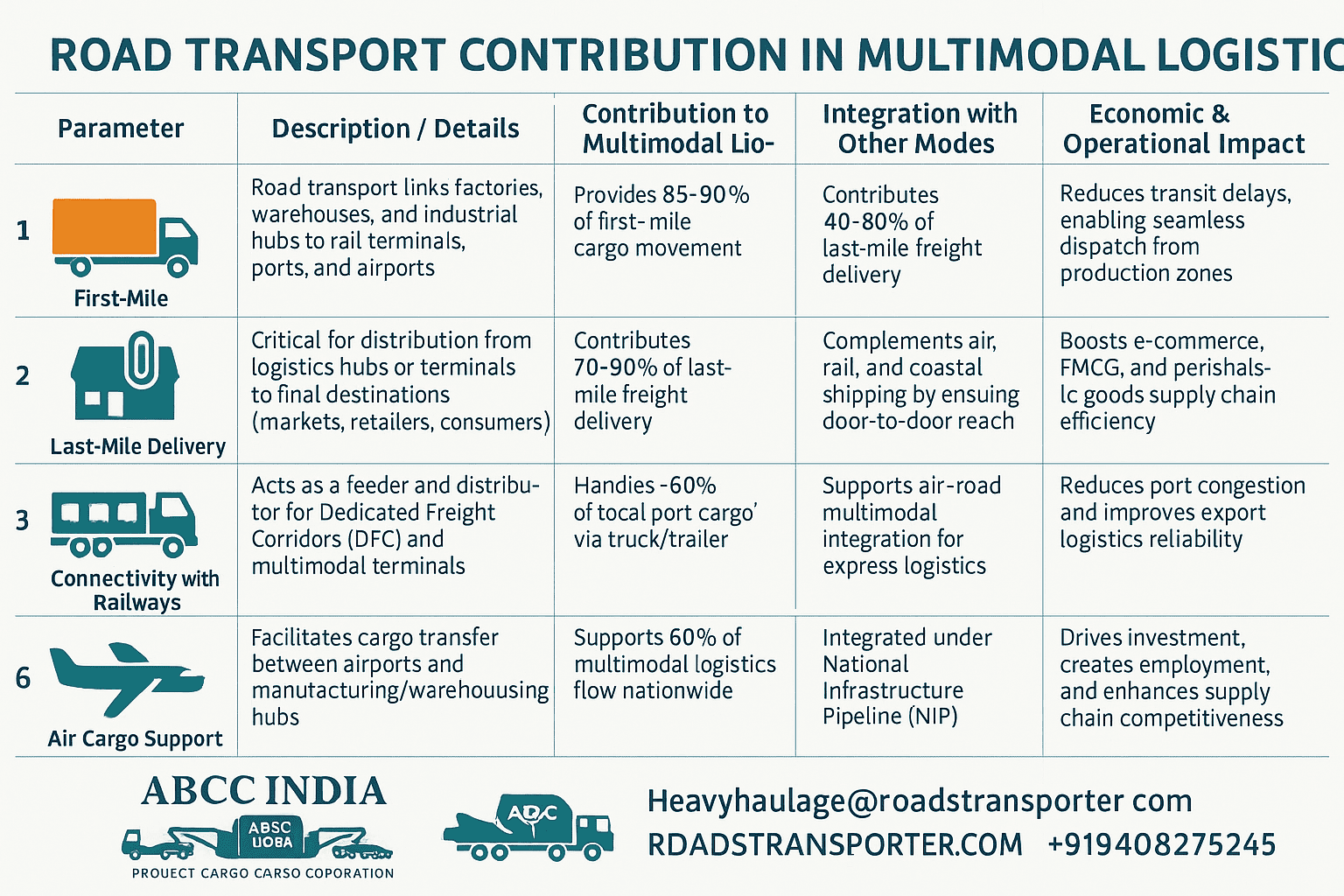
| 🔹 Parameter | 🚦 Description / Details | 📈 Contribution to Multimodal Logistics | 🏗️ Integration with Other Modes | 🌏 Economic & Operational Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. First-Mile Connectivity | Road transport links factories, warehouses, and industrial hubs to rail terminals, ports, and airports. | Provides 85–90% of first-mile cargo movement. | Connects directly to rail sidings, ICDs, CFSs, and port terminals. | Reduces transit delays, enabling seamless dispatch from production zones. |
| 2. Last-Mile Delivery | Critical for distribution from logistics hubs or terminals to final destinations (markets, retailers, consumers). | Contributes 70–80% of last-mile freight delivery. | Complements air, rail, and coastal shipping by ensuring door-to-door reach. | Boosts e-commerce, FMCG, and perishable goods supply chain efficiency. |
| 3. Connectivity with Railways | Acts as a feeder and distributor for Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFC) and multimodal terminals. | Handles feeder loading/unloading for rail cargo at major junctions. | Integrated under Bharatmala + Sagarmala + DFC network. | Balances bulk and light cargo, ensuring faster logistics cycles. |
| 4. Linkage to Ports & Inland Waterways | Roads connect Inland Container Depots (ICDs) and Dry Ports to coastal gateways. | Moves ~60% of total port cargo via truck/trailer. | Enables road–sea intermodal transport (important for exports/imports). | Reduces port congestion and improves export logistics reliability. |
| 5. Air Cargo Support | Facilitates cargo transfer between airports and manufacturing/warehousing hubs. | ~65% of air freight relies on road for pre/post-airport movement. | Supports air–road multimodal integration for express logistics. | Enables time-critical deliveries (pharma, electronics, high-value goods). |
| 6. National Highway Corridors | Major highways serve as economic corridors linking multiple modes of transport. | Supports 60% of multimodal logistics flow nationwide. | Aligned with PM Gati Shakti, Bharatmala, and NLP 2022. | Lowers logistics cost (target: <10% of GDP) and improves transit reliability. |
| 7. Industrial & Logistics Parks | Roads provide direct access to Multimodal Logistics Parks (MMLPs) and SEZs. | Enables multimodal cargo transfer (road–rail–port). | Integrated under National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP). | Drives investment, creates employment, and enhances supply chain competitiveness. |
| 8. Smart & Green Integration | Road networks adopting EV trucks, GPS, IoT, and FASTag for digital logistics. | Supports eco-friendly and tech-driven freight systems. | Works with digital multimodal platforms (ULIP, NLP Dashboard). | Promotes sustainable and transparent logistics operations. |
🚨 Major Road Transport Accidents in India (2004–2024)
| 📅 Year | 📍 Location / State | 🚍 Type / Cause | ⚰️ Deaths | 📰 Brief Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 | Kasganj, Uttar Pradesh | Bus–train collision at level crossing | 49 | Bus split into two on unmanned crossing; one of India’s deadliest road-rail disasters. |
| 2008 | Nagpur, Maharashtra | Train hit truck-trailer on level crossing | 58 | Lack of warning system at unmanned gate caused massive casualties. |
| 2013 | Himachal Pradesh | School bus fell into gorge | 28 (23 students) | Mountainous road failure and brake malfunction. |
| 2017 | Firozabad, Uttar Pradesh | Multiple vehicle pile-up on Yamuna Expressway | 21 | Dense fog and overspeeding led to serial collision. |
| 2019 | Karnataka, Mandya | Private bus caught fire after collision | 30 | Diesel leakage and blocked exits worsened the tragedy. |
| 2020 | Moradabad, Uttar Pradesh | Truck–bus collision on NH-24 | 25 | Migrant workers returning during lockdown killed; fatigue-related accident. |
| 2021 | Nashik, Maharashtra | Bus–tanker collision | 27 | Diesel tanker explosion on impact; widespread fire casualties. |
| 2022 | Barabanki, Uttar Pradesh | Truck hit stranded bus on highway | 18 | Night visibility failure and lack of warning signs. |
| 2023 | Doda, Jammu & Kashmir | Bus fell into gorge (mountain terrain) | 39 | Overloaded passenger bus lost control on sharp turn. |
| 2024 | Almora, Uttarakhand | Bus plunged into valley | 38 | Poor weather and narrow hill road caused fatal crash. |
📊 Annual Road Accident Statistics (India – MoRTH Data)
| 🗓️ Year | 🚗 Total Accidents | ⚰️ Total Deaths | 🚑 Injured Persons |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 470,403 | 157,593 | 464,715 |
| 2019 | 456,959 | 158,984 | 449,360 |
| 2020 | 372,181 | 138,383 | 346,747 |
| 2021 | 412,432 | 153,972 | 384,448 |
| 2022 | 461,312 | 168,491 | 443,366 |
🚧 ROAD TRANSPORT IN INDIA — PROBLEMS, REASONS, CHALLENGES & SOLUTIONS
| ⚙️ Category | 🛑 Problems / Issues | ⚠️ Underlying Reasons | 🧩 Key Challenges | 💡 Suggested Solutions / Improvements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Infrastructure Deficiency | Poor road conditions, potholes, weak bridges, uneven road surfaces | Inadequate maintenance budgets, heavy rainfall damage, poor material quality | Rapid deterioration of highways and rural roads | Regular road audits, use of long-lasting materials, and timely maintenance through public–private models |
| 2. Traffic Congestion | Long queues, bottlenecks in cities and toll plazas | Unplanned urban growth, lack of traffic management, increase in private vehicles | Reduced speed, longer travel time, and higher fuel consumption | Smart traffic systems (ITMS), improved public transport, and separate lanes for freight |
| 3. Road Safety Issues | High rate of accidents and fatalities | Overspeeding, fatigue, poor road signage, inadequate driver training | 1.5 lakh+ annual deaths; loss of GDP due to accidents | Strict enforcement of Motor Vehicles Act, better driver training, improved road signage, emergency lanes |
| 4. Environmental Impact | Air and noise pollution from diesel vehicles | Overdependence on fossil fuels, poor vehicle maintenance | Rising carbon emissions, poor urban air quality | Promote EVs, CNG/LNG trucks, emission testing, and green highway plantation drives |
| 5. High Logistics Cost | Costlier than global average (13–14% of GDP) | Inefficient route planning, poor coordination between modes | Reduced trade competitiveness | Integrate multimodal systems, develop logistics parks, digital freight management |
| 6. Overloading of Vehicles | Trucks carrying more than permitted weight | Weak enforcement and corruption at checkpoints | Road damage, increased wear on tires and brakes | Use digital weighing systems, strict penalties, and GPS-based monitoring |
| 7. Rural Accessibility Gaps | Villages without proper all-weather roads | Funding delays, terrain challenges | Isolation during monsoon and poor market connectivity | Expand PMGSY with better materials and bridges; focus on North-East and hilly areas |
| 8. Institutional & Policy Gaps | Fragmented coordination between central, state, and local bodies | Overlapping responsibilities and lack of unified planning | Delay in project approvals and execution | Strengthen coordination under PM Gati Shakti and implement integrated road planning |
| 9. Urban Transport Imbalance | Overcrowded city roads; weak public transport | Rapid migration, lack of metro/bus expansion | Increased private vehicle ownership | Promote EV-based city buses, metro expansion, shared mobility apps |
| 10. Technological Lag | Limited use of modern systems in maintenance and traffic | Lack of investment in digital infrastructure | Reactive maintenance instead of preventive | Adopt GIS, IoT, AI-based monitoring, and e-surveillance for highways |
India’s road transport problems are multi-dimensional — spanning infrastructure, management, and sustainability.
The way forward lies in smart technology, public–private partnerships, and sustainable multimodal integration to build safer and more efficient roads.
🏛️ GOVERNMENT CONTRIBUTIONS & BIG PROJECTS IN ROAD TRANSPORTATION SERVICES (INDIA)
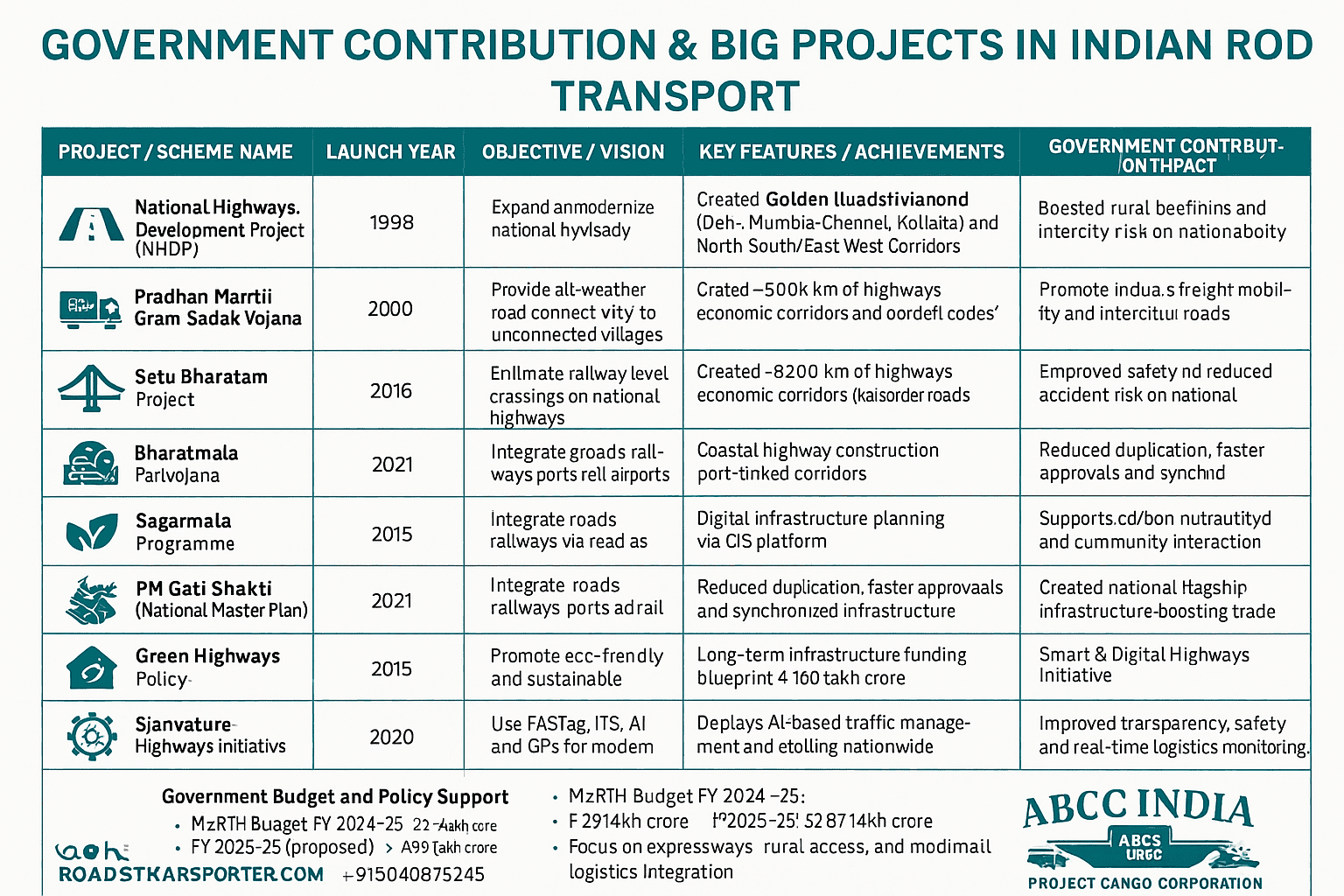
| 🏗️ Project / Scheme Name | 📅 Launch Year | 🎯 Objective / Vision | 🚦 Key Features / Achievements | 💡 Government Contribution / Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| National Highways Development Project (NHDP) | 1998 | Expand and modernize the national highway network. | Created Golden Quadrilateral (Delhi–Mumbai–Chennai–Kolkata) and North–South/East–West Corridors. | Transformed India’s freight mobility and intercity road connectivity. |
| Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) | 2000 | Provide all-weather road connectivity to unconnected villages. | Connected 1.8+ lakh rural habitations with durable rural roads. | Boosted rural economy, agriculture, and social inclusion. |
| Setu Bharatam Project | 2016 | Eliminate railway level crossings on national highways. | 208 ROBs/RUBs planned; 1,500+ old bridges rehabilitated. | Improved safety and reduced accident risk on national routes. |
| Bharatmala Pariyojana | 2017 | Develop 83,000+ km of highways, economic corridors, and border roads. | As of 2025: 26,425 km awarded, 19,826 km completed. | Major infrastructure investment to cut logistics costs and improve regional trade. |
| Sagarmala Programme | 2015 | Connect ports to hinterlands via road and rail. | Coastal highway construction, port-linked corridors. | Enabled port-led development and multimodal integration. |
| PM Gati Shakti (National Master Plan) | 2021 | Integrate roads, railways, ports, and airports for seamless connectivity. | Digital infrastructure planning via GIS platform. | Reduced duplication, faster approvals, and synchronized infrastructure growth. |
| Green Highways Policy | 2015 | Promote eco-friendly and sustainable road corridors. | Tree plantation and renewable lighting along highways. | Supports carbon neutrality and community participation. |
| National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP) | 2019 | Long-term infrastructure funding blueprint. | ₹100 lakh crore investment plan, includes major highway projects. | Accelerated road-building through PPP and private participation. |
| Signature Projects (MoRTH) | Ongoing | Prioritize large national expressways and tunnels. | Includes Delhi–Mumbai Expressway, Eastern Peripheral Expressway, Zoji La Tunnel, etc. | Created national flagship infrastructure boosting trade and tourism. |
| Smart & Digital Highways Initiative | 2020 | Use of FASTag, ITS, AI, and GPS for modern road systems. | Deployed AI-based traffic management and e-tolling nationwide. | Improved transparency, safety, and real-time logistics monitoring. |
📈 Government Budget and Policy Support
- MoRTH Budget FY 2024–25: ₹2.72 lakh crore
- FY 2025–26 (proposed): ₹2.87 lakh crore
- Focus on expressways, rural access, and multimodal logistics integration.
🧭 Key Insight
The Indian Government’s consistent focus on road connectivity, digital infrastructure, and sustainable transport has turned the sector into a growth engine.
Projects like Bharatmala, PM Gati Shakti, and Setu Bharatam are transforming India into a logistics and mobility powerhouse.
🚛 Private Companies’ Contributions in Road Transport in India

| 🔍 Area / Role | 🏷️ Nature of Contribution | 🔧 Functions / Examples | 🏢 Notable Players / Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure & Construction | Building, upgrading, and maintaining highways, expressways, bridges, tunnels | EPC contracts, BOT / PPP / HAM models | DRA Infracon (highways & expressways) |
| Road Materials & Products | Supplying critical materials like bitumen, asphalt, additives | Specialized bitumen supply & polymer-modified asphalt | Tiki Tar and Shell India Pvt Ltd (bitumen / road materials) |
| Toll Road Operation & Management | Running toll collections, maintenance, traffic management on road stretches | Toll-Operate-Transfer (TOT) and concession models | Adani Road Transport Ltd acquiring toll road operator DP Jain TOT |
| Logistics & Goods Transport | Freight movement, trucking, distribution, 3PL/4PL services | Long-haul trucking, express cargo, fleet operations | VRL Group — one of India’s largest private fleet operators |
| Public / Urban Transport & Mobility | Ride-hailing, last-mile delivery, bus operations, mobility services | Bike taxis, parcel delivery, shared mobility | Rapido — bike taxi, auto-rickshaw, parcel services |
| Private Participation in Government Projects | Partnership in highway projects, PPP models, hybrid contracts | Private investment share increasing under NIP & road PPPs | Private share in road projects ~15% now, expected to rise to ~40% |
| Maintenance & Rehabilitation | Periodic resurfacing, repair works on existing roads | Contracts for road upkeep, pavement rehabilitation | Various private contractors on state/national roads (EPC) |
| Technology & Smart Highway Services | Intelligent traffic systems, ITS, digital tolling, traffic monitoring | Deploying sensors, cameras, real-time analytics | Private firms collaborating under smart highway / ITS projects |
| Industrial & Specialized Transport | Moving heavy/ODC cargo, project logistics for industries | Heavy-lift transport, modular trailers, ODC handling | Many logistics companies active in heavy equipment transport |
🌍 MNC COMPANIES’ CONTRIBUTION IN ROAD TRANSPORTATION SERVICES IN INDIA
| 🏢 Contribution Area | ⚙️ Role of MNCs | 🚀 Impact / Value Addition | 🌏 Key Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Global Road Freight & Logistics | Provide end-to-end road freight forwarding, cross-border transport, and multimodal integration. | Enhanced reliability, connectivity, and export-import efficiency. | DHL (Germany) – extensive surface transport network; CJ Logistics (South Korea) – road freight and warehousing. |
| 2. Highway Development & Infrastructure | Invest in road construction, BOT/HAM/PPP projects, and smart highway assets. | Brings private capital, global engineering standards, and project speed. | Adani Enterprises (India-based MNC) – multiple national highway projects; L&T Infrastructure – PPP expressways. |
| 3. Technology & Digital Logistics | Introduce telematics, GPS tracking, AI-based routing, and Transport Management Systems (TMS). | Enables smart logistics, digital tolling, and real-time tracking of trucks. | UPS (USA), FedEx (USA) – advanced routing systems used in India operations. |
| 4. Sustainable Transport Initiatives | Deploy electric and LNG/CNG trucks, promote fuel-efficient fleets. | Reduces emissions and promotes eco-friendly freight logistics. | GreenLine Mobility, DHL GoGreen Solutions – carbon-neutral freight practices. |
| 5. Collaboration with Indian Firms | Partner with Indian logistics companies and truck operators for wider coverage. | Facilitates technology transfer, training, and efficiency gains. | NYK Logistics (Japan) with Indian 3PL firms; Maersk (Denmark) in inland road transport. |
| 6. Warehousing & Supply Chain Integration | Develop automated warehouses linked to road freight corridors. | Strengthens last-mile distribution and reduces storage costs. | TVS Supply Chain Solutions (India-based multinational); DB Schenker (Germany) in industrial logistics. |
| 7. Urban & Last-Mile Connectivity | Handle e-commerce delivery, city logistics, and time-sensitive cargo. | Enhances speed, reliability, and service quality in urban zones. | Amazon Transportation Services, DHL Express India, Blue Dart (DHL subsidiary). |
| 8. Investment in Skill Development & Safety | Training programs for drivers, logistics professionals, and road safety awareness. | Improves workforce skill and reduces accident risks. | MNCs under CSR projects in road safety and logistics education initiatives. |
🧭 Key Insight
MNCs bring global innovation, capital, sustainability, and technology to India’s road transport sector — complementing government infrastructure programs and enabling integration with global logistics networks.
🚆 Rail Transport in India for Public and Goods
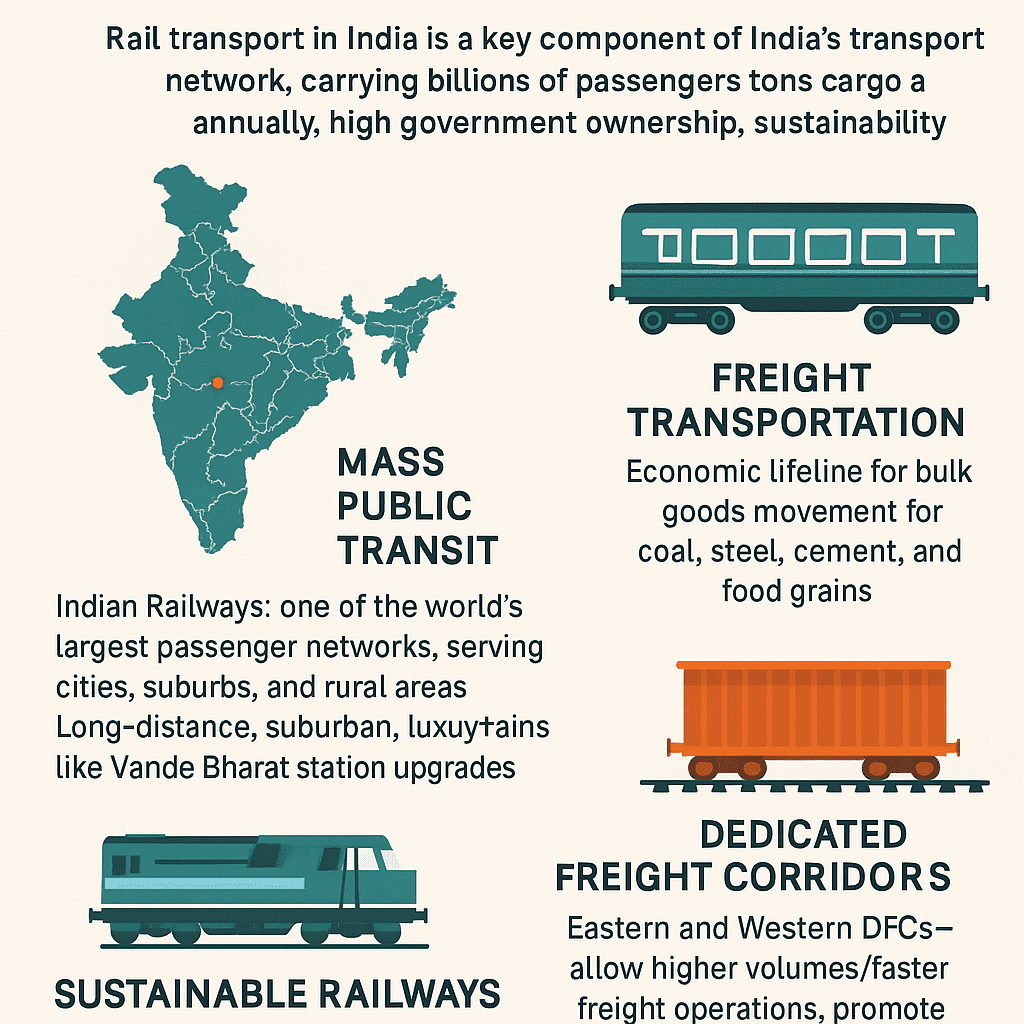
Rail transport in India stands as one of the most vital components of the country’s economic and social framework. It is not just a mode of travel or freight movement but a symbol of connectivity, unity, and industrial growth. With over 68,000 kilometers of route length, India operates one of the largest railway networks in the world, second only to China and Russia in scale. From suburban trains that pulse through Mumbai’s lifeline to freight trains carrying coal, cement, and food grains, Indian Railways connects every corner of the nation.
🏗️ 1. Historical Evolution of Indian Railways
The journey of rail transport in India began on 16 April 1853, when the first passenger train ran between Mumbai (Bori Bunder) and Thane, covering 34 kilometers. What started as a colonial infrastructure project evolved into the backbone of an independent nation’s development.
- 1850s–1900s: Expansion under British administration linked major ports (Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata) to inland cities for trade.
- 1947 (Independence): The network stood at about 53,000 km but required modernization and integration.
- Post-Independence Period: Focus shifted from raw material transport to public mobility, industrial supply chains, and national defense.
- 21st Century: Indian Railways entered an era of modernization, digitalization, and high-speed ambitions — reflecting the country’s economic momentum.
🚉 2. Structure and Role of Indian Railways
Indian Railways, under the Ministry of Railways (Government of India), is a state-owned enterprise responsible for rail transport across the nation. It operates under 18 zones, including Northern, Western, Central, Southern, and Eastern Railways, with thousands of stations connecting both urban and rural India.
It serves two fundamental roles:
- Passenger Transport: Affordable, accessible, and extensive service for billions of travelers each year.
- Freight Transport: Bulk goods movement for industries, agriculture, and commerce.
🚍 3. Rail Transport for Public Mobility
3.1. Mass Movement and Accessibility
Indian Railways carries over 23 million passengers every day, making it the largest passenger carrier in the world. This includes:
- Long-distance express and mail trains.
- Suburban trains for city commuters.
- Local passenger trains connecting small towns and rural areas.
For many citizens, especially in semi-urban and rural regions, trains remain the most affordable and reliable means of long-distance travel.
3.2. Types of Passenger Services
- Express & Superfast Trains: Rajdhani, Shatabdi, Duronto, Vande Bharat — high-speed and premium services.
- Passenger Trains: Stop frequently, connecting smaller towns.
- Suburban Trains: Operate in metro regions like Mumbai, Chennai, and Kolkata.
- Luxury Trains: Palace on Wheels, Maharajas’ Express — promote heritage tourism.
3.3. Inclusivity & Accessibility
Indian Railways also focuses on inclusivity:
- Concessional tickets for students, elderly citizens, and differently abled passengers.
- Upgraded station facilities with digital displays, lifts, and escalators.
- Integration of digital ticketing and UTS mobile apps for ease of booking.
3.4. Modernization and Comfort
Recent reforms include:
- Vande Bharat Express: India’s first semi-high-speed train (up to 160 km/h).
- Station Redevelopment Program: Modernizing 1,300+ stations with airport-like amenities.
- 100% electrification target by 2030 for green and sustainable passenger services.
🚚 4. Rail Transport for Goods and Freight
4.1. Economic Lifeline
Railways are the backbone of India’s freight ecosystem, carrying nearly 1.5 billion tonnes of goods annually. Major commodities transported include:
- Coal (40% of total freight)
- Steel, cement, fertilizers, iron ore
- Food grains and agricultural produce
- Petroleum and industrial products
4.2. Freight Corridors & Multimodal Integration
To meet rising demand, India is developing Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFCs):
- Eastern DFC: Between Ludhiana and Dankuni (Kolkata).
- Western DFC: Between Dadri (Delhi NCR) and Jawaharlal Nehru Port (Mumbai).
These corridors allow heavy freight trains to run at higher speeds (up to 100 km/h) without interfering with passenger services, drastically improving efficiency and reliability.
4.3. Private and Multimodal Partnerships
The government is opening freight services to private and joint ventures to enhance capacity. The PM Gati Shakti initiative integrates rail–road–port–air systems to enable seamless logistics connectivity.
Companies like ABCC INDIA PROJECT CARGO CORPORATION and other logistics leaders benefit by coordinating heavy and ODC cargo through rail-linked depots and terminals.
⚙️ 5. Infrastructure and Technological Advancements
5.1. Electrification and Energy Efficiency
More than 90% of broad-gauge routes are now electrified. Indian Railways aims for Net Zero Carbon Emission by 2030 — the world’s largest green transport initiative.
5.2. Signaling and Safety
Implementation of Automatic Train Protection (ATP) and KAVACH system improves train control and collision avoidance.
Track renewals and sensor-based condition monitoring ensure better safety standards.
5.3. Digital and Smart Railways
- Real-time GPS train tracking via “Rail Drishti” and “SFOORTI” dashboards.
- RFID tagging for wagons and AI-based predictive maintenance.
- Smart ticketing and e-freight systems for paperless logistics.
🧭 6. Challenges in Rail Transport
Despite its vast reach and potential, Indian Railways faces several operational and infrastructural challenges:
| ⚠️ Challenge | 🧩 Description |
|---|---|
| Overcrowding | High passenger demand causes congestion and limited comfort. |
| Aging Infrastructure | Many bridges, tracks, and signaling systems need modernization. |
| Freight Competition | Road transport dominates short-distance cargo due to flexibility. |
| Operational Delays | Shared tracks for goods and passenger trains cause scheduling conflicts. |
| Safety Concerns | Accidents from human error or outdated systems in some regions. |
Addressing these requires continuous modernization, investment, and policy innovation.
🌱 7. Sustainability and Green Transition
Indian Railways is a global model for sustainable mass transport:
- Solar Power: Installed solar panels at stations and coach rooftops.
- Bio-toilets: 70,000+ passenger coaches fitted.
- Plastic-free stations and waste recycling programs.
- Green Certified Buildings: Many stations certified under IGBC standards.
Through these steps, Indian Railways aligns with India’s climate and clean energy goals under the Paris Agreement.
🚄 8. The Future of Rail Transport in India
The future vision of Indian Railways is anchored on speed, safety, and sustainability:
- High-Speed Rail Projects: Mumbai–Ahmedabad Bullet Train under construction.
- Dedicated Suburban Corridors: Bengaluru and Mumbai local upgrades.
- National Rail Plan 2030: Forecasts passenger and freight needs for next 25 years.
- Integration with PM Gati Shakti: Strengthening multimodal logistics parks (MMLPs) and regional freight hubs.
By 2040, India aims to have seamless digital rail connectivity, 100% electrification, AI-based maintenance, and global-class high-speed corridors.
🏁 Rail transport in India is not just a physical network — it’s a social, economic, and environmental force that unites the country.
For the public, it provides affordable, inclusive mobility. For industry, it ensures the steady flow of goods that keeps the economy moving.
As technology, policy, and sustainability converge, Indian Railways is on track to redefine the future of mobility — connecting not just cities and industries, but also the aspirations of over a billion people.
🚆 EVOLUTION OF RAIL TRANSPORT IN INDIA
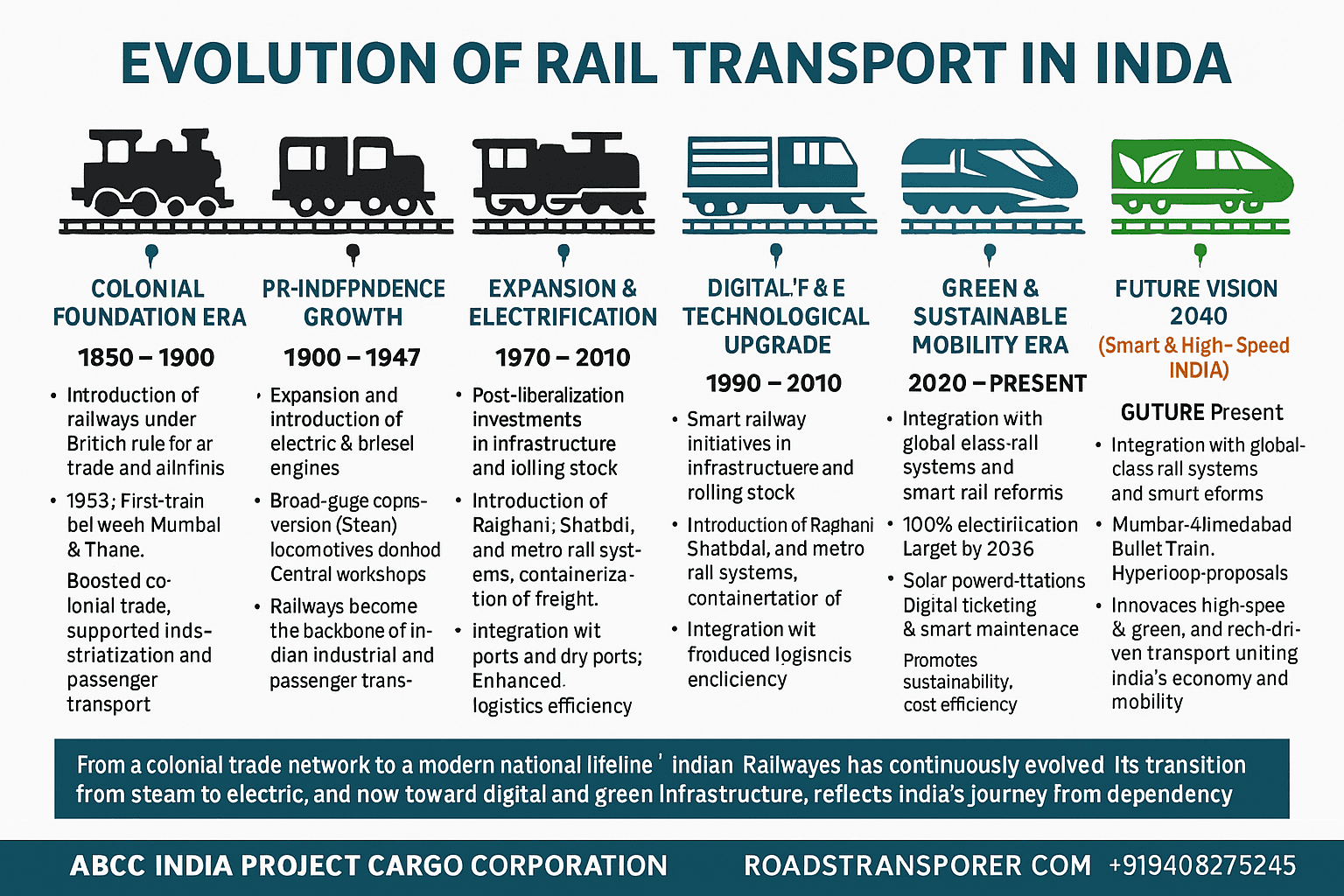
| 🕰️ Era / Timeline | 🏗️ Key Developments | 🚄 Milestones / Highlights | 🌍 Impact on Public & Goods Transport |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1850 – 1900 (Colonial Foundation Era) | Introduction of railways under British rule for trade and administration. | 1853: First train between Mumbai & Thane; network expanded to 9,000 km by 1880. | Boosted colonial trade, connected ports with inland raw material sources. |
| 1900 – 1947 (Pre-Independence Growth) | Expansion and consolidation under private & British companies. | 42 railway companies merged; steam locomotives dominated; central workshops established. | Railways became the backbone of Indian industrial and passenger transport. |
| 1947 – 1970 (Post-Independence Reorganization) | Nationalization and integration of fragmented systems into Indian Railways. | Creation of zones, new locomotive factories at Chittaranjan & Varanasi; focus on rural accessibility. | Strengthened domestic trade, supported industrialization, enhanced social connectivity. |
| 1970 – 1990 (Expansion & Electrification Era) | Modernization and introduction of electric & diesel engines. | Broad-gauge conversion, electric locomotives (WAM & WAG series), passenger comfort upgrades. | Increased freight capacity, reduced dependency on imported coal, faster services. |
| 1990 – 2010 (Liberalization & Technological Upgrade) | Post-liberalization investments in infrastructure and rolling stock. | Introduction of Rajdhani, Shatabdi, and metro rail systems; containerization of freight. | Integration with ports and dry ports; improved logistics efficiency. |
| 2010 – 2020 (Digital & Dedicated Corridor Age) | Smart railway initiatives, modernization of signaling, DFC projects launched. | Western & Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridors; high-speed Vande Bharat trains introduced. | Enhanced freight reliability and passenger comfort; multimodal logistics development. |
| 2020 – Present (Green & Sustainable Mobility Era) | Electrification, green energy adoption, and smart rail reforms. | 100% electrification target by 2030; solar-powered stations; digital ticketing & smart maintenance. | Promotes sustainability, cost efficiency, and eco-friendly freight & passenger operations. |
| Future Vision 2040 (Smart & High-Speed India) | Integration with global-class rail systems and multimodal logistics hubs. | Mumbai–Ahmedabad Bullet Train, Hyperloop proposals, AI-based rail operations. | Seamless, high-speed, green, and tech-driven transport uniting India’s economy and mobility. |
🧭 Insight
🚆 RAIL TRANSPORT IN INDIA — EXPANSION (AT A GLANCE)
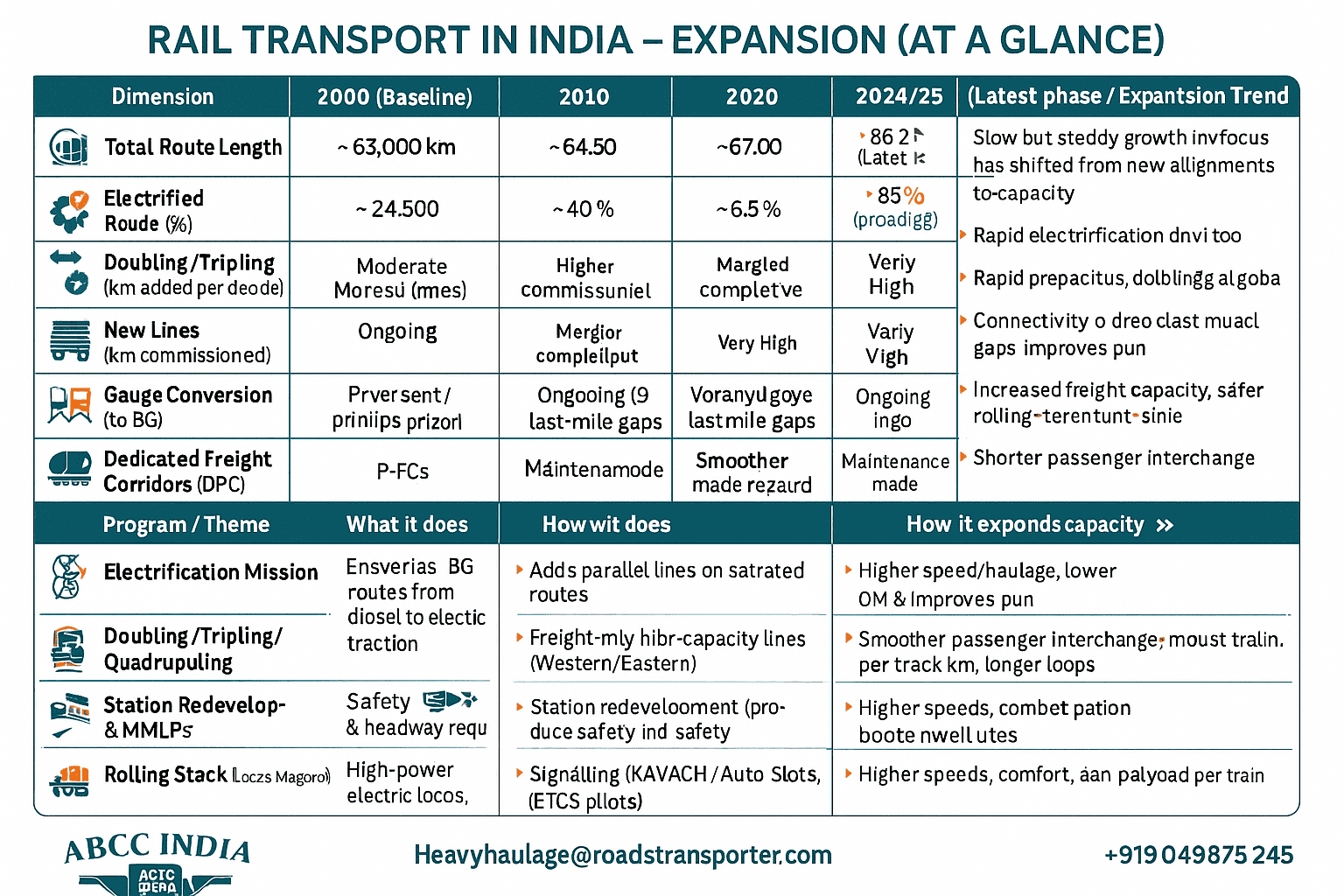
| 📌 Dimension | 🗓️ 2000 (Baseline) | 🗓️ 2010 | 🗓️ 2020 | 🗓️ 2024/25 (Latest phase) | 📈 Expansion Trend / Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Route Length (km) | ~63,000 | ~64,500 | ~67,000 | ~68,000+ | Slow but steady network growth; focus has shifted from new alignments to capacity (doubling, electrification). |
| Electrified Route (%) | ~25–30% | ~40% | ~65–70% | ~85–90% (broad-gauge) | Rapid electrification drive for lower fuel cost, higher throughput, greener operations. |
| Doubling/Tripling (km added per decade) | Low | Moderate | High | Very High | Capacity augmentation prioritized on high-density corridors; fewer single lines on trunk routes. |
| New Lines (km commissioned) | Limited | Moderate | High (esp. NE & J&K access)** | Ongoing (strategic & last-mile gaps)** | Connectivity to previously unserved districts; strategic border access and industrial links. |
| Gauge Conversion (to BG) | Active | Nearing completion | Largely complete | Maintenance mode | Meter/narrow to broad-gauge transition mostly done; standardization benefits rolling stock interchange. |
| Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFC) | – | Planning & land | Construction | Western & Eastern DFC sections operational/near-complete | Separates freight from passenger; boosts speed, reliability, and terminal ecosystem. |
| Average Freight Speed (km/h) | ~23–25 | ~25–28 | ~35 (DFC sections higher) | ~40+ on upgraded/DFC sections | Higher speeds from track renewal, auto-signalling, and longer loops. |
| Annual Freight (billion tonne-km) | Rising | Rising | Strong growth | Strong growth | Coal, steel, cement, foodgrains, containers remain mainstays; more containers and auto rakes. |
| Passenger Services (train sets/day) | High but legacy | Increased frequencies | Rationalised + premium services | Semi-HS (e.g., Vande Bharat) scaling | Focus on faster intercity, safer LHB coaches, and punctuality via traffic discipline. |
| Stations: Redevelopment & AMENITIES | Limited upgrades | Pilot modernisations | 100s taken up | 1,000+ stations under redevelopment pipeline | Better concourses, accessibility, digital ticketing, integrated terminals. |
| Signalling & Safety | Conventional | Auto block on select routes | TPWS/ATP pilots | KAVACH/ATP scaling, more automatic signalling, longer loops | Collision avoidance, centralized control (OCC), asset monitoring. |
| Rolling Stock (Locos/Wagons) | Diesel-heavy | Electrification push | High electric loco output | High-power electric locos; aluminium/HS wagons | Higher haulage, lower energy use; push for lightweight, higher-speed wagons. |
| Terminals & MMLPs | Few ICDs | ICD/CFS growth | Pvt. freight terminals policy | Multimodal Logistics Parks + Gati Shakti integration | Rail-road-port-air links improve end-to-end cost and time. |
| Sustainability | Early steps | Energy efficiency focus | Solar rooftops, LEDs | Net-zero target path; near-total BG electrification | Emissions reduction via electrification + regenerative braking + modal shift. |
🧭 PROJECT/PROGRAM LENSES (WHAT DROVE THE EXPANSION)
| 🚀 Program / Theme | 🎯 What it does | 🔄 How it expands capacity |
|---|---|---|
| Electrification Mission | Converts BG routes from diesel to electric traction | Higher speed/haulage, lower O&M and emissions |
| Doubling/Tripling/Quadrupling | Adds parallel lines on saturated routes | Cuts waiting time, raises throughput, improves punctuality |
| Dedicated Freight Corridors | Freight-only high-capacity lines (Western/Eastern) | Faster/longer/heavier rakes; decongests passenger lines |
| Station Redevelopment | Modern terminals, better access & safety | Smoother passenger interchange; boosts dwell efficiency |
| Signalling (KAVACH/Auto Block/ETCS pilots) | Safety & headway reduction | More trains per track km; fewer human-error risks |
| Terminals & MMLPs | Rail-road-port-air consolidation hubs | Shorter first/last mile; lower logistics cost |
| Rolling Stock Modernisation | High-power electric locos, LHB coaches, modern wagons | Higher speeds, comfort, and payload per train |
🚨 Major Rail Accidents in India (2000–2023)
| 📅 Date / Year | 📍 Location / State | 🚆 Type / Cause | ⚰️ Deaths / Casualties | 📝 Notes / Additional Info |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| May 2002 | Jaunpur, Uttar Pradesh | Derailment / Sabotage (broken rail / fishplate) | ~12 killed, ~80 injured | Shramjeevi Express derailed due to missing plates. |
| Oct 2005 | Valigonda, Andhra Pradesh | Derailed & plunged into river (flood / rain + track washout) | ~100 killed | Repalle-Secunderabad Delta Passenger; monsoon wash-out suspected. |
| Nov 2016 | Kanpur / Pukhrayan, Uttar Pradesh | Derailment (high speed) | ~150 killed, many more injured | Indore-Patna Express crash, one of deadliest in recent decades. |
| Jan 2022 | Alipurduar (WB) | Derailment | ~9 dead, ~36 injured | Bikaner-Guwahati Express derailed. |
| Jun 2023 | Balasore, Odisha | Multi-train collision / derailment | ~280 killed, ~900+ injured | Triple-train crash: Coromandel Express, Bengaluru-Howrah Express, goods train. |
| 2024–25 | (Various) | Collisions, derailments, level crossing incidents | Many fatalities | In 2024–25, 31 train accidents reported (3 collisions, 24 derailments, 1 level crossing, 3 fire accidents). |
🚆 RAIL TRANSPORT IN INDIA — PROBLEMS, REASONS, CHALLENGES & SOLUTIONS
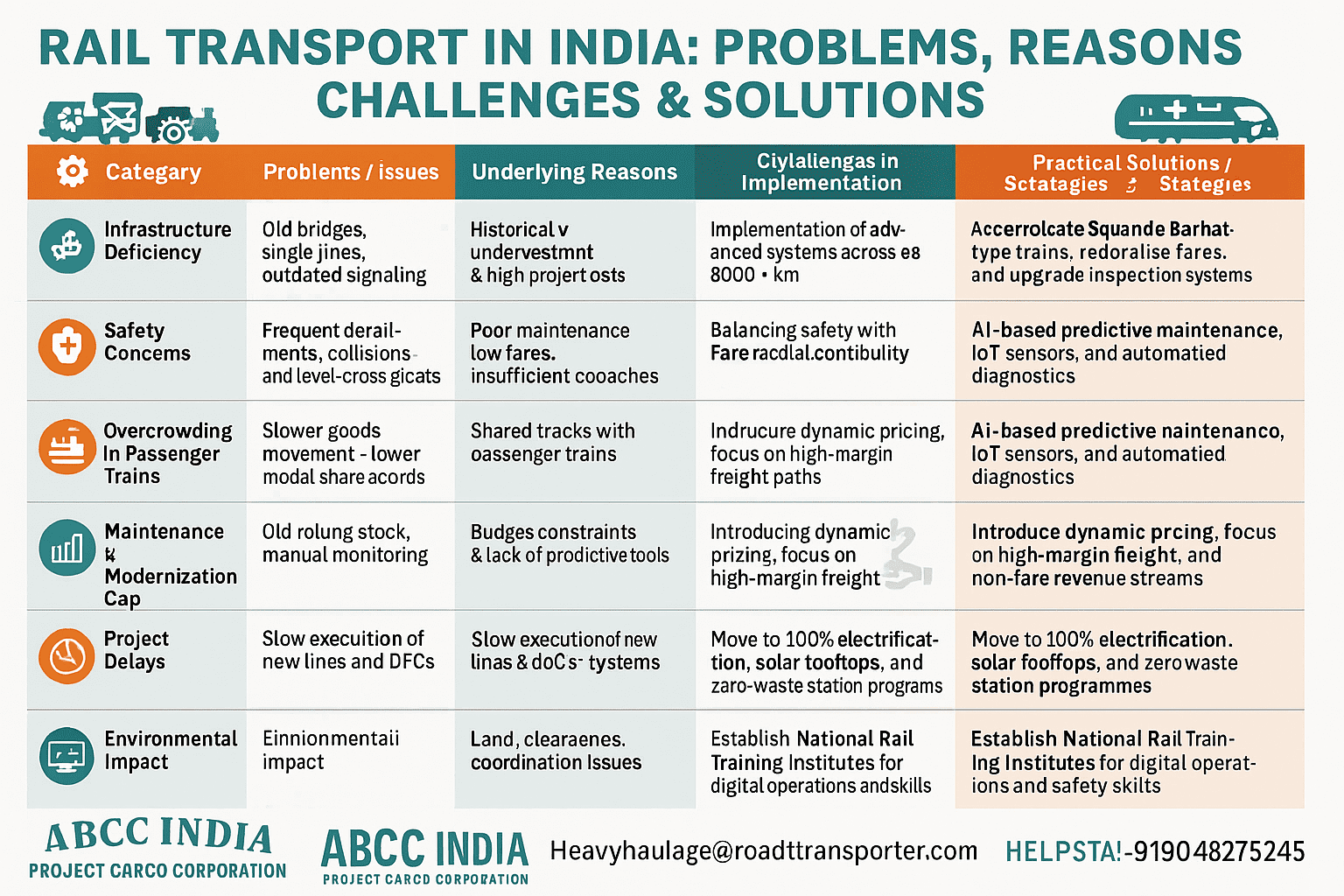
| ⚙️ Category | 🚧 Problems / Issues | 🔍 Underlying Reasons | 🧩 Challenges in Implementation | 💡 Practical Solutions / Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Infrastructure Deficiency | Old bridges, single lines, outdated signaling, limited tracks | Historical underinvestment and high project costs | Land acquisition, funding delays | Accelerate track doubling, auto-signaling, and bridge rehabilitation through PPP models |
| 2. Safety Concerns | Frequent derailments, collisions, and level-crossing accidents | Poor maintenance, human error, aging assets | Implementation of advanced systems across 68,000+ km | Roll out KAVACH (ATP) nationwide, enhance crew training, and upgrade inspection systems |
| 3. Overcrowding in Passenger Trains | Excess demand, especially on suburban and intercity routes | Population growth, low fares, insufficient coaches | Limited manufacturing capacity, long approval cycles | Introduce Vande Bharat-type trains, rationalize fares, and expand suburban corridors |
| 4. Freight Inefficiency | Slower goods movement and lower modal share vs. roads | Shared tracks with passenger trains | Capacity constraints, non-priority freight paths | Expand Dedicated Freight Corridors, digitize freight booking, and allow private terminals |
| 5. Maintenance & Modernization Gap | Old rolling stock, manual monitoring | Budget constraints and lack of predictive tools | Balancing safety with operational continuity | Adopt AI-based predictive maintenance, IoT sensors, and automated diagnostics |
| 6. Financial Sustainability | Operating ratio >95%, losses in passenger segment | Cross-subsidization and rising fuel & wage costs | Fare rationalization is politically sensitive | Introduce dynamic pricing, focus on high-margin freight, and non-fare revenue streams |
| 7. Project Delays | Slow execution of new lines and DFCs | Land, clearances, coordination issues | Multi-agency delays | Empower National Rail Plan Taskforce, use Gati Shakti digital platform for approvals |
| 8. Environmental Impact | Diesel use, noise, waste at stations | Incomplete electrification and poor waste systems | Funding and operational transitions | Move to 100% electrification, solar rooftops, and zero-waste station programs |
| 9. Technology & Data Gaps | Manual control, low automation, and data silos | Legacy systems | Integration across 18 zones and diverse tech stacks | Adopt Unified Digital Rail Network (UDRN) for real-time data sharing |
| 10. Human Resource Challenges | Skill gaps, fatigue, aging workforce | Limited upskilling programs | Training capacity and budget | Establish National Rail Training Institutes for digital operations and safety skills |
🧭 Key Insight
The modernization of Indian Railways requires balanced investment in both infrastructure and technology.
The future lies in dedicated freight systems, digital automation, and green energy — ensuring both economic efficiency and passenger safety.
🏛️ GOVERNMENT CONTRIBUTION & BIG PROJECTS IN RAIL TRANSPORTATION SERVICES IN INDIA
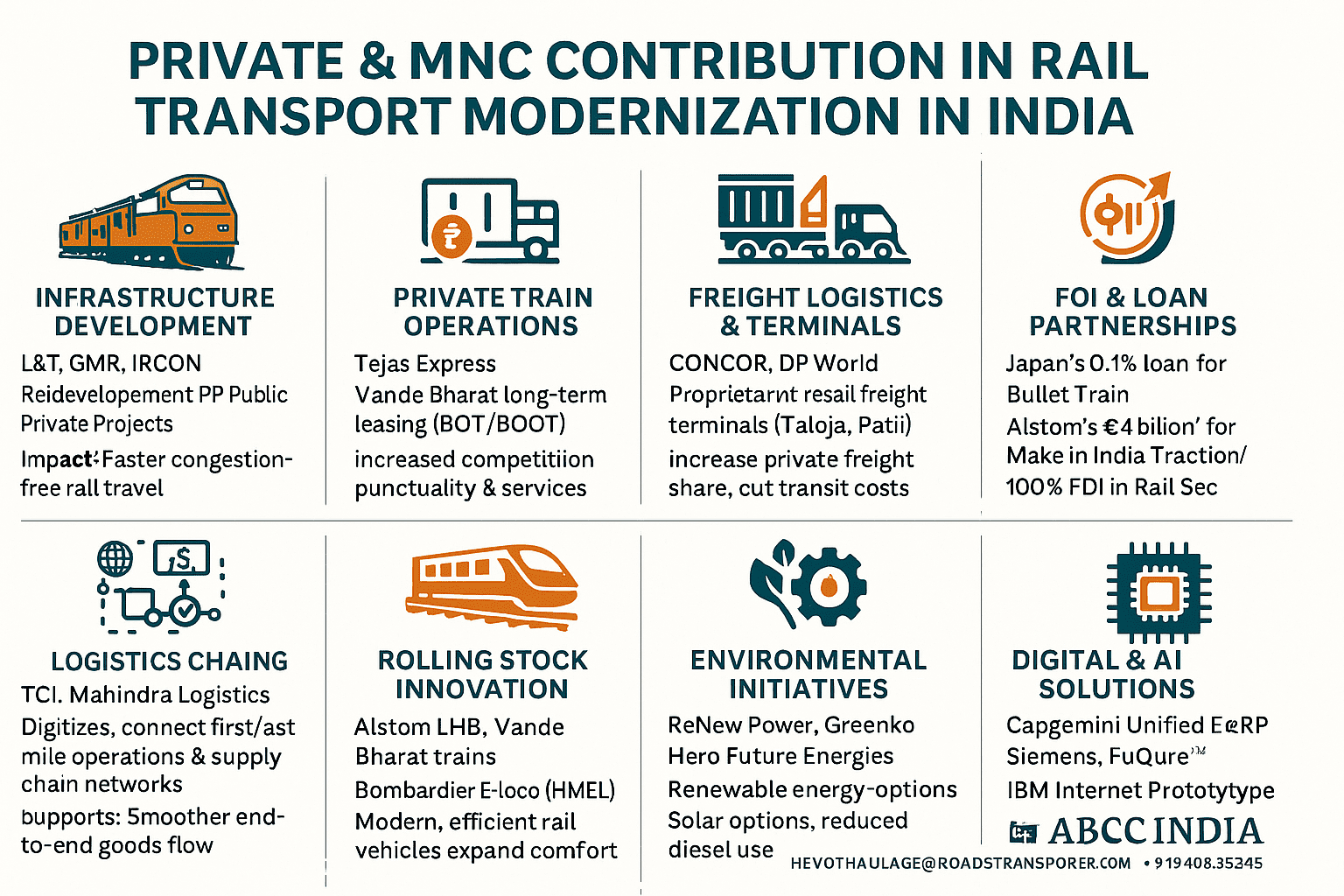
| 🚄 Category | 🧩 Project / Initiative | 🏗️ Description & Objective | 💰 Approx. Investment / Length | 🌍 Impact on Public & Goods Transport |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFC) | Western & Eastern DFC | High-capacity freight-only lines between Delhi–Mumbai & Ludhiana–Dankuni | ₹1.24 lakh crore (combined) | Decongests passenger routes, boosts freight efficiency by 50% |
| 2️⃣ High-Speed Rail Projects | Mumbai–Ahmedabad Bullet Train | India’s first high-speed rail (up to 320 km/h) by NHSRCL | ₹1.1 lakh crore (508 km) | Fast passenger travel, technology transfer from Japan |
| 3️⃣ Station Redevelopment Program | Amrit Bharat & RAILWAY STATION REDEVELOPMENT SCHEME | Redevelopment of 1,300+ stations with modern facilities | ₹30,000 crore | Smart, accessible, and passenger-friendly infrastructure |
| 4️⃣ Gati Shakti & MMLPs | PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan | Integration of road, rail, air, and port infrastructure | ₹100 lakh crore+ across modes | Boosts multimodal logistics and reduces transit time |
| 5️⃣ Electrification Drive | Mission 100% Electrification by 2030 | Conversion of all broad-gauge routes to electric traction | 68,000 km+ | Cuts diesel dependency, saves ₹14,000 crore annually |
| 6️⃣ New Line & Expansion Projects | 488 projects across 27 states | New lines, doubling, gauge conversion, and multitracking | ₹7.44 lakh crore (~44,488 km) | Increases capacity and regional connectivity |
| 7️⃣ Northeastern Connectivity | Bairabi–Sairang, Dimapur–Zubza | Rail access to Mizoram, Nagaland, Manipur | ₹20,000 crore+ | Boosts regional growth and national integration |
| 8️⃣ Strategic Bridges & Tunnels | Chenab Bridge (J&K), Bogibeel (Assam) | Record-breaking engineering feats for terrain access | ₹5,000 crore+ | Strengthens defense & trade logistics |
| 9️⃣ Safety & Modern Signaling | KAVACH & Automatic Train Protection | Indian-made safety tech to prevent collisions | Pan-India rollout | Enhances operational safety and punctuality |
| 🔟 PPP & Private Investment | Station & Terminal Redevelopment PPPs | Private participation under DBFOT & BOT models | 100+ stations | Improves amenities and attracts private innovation |
| 1️⃣1️⃣ Rolling Stock Modernization | Make in India locomotive factories | Madhepura (electric) & Marhowra (diesel) | ₹40,000 crore+ | Modern, high-efficiency locomotives for heavy loads |
| 1️⃣2️⃣ Digital Rail Reforms | IR Digital Dashboard, SFOORTI, AI-based monitoring | Data-driven operations, predictive maintenance | Ongoing | Transparent, faster, and safer rail management |
🧭 KEY TAKEAWAYS
- The Government of India has shifted focus from expansion to efficiency — electrification, digitalization, and freight segregation.
- The Dedicated Freight Corridors, Gati Shakti, and Amrit Bharat Station schemes mark a new era of multimodal, smart, and sustainable rail transport.
- Public-private synergy is key to achieving Vision 2040 for a high-speed, green, and globally competitive rail network.
🏗️ Areas Where Private Companies Contribute to Rail in India

| 📌 Area of Contribution | 🔧 What Private / Corporate Entities Do | 📊 Examples / Key Players | 🎯 Value Added / Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rolling Stock Manufacturing & Supply | Build wagons, coaches, EMUs, components, shells | Texmaco Rail & Engineering Ltd. builds wagons, coaches, and parts. | Private firms help meet demand, reduce lead time, bring quality & innovation |
| Rail Infrastructure & EPC Contracts | Undertake engineering, civil works, track laying, bridges | Companies like Dineshchandra R. Agrawal Infracon (DRA Infracon) are active in rail/metros/EPC contracts. | Helps scale project delivery capacity, engages private capital and expertise |
| Private Train Operations / Train Services | Operate certain mail/express services under private contracts | Private sector allowed to run 151 trains over 109 routes (starting 2020) under pilot scheme | Introduces competition, service quality, modern amenities |
| Outsourced Services & Amenities | Cleaning, catering, station services, parking, vending | Indian Railways already outsources cleaning, toilet management, etc. | Improves station experience, enables IR to focus on core operations |
| Signalling, Digital & Technology Systems | Private tech firms provide signaling, software, detection, IoT systems | Private-sector participation encouraged in infrastructure renovation and system upgrades | Brings innovation, automation, predictive maintenance |
| Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) / Joint Ventures | Participate in station redevelopment, terminals, logistics parks | Parliamentary committee pushing for private investments in rolling stock, station PPPs | Enables shared risk, better design, and faster execution |
| Export / International Projects | Indian private rail firms bidding in global markets | Texmaco exports rolling stock and services abroad | Helps Indian firms scale, improves global competitiveness |
| Specialized Manufacturing & Components | Provide specialized parts: electronics, signaling gear, rail components | Private firms partner with international firms for rail parts | Strengthens supply chains, reduces import dependence |
🌍 MNC COMPANIES’ CONTRIBUTION IN RAIL TRANSPORTATION SERVICES IN INDIA
| 🏢 Contribution Area | ⚙️ What MNCs Do | 🚄 Key Companies / Examples | 💡 Impact / Value Addition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ Rolling Stock & Locomotive Manufacturing | Design, supply, and assemble high-horsepower electric & diesel locomotives | Alstom (France) – 12,000 HP WAG-12 electric locomotives (Madhepura)Wabtec/GE (USA) – 4,500 HP diesel locos (Marhowrah JV)Siemens (Germany) – supplies electric traction equipment | Boosts indigenous production, global standards, “Make in India” capability |
| 2️⃣ Rail Electrification & Signaling Systems | Provide advanced traction and signaling technologies | Alstom, Siemens, Hitachi Rail (Japan) | Enhances safety, reduces accidents, enables high-speed network operation |
| 3️⃣ Metro & Urban Rail Projects | Manufacture metro coaches, provide automation, signaling, and maintenance | Alstom, Bombardier (Canada), Siemens, Hitachi Rail | Improves urban mobility, supports Smart Cities & sustainable transport |
| 4️⃣ Technology & Digital Systems | Supply AI, IoT, predictive maintenance, and automation tech | IBM, Capgemini, Siemens Mobility | Enables smart scheduling, predictive safety, and energy-efficient operation |
| 5️⃣ Green Rail & Energy Efficiency | Introduce hybrid, regenerative braking, and clean-energy solutions | Alstom, Wabtec, ABB | Reduces emissions, supports India’s carbon-neutral rail target (2030) |
| 6️⃣ Freight & Logistics Integration | Collaborate on freight corridors and multimodal hubs | DP World, Maersk, DB Schenker, DHL | Strengthens freight connectivity, global supply-chain integration |
| 7️⃣ Joint Ventures & Partnerships | Co-invest in manufacturing, R&D, and operations with Indian Railways | Alstom India JV, GE-IR JV, Hitachi–IRCON collaborations | Combines foreign technology with Indian manpower & scale |
| 8️⃣ Consulting & Project Management | Provide system design, safety audits, project feasibility | KPMG, AECOM, SYSTRA, WSP | Enhances planning accuracy, efficiency, and safety standards |
| 9️⃣ Skill Development & CSR | Conduct training, research, and sustainability programs | Alstom Foundation, Siemens India CSR, Wabtec Training Centers | Improves workforce capability and community engagement |
🧭 KEY INSIGHTS
- MNCs drive technology transfer, modernization, and global connectivity in India’s rail ecosystem.
- Their partnerships accelerate digital rail transformation, sustainable traction, and skill development.
- India’s Vision 2040 rail modernization will rely heavily on these collaborations under Make in India + PPP frameworks.
✈️ Air Transport in India: A Skyway of Progress and Connectivity
🌍 Introduction: From Wings of Dreams to Engines of Growth
Air transport in India represents not just a mode of travel but a symbol of the nation’s transformation — from a country of limited accessibility to one of expansive connectivity. Over the past century, India’s aviation journey has evolved from early biplanes landing on grassy airstrips to modern jets connecting the remotest corners of the country with the global network.
Air transport, by its nature, embodies speed, precision, and reliability. It connects lives, reduces distances, and empowers industries — from tourism and healthcare to logistics and national defense. For both public mobility and goods transportation, India’s skies have become vital corridors of commerce and opportunity.
🛫 Historical Evolution: From Independence to Innovation
India’s aviation story began in 1911 with the world’s first official airmail flight between Allahabad and Naini. After independence in 1947, the newly formed nation inherited a small fleet of aircraft and a few domestic routes. Gradually, state-run carriers like Air India and Indian Airlines established the foundation of national and international connectivity.
However, the real revolution came after 1991’s economic liberalization, when the skies opened to private operators. Airlines like Jet Airways, SpiceJet, and IndiGo democratized air travel, turning it from a luxury for the elite into an accessible public utility. Today, India’s aviation industry stands among the top three in the world, with over 150 airports and a rapidly growing air cargo network.
👥 Public Air Transport: Bridging People and Possibilities
For the general public, air transport is not merely about travel — it is about access to opportunity. It connects students, entrepreneurs, workers, and families across vast geographies, cutting travel times that once spanned days into mere hours.
🏙️ Urban and Regional Connectivity
The UDAN Scheme (Ude Desh ka Aam Nagrik) launched in 2017 revolutionized regional air travel. Its mission: to make flying affordable and connect Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities. Over 450 new routes have been awarded, linking towns like Jharsuguda, Belagavi, and Darbhanga to metros such as Delhi and Mumbai.
This initiative turned idle airstrips into active airports, giving millions of citizens first-time access to air travel and spurring regional economies.
🧭 Passenger Growth and Global Reach
India’s domestic passenger market has surged from 25 million in 2003 to over 150 million in 2024, reflecting both economic growth and aspirational mobility. Airlines like IndiGo and Air India dominate domestic skies, while international carriers such as Emirates, Lufthansa, and Singapore Airlines interlink India with 60+ countries.
Airports like Delhi (IGI) and Mumbai (CSMIA) now rival global hubs in efficiency and scale, while new greenfield airports — Jewar (Noida) and Mopa (Goa) — promise to shape the next decade of expansion.
🚚 Goods Air Transport: The Silent Engine of Trade
While passenger planes make the headlines, air cargo drives the backbone of modern trade. It ensures that medicines, machinery, electronics, perishables, and even e-commerce parcels reach their destinations within hours instead of days.
📦 Domestic Air Cargo Movement
India’s air cargo tonnage grew from around 0.8 million tonnes in 2000 to over 3.5 million tonnes in 2023, showing how crucial it has become for supply chain efficiency. Domestic freight operations connect production centers in Chennai, Bengaluru, and Ahmedabad with consumption hubs like Delhi and Mumbai.
🌐 International Air Freight Corridors
Internationally, airports such as Delhi, Mumbai, Hyderabad, and Chennai serve as cargo gateways linking India to the Middle East, Europe, and Southeast Asia. The government’s National Air Cargo Policy (NACP 2019) envisions India as a global transshipment hub, reducing dependency on foreign logistics routes.
Specialized freighters operated by Blue Dart Aviation, SpiceXpress, and Air India Cargo, as well as global players like FedEx, UPS, and DHL, enhance time-sensitive delivery — vital for sectors like pharmaceuticals, automotive, and electronics.
⚙️ Infrastructure & Technology: Powering the Skies
India’s aviation infrastructure has undergone a digital and structural transformation in the last decade.
- Modern Terminals: Smart, modular designs with biometric boarding, AI-powered check-ins, and sustainability features.
- Cargo Terminals: Dedicated cold chain and express handling facilities at airports like Hyderabad and Ahmedabad.
- Air Navigation: India’s GAGAN satellite system improves flight safety, while DigiYatra ensures paperless passenger flow.
- Green Aviation: Focus on solar-powered airports (Cochin is the world’s first fully solar airport) and SAF (Sustainable Aviation Fuel) pilots.
🔄 Public & Goods Synergy: Dual Growth Drivers
The synergy between passenger and freight aviation is shaping a multimodal future. As industrial output and consumer demand rise, so does the need for efficient logistics.
- E-commerce & Express Cargo: Amazon Air, Delhivery, and Bluedart use dedicated air fleets for 24-hour delivery cycles.
- Pharma & Perishable Logistics: Specialized temperature-controlled air routes carry vaccines and fresh produce globally.
- Tourism & Trade: Tourist flights boost local economies, while belly cargo in passenger jets supports export growth.
Thus, air transport serves as a dual engine— accelerating both economic inclusion and global trade participation.
⚠️ Challenges in Indian Air Transport
Despite remarkable progress, challenges persist:
- High Fuel Costs: Aviation turbine fuel (ATF) remains heavily taxed.
- Airport Congestion: Delhi, Mumbai, and Bengaluru operate near capacity.
- Limited Regional Infrastructure: Many small towns lack night-landing and cargo-handling facilities.
- Regulatory Complexity: Multiple agencies and overlapping policies slow innovation.
- Environmental Concerns: Aviation emissions require stronger offset mechanisms.
To address these, the focus is shifting toward public–private partnerships, digitalization, and regional airport upgradation.
🌱 Future Outlook: Vision 2040
India’s National Civil Aviation Policy envisions making the country a global aviation hub by 2040. The plan includes:
- 200+ operational airports
- 2,000+ new aircraft
- Dedicated Air Freight Corridors integrated with ports and rail
- Introduction of Electric VTOL (Vertical Take-Off and Landing) aircraft for short routes
- Expansion of air cargo villages and MMLPs (Multi Modal Logistics Parks)
As India targets becoming a $10-trillion economy, air transport will serve as the vital link between production, consumption, and export ecosystems.
🛩️ Skyways to Sustainable Growth
Air transport in India stands at the crossroads of inclusivity, innovation, and integration. It empowers citizens, supports industries, strengthens trade, and connects India to the global economy.
From rural airstrips to high-speed corridors, from passenger convenience to freight efficiency — the Indian sky is no longer a limit; it is a pathway to progress.
In the coming decades, the success of Indian aviation will depend not only on aircraft and airports but also on the vision to balance growth with sustainability — making the sky a shared, sustainable, and equitable resource for all.
✈️ India: State-wise & UT-wise Key Airports (Capacity & Contribution)
| No | State / UT | Airport name | City | Approx. capacity* | Why it’s notable / best contribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Andhra Pradesh | Visakhapatnam International Airport | Visakhapatnam | ~7–8 MPPA | Eastern naval–industrial hub; mixes tourism, IT, port-linked cargo. |
| 2 | Arunachal Pradesh | Donyi Polo Airport | Itanagar (Hollongi) | ~1 MPPA | New greenfield gateway improving NE regional access under UDAN. |
| 3 | Assam | Lokpriya Gopinath Bordoloi Int’l | Guwahati | ~8–10 MPPA | Northeast’s primary hub; connects all NE capitals and metros. |
| 4 | Bihar | Jay Prakash Narayan Airport | Patna | ~7–8 MPPA | High-density origin–destination traffic; crucial for migrant & biz travel. |
| 5 | Chhattisgarh | Swami Vivekananda Airport | Raipur | ~4–5 MPPA | Connects mineral/steel belt; steady cargo & regional links. |
| 6 | Goa | Manohar International (Mopa) | North Goa | ~4–8 MPPA | New tourism gateway; decongests Dabolim; strong intl charter pull. |
| 7 | Gujarat | Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel Int’l | Ahmedabad | ~14–20 MPPA | Western mega-city hub; pharma, textiles, auto & trade corridors. |
| 8 | Haryana | Hisar (under expansion) | Hisar | ~0.5–1 MPPA | State’s civil aviation push; training/MRO focus; feeds NCR. |
| 9 | Himachal Pradesh | Kangra (Gaggal) Airport | Dharamshala | ~1 MPPA | Hill-tourism lifeline; difficult terrain access for public services. |
| 10 | Jharkhand | Birsa Munda Airport | Ranchi | ~3–5 MPPA | Connects mining/agri state; rising domestic routes. |
| 11 | Karnataka | Kempegowda Int’l (BLR) | Bengaluru | ~45–50 MPPA | India’s tech capital hub; large belly-cargo & international network. |
| 12 | Kerala | Cochin International (CIAL) | Kochi | ~12–15 MPPA | World’s first fully solar-powered airport; Gulf corridor & perishables. |
| 13 | Madhya Pradesh | Devi Ahilya Bai Holkar | Indore | ~3–7 MPPA | Central India business hub; pharma/engineering exports. |
| 14 | Maharashtra | Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Int’l | Mumbai | ~50–60 MPPA | India’s #2 gateway by traffic; finance, film, pharma, global links. |
| 15 | Manipur | Imphal (Tulihal) Airport | Imphal | ~2–3 MPPA | Strategic NE hub; cross-border proximity; essential for medical lift. |
| 16 | Meghalaya | Shillong (Umroi) Airport | Shillong | ~0.5–1 MPPA | Improves hill state access; UDAN connectivity to metros. |
| 17 | Mizoram | Lengpui Airport | Aizawl | ~0.5–1 MPPA | Vital public lifeline for remote terrain; medical/essential freight. |
| 18 | Nagaland | Dimapur Airport | Dimapur | ~1–2 MPPA | Only major airport in state; trade and defence utility. |
| 19 | Odisha | Biju Patnaik Int’l | Bhubaneswar | ~8 MPPA | Eastern knowledge/IT/tourism hub; coastal & temple corridor. |
| 20 | Punjab | Sri Guru Ram Dass Jee Int’l | Amritsar | ~5–8 MPPA | Strong diaspora routes; religious tourism; pharma/food exports. |
| 21 | Rajasthan | Jaipur International | Jaipur | ~8–10 MPPA | Tourism-heavy; gems & jewellery export via belly-cargo. |
| 22 | Sikkim | Pakyong Airport | Pakyong (Gangtok region) | ~0.2–0.5 MPPA | High-altitude engineering; critical hill access under UDAN. |
| 23 | Tamil Nadu | Chennai International | Chennai | ~20–30 MPPA | South India trade-port-auto triangle; MRO, cargo corridors. |
| 24 | Telangana | Rajiv Gandhi Int’l (HYD) | Hyderabad | ~25–30 MPPA | Pharma/biotech air-cargo leader; expanding int’l hub. |
| 25 | Tripura | Maharaja Bir Bikram | Agartala | ~3–5 MPPA | Gateway to Bangladesh border trade; NE regional node. |
| 26 | Uttar Pradesh | Chaudhary Charan Singh Int’l | Lucknow | ~10 MPPA | Growing hub for central-east UP; Jewar (Noida) mega-hub coming. |
| 27 | Uttarakhand | Dehradun (Jolly Grant) | Dehradun | ~3–5 MPPA | Char Dham & eco-tourism access; hill-state connectivity. |
| 28 | West Bengal | Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose Int’l | Kolkata | ~25–30 MPPA | Eastern India’s biggest hub; Bay-of-Bengal trade routes. |
| 29 | Andaman & Nicobar (UT) | Veer Savarkar | Port Blair | ~3–5 MPPA | Island lifeline; tourism & defence; weather-resilient ops. |
| 30 | Chandigarh (UT) | Shaheed Bhagat Singh Int’l | Chandigarh/Mohali | ~5–8 MPPA | Joint Punjab–Haryana gateway; planned tri-city growth. |
| 31 | Dadra & Nagar Haveli and Daman & Diu (UT) | Diu Airport | Diu | ~0.3–0.5 MPPA | Tourism-centric runway; connects coastal UT cluster. |
| 32 | Delhi (NCT) | Indira Gandhi Int’l (DEL) | New Delhi | ~65–70 MPPA | India’s busiest hub; major global connectivity & cargo trans-shipment. |
| 33 | Jammu & Kashmir (UT) | Sheikh ul-Alam (Srinagar) | Srinagar | ~7–10 MPPA | Valley lifeline; tourism & defence logistics. |
| 34 | Ladakh (UT) | Kushok Bakula Rimpochee | Leh | ~1–2 MPPA | High-altitude operations; strategic & tourism access. |
| 35 | Lakshadweep (UT) | Agatti Airport | Agatti | ~0.2 MPPA | Only link to island chain; essential services & tourism. |
| 36 | Puducherry (UT) | Puducherry Airport | Puducherry | ~0.5 MPPA | Regional tourism/AYUSH hub; relieves Chennai for short-haul. |
✈️ EVOLUTION OF AIR TRANSPORT IN INDIA (1911–2040)
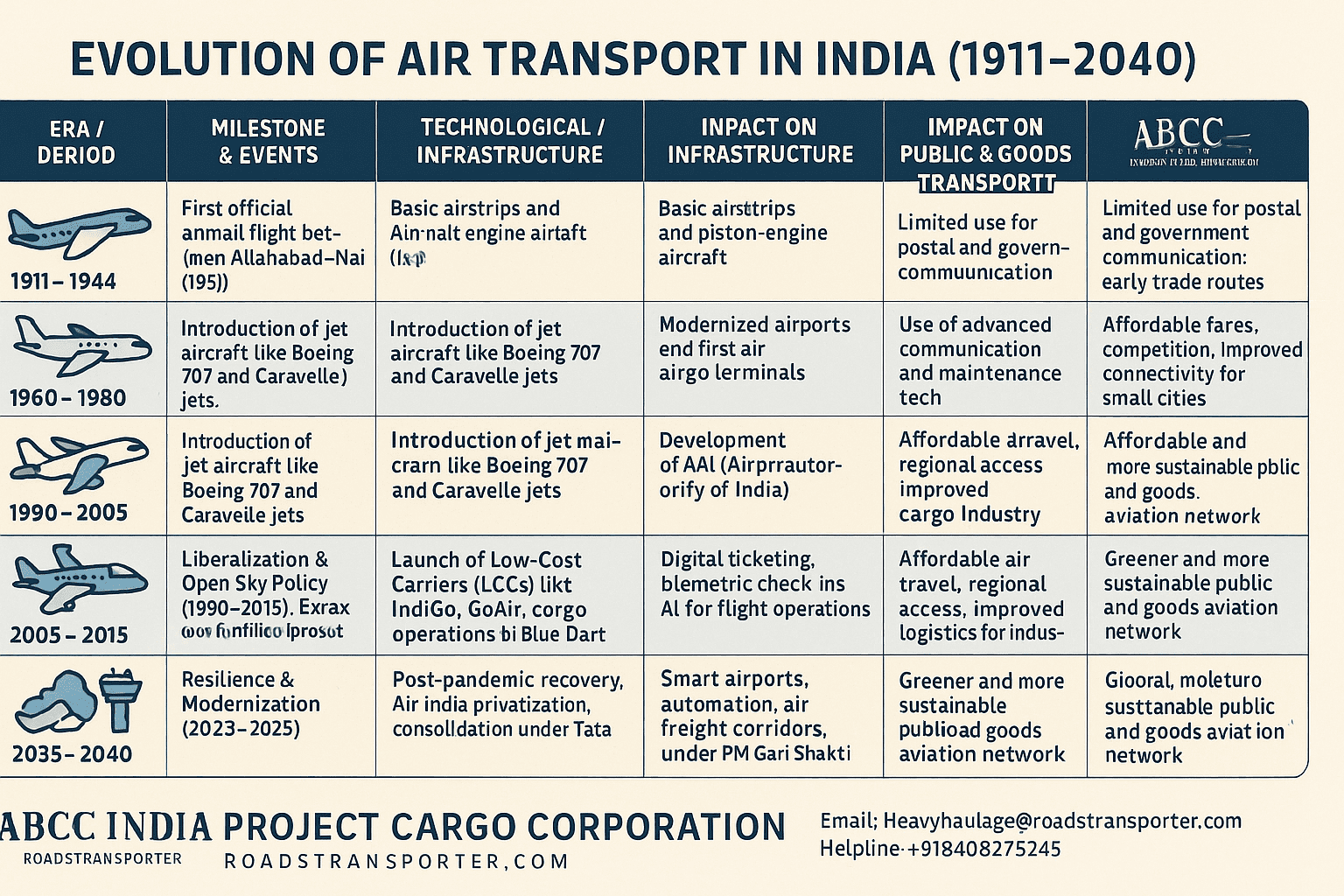
| 🕰️ Era / Period | 🛫 Milestone & Events | ⚙️ Technological / Infrastructure Development | 🌍 Impact on Public & Goods Transport |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1911 – 1947 (Colonial Era) | First official airmail flight between Allahabad–Naini (1911); Tata Sons begins air mail service (1932). | Basic airstrips and piston-engine aircraft. | Limited use for postal and government communication; early trade routes. |
| 1947 – 1960 (Post-Independence Formation) | Formation of Air India as national carrier; nationalization of private airlines (1953). | Establishment of DGCA; first domestic terminals built. | Improved national connectivity; growing public confidence in air travel. |
| 1960 – 1980 (Expansion Era) | Introduction of jet aircraft like Boeing 707 and Caravelle jets. | Modernized airports (Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai); radar systems. | Enhanced speed, safety, and passenger comfort; growing business travel. |
| 1980 – 1990 (Liberalization Preparation) | Indian Airlines modernized; first air cargo terminals initiated. | Use of advanced communication and maintenance tech. | Rise of middle-class travelers and export of perishables by air. |
| 1990 – 2005 (Liberalization & Open Sky Policy) | Private airlines permitted; entry of Jet Airways, Air Sahara, and SpiceJet. | Development of AAI (Airports Authority of India); airport privatization begins. | Affordable fares, competition, improved connectivity for small cities. |
| 2005 – 2015 (Infrastructure & Cargo Boom) | Launch of Low-Cost Carriers (LCCs) like IndiGo, GoAir; cargo operations by Blue Dart, Air India Cargo. | New international terminals; e-ticketing, cargo automation, cold chain facilities. | Surge in domestic travelers and fast-growing express cargo industry. |
| 2015 – 2020 (Regional & Digital Growth) | UDAN Scheme launched to connect small towns; new greenfield airports. | Digital ticketing, biometric check-ins, AI for flight operations. | Affordable air travel, regional access, and improved logistics for industries. |
| 2020 – 2025 (Resilience & Modernization) | Post-pandemic recovery, Air India privatization, consolidation under Tata Group. | Smart airports, automation, air freight corridors under PM Gati Shakti. | Strong revival in both passenger and air cargo volumes. |
| 2025 – 2035 (Future Growth Phase) | Expansion of Green Airports and EV/Hybrid aircraft development. | Integration with AI-based traffic management and electric aircraft trials. | Greener and more sustainable public and goods aviation network. |
| 2035 – 2040 (Vision 2040 Era) | India among top 3 global aviation hubs; 200+ airports, 2,000 aircraft projected. | Fully digital, net-zero carbon aviation ecosystem. | Seamless global connectivity and eco-friendly logistics dominance. |
🧭 INSIGHT
From Tata’s first mail flight in 1932 to India’s Vision 2040 Smart Aviation Era, air transport has evolved from luxury to necessity — serving as a bridge between people, progress, and prosperity.
✈️ AIR TRANSPORT IN INDIA — EXPANSION OVER TIME (2000–2040)
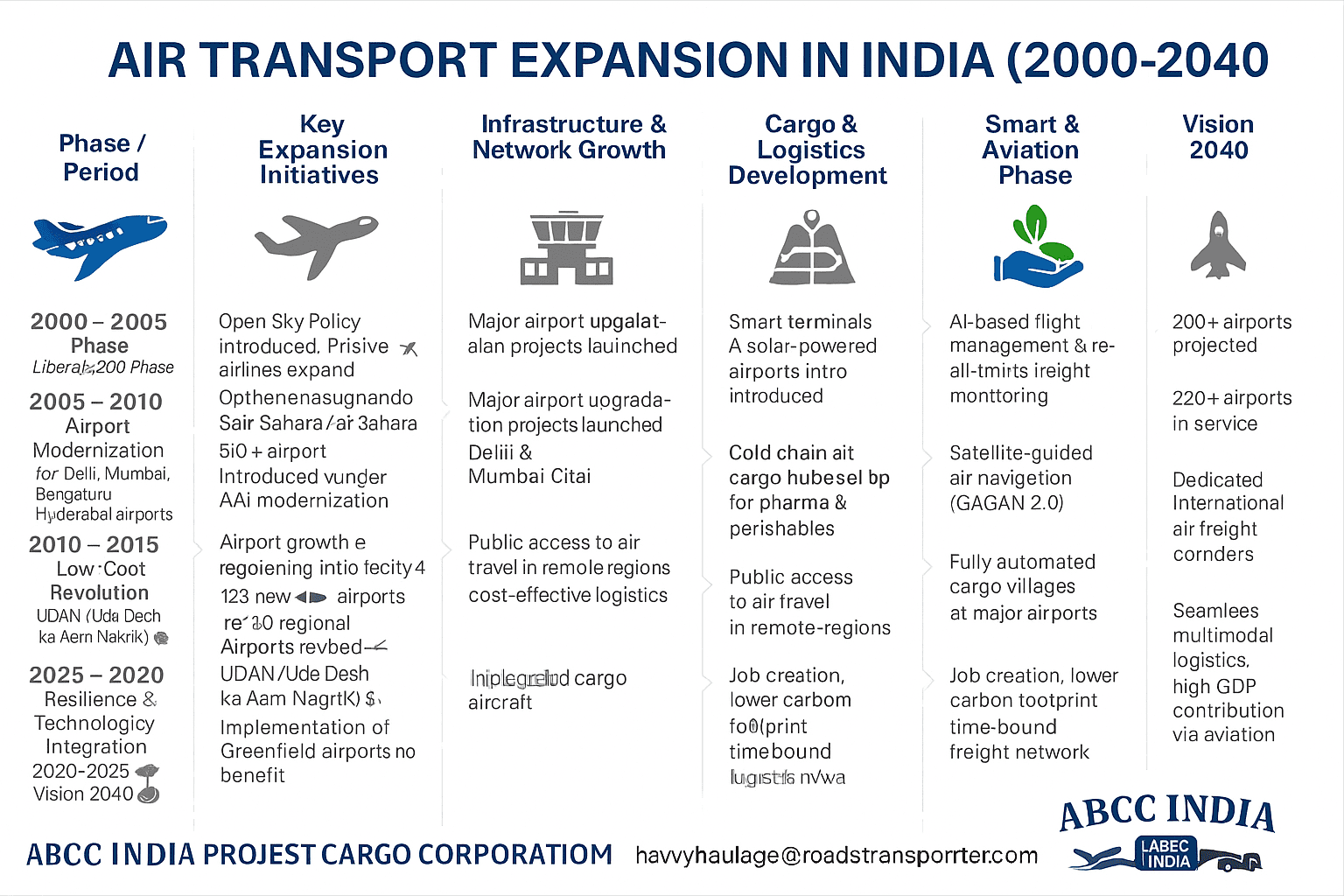
| 📆 Phase / Period | 🛫 Key Expansion Initiatives | 🏗️ Infrastructure & Network Growth | 📦 Cargo & Logistics Development | 🌍 Public & Economic Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000–2005 (Early Liberalization Phase) | Open Sky Policy introduced; Private airlines expand operations (Jet Airways, Air Sahara). | 50+ airports operationalized under AAI modernization. | Air cargo begins organized structure with Air India Cargo, Blue Dart. | Boost in passenger growth & business connectivity; freight corridors initiated. |
| 2005–2010 (Airport Modernization) | PPP model introduced for Delhi, Mumbai, Bengaluru, Hyderabad airports. | Major airport upgradation projects launched; improved terminals & runways. | Establishment of cargo hubs in Delhi & Mumbai. | Improved global competitiveness; increased FDI in aviation. |
| 2010–2015 (Low-Cost Revolution) | Rise of IndiGo, SpiceJet, GoAir; expansion into regional routes. | 90+ airports active; Greenfield projects initiated (Mopa, Navi Mumbai). | Growth of express cargo (e-commerce delivery chains). | Affordable travel accessible to Tier-2 cities; employment generation. |
| 2015–2020 (Regional Connectivity Era) | UDAN (Ude Desh ka Aam Nagrik) scheme launched. | 125 new routes; 40+ regional airports revived. | Cold chain air cargo hubs set up for pharma & perishables. | Public access to air travel in remote regions; cost-effective logistics. |
| 2020–2025 (Resilience & Technology Integration) | Post-pandemic air travel revival; Air India privatization. | Smart terminals & solar-powered airports introduced. | E-commerce air freight grows 300%; integrated logistics corridors developed. | Digital passenger processing; efficient cargo turnaround times. |
| 2025–2030 (Sustainability & Capacity Growth) | 200+ airports projected; second airports for metros like Chennai, Pune. | Implementation of Greenfield airports & MMLPs (Multi-Modal Logistics Parks). | Introduction of electric cargo aircraft trials. | Job creation, lower carbon footprint, time-bound freight network. |
| 2030–2035 (Smart Aviation Phase) | AI-based flight management & real-time freight monitoring. | Satellite-guided air navigation (GAGAN 2.0). | Fully automated cargo villages at major airports. | Improved airspace efficiency; digital logistics integration. |
| 2035–2040 (Vision 2040) | India among top 3 global aviation markets. | 220+ airports operational; 2,500 aircraft in service. | Dedicated international air freight corridors. | Seamless multimodal logistics; high GDP contribution via aviation. |
🧭 Key Insights
- India’s air network has expanded from 50 airports in 2000 to over 150 operational airports in 2025, with Vision 2040 targeting 220+.
- The synergy between public air transport and air cargo logistics under Gati Shakti and UDAN drives balanced growth.
- Future expansion will prioritize green aviation, digital freight systems, and regional inclusivity.
🛫 AIR TRANSPORT CONTRIBUTION IN MULTIMODAL LOGISTICS IN INDIA
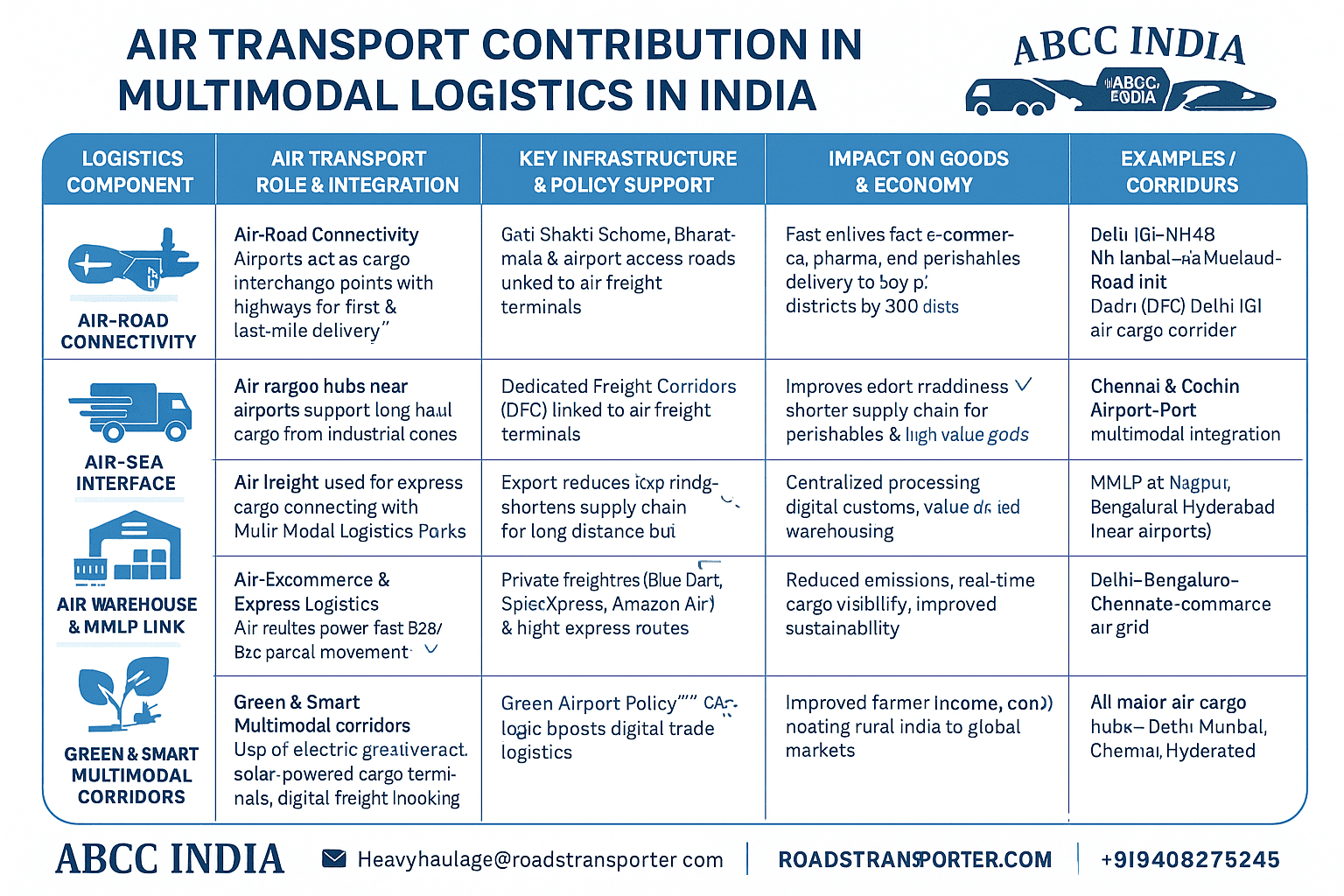
| 🚚 Logistics Component | 🛫 Air Transport Role & Integration | ⚙️ Key Infrastructure & Policy Support | 📦 Impact on Goods & Economy | 🌍 Examples / Corridors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ Air–Road Connectivity | Airports act as cargo interchange points with highways for first & last-mile delivery. | Gati Shakti Scheme, Bharatmala & airport access roads; dedicated truck parking & cold storage zones. | Enables fast e-commerce, pharma, and perishables delivery to 300+ districts. | Delhi IGI–NH48 corridor, Hyderabad–Nagpur–Mumbai road link. |
| 2️⃣ Air–Rail Integration | Rail cargo hubs near airports support long-haul cargo from industrial zones. | Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFC) linked to air freight terminals. | Reduces logistics cost and turnaround time for long-distance bulk shipments. | Dadri (DFC)–Delhi IGI air cargo corridor. |
| 3️⃣ Air–Sea Interface | Air freight used for express cargo connecting to ports for exports/imports. | Sagarmala and National Air Cargo Policy (NACP) link airports to port cities. | Improves export readiness, shortens supply chain for perishables & high-value goods. | Chennai & Cochin Airport–Port multimodal integration. |
| 4️⃣ Air–Warehouse & MMLP Link | Air cargo terminals integrated with Multi Modal Logistics Parks (MMLPs). | Airports Authority of India’s cargo village concept, cold chain logistics zones. | Centralized processing, digital customs, & value-added warehousing. | MMLP at Nagpur, Bengaluru, Hyderabad (near airports). |
| 5️⃣ Air–E-commerce & Express Logistics | Air routes power fast B2B/B2C parcel movement. | Private freighters (Blue Dart, SpiceXpress, Amazon Air) & night express routes. | 24-hour delivery in metros; boosts digital trade logistics. | Delhi–Bengaluru–Chennai e-commerce air grid. |
| 6️⃣ Green & Smart Multimodal Corridors | Use of electric ground vehicles, solar-powered cargo terminals, digital freight tracking. | Green Airport Policy, GAGAN navigation, PM Gati Shakti. | Reduced emissions, real-time cargo visibility, improved sustainability. | Cochin, Delhi, and Pune smart air cargo terminals. |
| 7️⃣ Regional Air Cargo Connectivity | Expansion under Krishi Udan Scheme for perishable goods. | Integration of 58 regional airports with agri-export hubs. | Improves farmer income, connects rural India to global markets. | Nashik, Guwahati, Bagdogra air cargo corridors. |
| 8️⃣ Policy & Economic Integration | National Logistics Policy 2022 recognizes aviation as a key enabler. | Focus on logistics cost reduction from 13% to 8% of GDP. | Enhances India’s competitiveness in manufacturing and exports. | All major air cargo hubs – Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Hyderabad. |
🧭 KEY INSIGHTS
- Air transport is now the fastest-growing multimodal component, linking road, rail, and sea routes through national logistics hubs.
- With initiatives like UDAN, Gati Shakti, and Krishi Udan, aviation has shifted from passenger priority to cargo efficiency and logistics integration.
- Air-based multimodal connectivity ensures speed, reliability, and sustainability — essential for perishable, time-bound, and high-value goods.
✈️ Major Air Transport Accidents in India (Approx. 2005 – 2025)

| 📅 Year | 📍 Location / Flight | 🛩️ Type / Cause (if known) | ⚰️ Fatalities / Casualties | 📝 Remarks / Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | Mangalore (Air India Express Flight 812) | Runway overrun / landing overshoot | ~158 deaths out of 166 onboard | One of the deadliest modern crashes in India; prompted stricter runway safety norms (www.ndtv.com) |
| 2020 | Kozhikode (Calicut) | Runway overrun in heavy rain (tabletop runway) | 21 deaths (The Pioneer) | Raised concerns about runway design and aircraft landing protocols in monsoon conditions (The Pioneer) |
| 2025 | Ahmedabad (Air India Flight AI-171) | Crash just after take-off | ~241+ deaths (1 survivor) (1001crash.com) | Very recent disaster involving a Boeing 787; under investigation |
✈️ AIR TRANSPORT IN INDIA — PROBLEMS, REASONS, CHALLENGES & SOLUTIONS
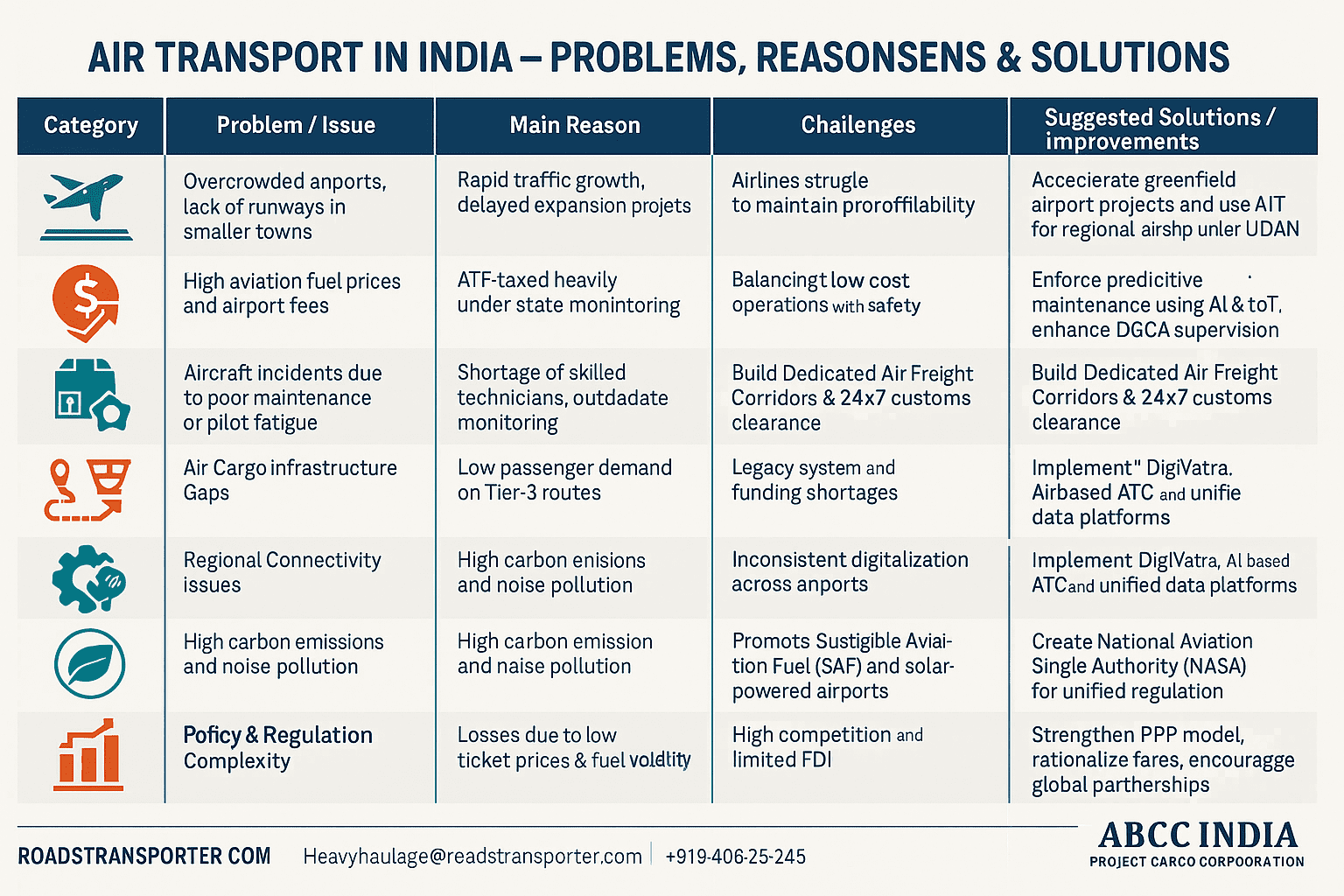
| ⚙️ Category | 🚨 Problem / Issue | 🔍 Main Reason | 🧩 Challenges | 💡 Suggested Solutions / Improvements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ Infrastructure Limitations | Overcrowded airports, lack of runways in smaller towns | Rapid traffic growth, delayed expansion projects | High land cost and limited state coordination | Accelerate greenfield airport projects and use regional airstrips under UDAN |
| 2️⃣ High Operating Costs | High aviation fuel prices and airport fees | ATF taxed heavily under state VAT | Airlines struggle to maintain profitability | Bring ATF under GST framework, offer tax relief for regional routes |
| 3️⃣ Safety and Maintenance Gaps | Aircraft incidents due to poor maintenance or pilot fatigue | Shortage of skilled technicians, outdated monitoring | Balancing low-cost operations with safety | Enforce predictive maintenance using AI & IoT, enhance DGCA supervision |
| 4️⃣ Air Cargo Infrastructure Gaps | Limited cold storage, customs delays, and poor multimodal linkage | Lack of air cargo villages and automation | Longer cargo dwell time at major airports | Build Dedicated Air Freight Corridors & 24×7 customs clearance |
| 5️⃣ Regional Connectivity Issues | Low passenger demand on Tier-3 routes | Lack of affordable regional aircraft & airport support | Low load factors, seasonal demand | Subsidize UDAN routes, promote short-haul electric/hybrid aircraft |
| 6️⃣ Technological Lag | Limited automation and data integration | Legacy systems and funding shortages | Inconsistent digitalization across airports | Implement DigiYatra, AI-based ATC, and unified data platforms |
| 7️⃣ Environmental Concerns | High carbon emissions and noise pollution | Dependence on jet fuel, limited green alternatives | Rising global pressure for carbon neutrality | Promote Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) and solar-powered airports |
| 8️⃣ Policy & Regulation Complexity | Multi-agency control slows decisions | Overlapping DGCA, BCAS, AAI frameworks | Fragmented accountability | Create National Aviation Single Authority (NASA) for unified regulation |
| 9️⃣ Skill & Manpower Shortage | Lack of skilled pilots, ATC staff, ground handlers | Training infrastructure lagging demand | Flight cancellations, overwork, errors | Establish National Aviation Training Institutes and e-learning modules |
| 🔟 Financial Sustainability | Losses due to low ticket prices & fuel volatility | High competition and limited FDI | Airline bankruptcies, reduced investor confidence | Strengthen PPP model, rationalize fares, encourage global partnerships |
🧭 KEY INSIGHTS
- India’s aviation system is expanding rapidly but still constrained by infrastructure, regulation, and manpower.
- Digital transformation, multimodal cargo integration, and sustainability are the three pillars for long-term resilience.
- Collaboration between private players, policymakers, and logistics partners like ABCC INDIA PROJECT CARGO CORPORATION can enable a more efficient national aviation ecosystem.
🏛 GOVERNMENT CONTRIBUTION & MAJOR AIR TRANSPORT PROJECTS IN INDIA
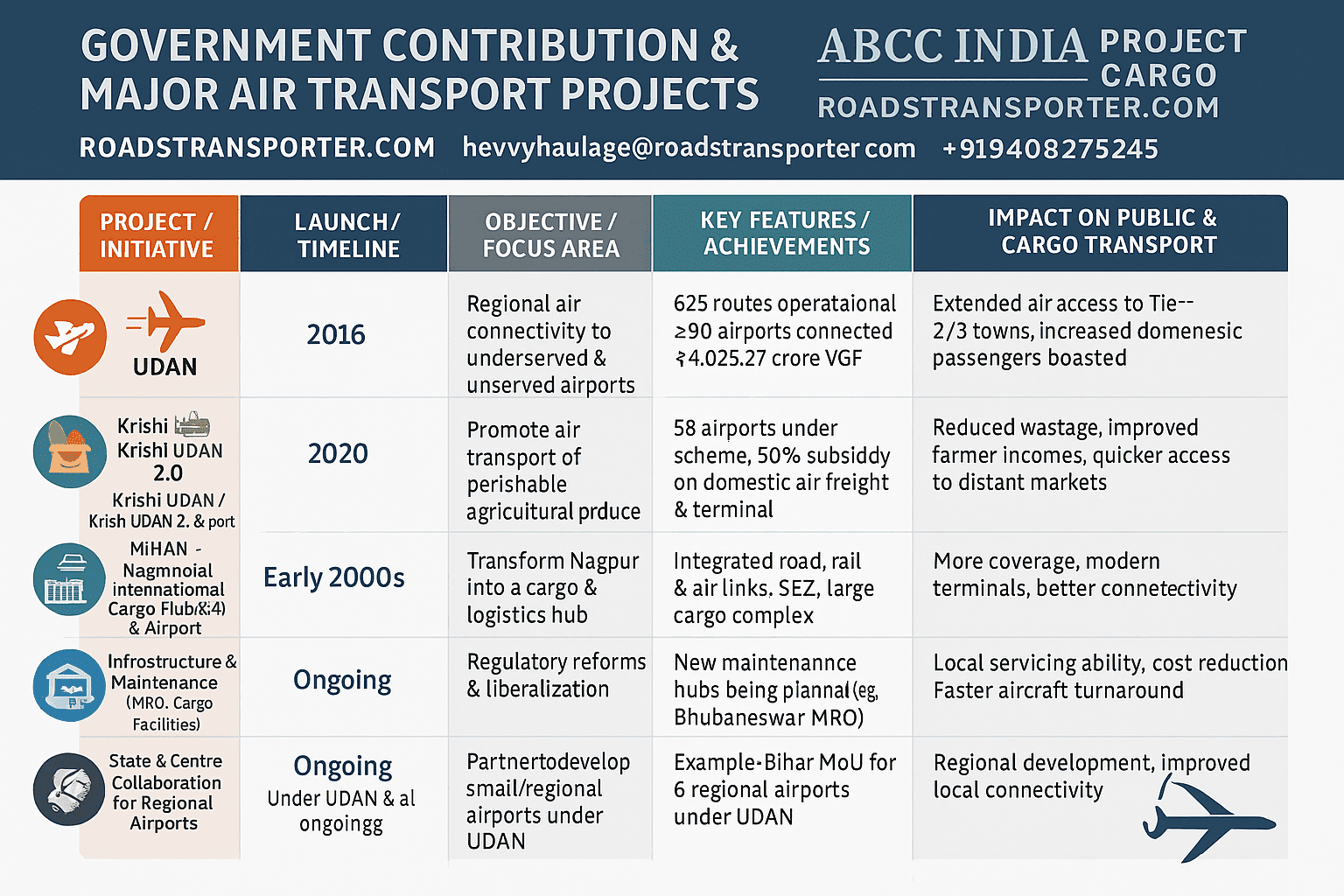
| 📌 Project / Initiative | 🗓️ Launch / Timeline | 🎯 Objective / Focus Area | 🏗️ Key Features / Achievements | 📈 Impact on Public & Cargo Transport |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UDAN (Ude Desh Ka Aam Nagrik) | 2016 – present | Regional air connectivity to underserved & unserved airports | 625 routes operational, ~90 airports connected, ₹4,023.37 crore VGF disbursed | Extended air access to Tier-2/3 towns, increased domestic passengers, boosted regional trade |
| Krishi UDAN / Krishi UDAN 2.0 | 2020 – present | Promote air transport of perishable agricultural produce | 58 airports under scheme, 50% subsidy on domestic air freight & terminal, support for 41 crops | Reduced wastage, improved farmer incomes, quicker access to distant markets |
| MIHAN – Nagpur Multimodal International Cargo Hub & Airport | Early 2000s – ongoing | Transform Nagpur into a cargo & logistics hub | Integrated road, rail & air links; SEZ; large cargo complex | Central cargo hub for India, leverages multimodal connectivity |
| Airport Network Expansion & Modernization | 2015 – present | Upgrade existing airports & develop greenfield airports | India’s airport count grew from 74 (2014) to 159 (2024) | More coverage, modern terminals, better connectivity |
| National Civil Aviation Policy (NCAP 2016) | 2016 | Regulatory reforms & liberalization | Encouraged competition, policy clarity, subsidies in regional routes | More private participation, better service standards |
| Infrastructure & Maintenance (MRO / Cargo Facilities) | Ongoing | Build MRO hubs, cargo terminals, express logistics assets | New maintenance hubs being planned (e.g. Bhubaneswar MRO) | Local servicing ability, cost reduction, faster aircraft turnaround |
| State & Centre Collaboration for Regional Airports | Ongoing | Partner to develop small/regional airports under UDAN | Example: Bihar MoU for 6 regional airports under UDAN | Regional development, improved local connectivity |
| Incentives & Subsidies / VGF | Under UDAN & related schemes | Provide financial support to airlines on unviable routes | Viability Gap Funding, waiver of landing/parking charges, fuel subsidies | Encourages airlines to operate in less profitable but socially important routes |
✈️ Private Sector Roles in India’s Air Transport

| 🏷 Area of Contribution | 🔧 Activities / Services Provided | 🏢 Representative Companies / Examples | 🌟 Impact / Value Addition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Airport Development & Management | Design, build, operate airports under PPP / concession model | GMR Group operates IGI Delhi, Hyderabad & Goa airports. Adani Group is acquiring/operating multiple airports and expanding infrastructure. | Brings efficiency, global practices, investment, better passenger experience |
| 2. Air Charter / Business Aviation | Private jet leasing, charter services, corporate aviation | JetSetGo – India’s largest private jet & helicopter operator. TajAir – non-scheduled operator & luxury charter flights. GMR Aviation (Private arm) – aircraft charter services. | Fills niche demand, premium segment, connectivity to remote areas and executives |
| 3. Ground Handling & Airport Services | Baggage, cargo & ramp handling, cabin cleaning, fueling, cargo handling | AI Airport Services Limited (AIASL) – ground handling services at 82 airports. Celebi (international firm) historically handled ground services at multiple Indian airports (though recent clearance issues). | Improves operational turnaround, cargo handling, efficiency at airports |
| 4. Airport Infrastructure & Construction | Runway complex works, terminal construction, cargo facility construction | Mordor Intelligence lists top aviation infrastructure firms: GMR Infrastructure, Adani, L&T, Tata. | Helps scale airport growth, modernization, and capacity expansion |
| 5. Technology & Aviation Support Services | Airline management, ticketing, revenue management, cargo representation, logistics | Bird Travels / Bird Group – manages airline distribution, cargo representation, airport supervision. | Enhances airline operations, distribution reach, cargo sales, integration |
| 6. Regional & Low-Cost Carrier Operations | Operating smaller / niche routes, connecting under-served regions | Fly91 – new low-cost regional airline (commenced 2024) serving tier-2/3 cities. | Supports gap in connectivity, complementing government regional schemes |
| 7. Private MRO / Maintenance Services | Maintenance, repair, overhaul work for aircraft | Some private firms and international companies partner or invest in MRO units (not large public data) | Reduces dependency on foreign MROs, lowers turnaround time, supports aviation growth |
🌐 MNC COMPANIONS’ CONTRIBUTION IN AIR TRANSPORT SERVICES IN INDIA

| 🏢 Area / Role | 🔧 What the MNC / Foreign Partner Does / Brings | 📌 Examples / Illustrations | 🌟 Value / Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Equity / Foreign Investment & Shares | Investment in Indian airlines, airport companies, or equity stakes | Under India’s FDI policy, foreign airlines can invest up to 49% in Indian scheduled air services (with government approval). | Brings capital, global best practices, and encourages institutional investor confidence |
| 2. Cargo Airline Participation / Shareholding | Foreign entities holding or controlling cargo airline stakes | Quikjet Airlines — Switzerland-based Farnair acquired a stake earlier in Quikjet. | Enables transfer of global cargo operation expertise, integration with international supply chains |
| 3. Technology, Systems & Training Partnerships | Providing pilot training, avionics, maintenance systems, simulation & technology transfer | Air India + Airbus establishing advanced pilot training center in Gurugram. | Raises skill levels, ensures high standard training, reduces dependence on imports |
| 4. Airport / Infrastructure PPP & Management | Foreign firms participating in airport operations, terminal management, or infrastructure development | Private sector + foreign investment contributing in airport expansion under PPP models. (Part of the estimates: private sector contribution US$ 7.5 billion toward airport projects). | Operational efficiency, better design, global passenger experience |
| 5. Global Airline Partnerships / Codeshare & Alliances | MNC airlines partnering with Indian carriers for route sharing, code sharing, joint operations | IndiGo entered a partnership with Delta, Air France-KLM, Virgin Atlantic to link India with Europe/North America. | Extends global reach of Indian carriers, improves connectivity and choice for passengers |
| 6. General Sales & Cargo Sales / Representation | MNCs acting as cargo sales agents, general sales organizations (GSAs), and marketing representation | M&C Aviation operates in India, offering cargo sales, airline marketing and operations support. | Enhances cargo sales reach, uses global networks to fill capacity, improves revenue for airlines |
| 7. Leasing & Financing of Aircraft | Foreign lessors and financiers supplying aircraft on lease or financing deals | Aviation investment firms or lessors worldwide engage with Indian carriers (article on investing in Indian aviation). | Helps Indian airlines expand fleets without full upfront capital; fosters fleet modernization |
| 8. Maintenance, Repair & Overhaul (MRO) & Component Supply | Foreign MRO companies or global parts manufacturers working with Indian operations | Global OEMs / MNC firms supply parts, systems, or oversight to Indian aircraft maintenance contracts (discussed in aviation investment context). | Improves reliability, reduces downtime, brings global standards to MRO operations |
🌊 Water Transport in India for Public and Goods
⚓ Introduction: India’s Aquatic Arteries of Trade and Connectivity
India’s water transport system is one of the oldest and most cost-effective forms of movement for people and goods. From the Indus Valley Civilization’s ancient dockyards to today’s vast river and coastal shipping network, waterways have been a silent force shaping the nation’s economy, culture, and trade. With over 14,500 km of navigable waterways, including rivers, canals, backwaters, and coastal routes, India holds immense potential to transform its transport ecosystem through sustainable and multimodal integration.
🚢 Historical Perspective: From Ancient Trade Routes to Modern Revival
Waterways in India have been vital since prehistoric times. Ancient ports such as Lothal, Muziris, and Bharuch connected India with Mesopotamia, Arabia, and East Africa. Inland water transport thrived along rivers like the Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Godavari, serving as major trade arteries. During the British era, canal networks and inland ports developed to move agricultural and raw goods inland to coastal export hubs.
Post-independence, however, the focus shifted to rail and road infrastructure. As a result, waterways were underutilized for decades. But in recent years, the Government of India and private players have renewed their focus on revitalizing inland and coastal shipping under the Sagarmala and Jal Marg Vikas Project (JMVP), aiming to restore this eco-friendly and low-cost mode to its rightful place in the logistics ecosystem.
🧭 Structure of Water Transport in India
Water transport in India is divided mainly into two segments:
- Inland Water Transport (IWT) — Navigable rivers, canals, and backwaters within the country.
- Coastal and Maritime Transport — Ports and shipping routes along the 7,500 km coastline, connecting domestic and international destinations.
🏞 Inland Waterways
India has declared 111 National Waterways (NWs), managed by the Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI). Key operational routes include:
- National Waterway-1 (Ganga–Bhagirathi–Hooghly): Haldia to Prayagraj – ~1,620 km
- National Waterway-2 (Brahmaputra): Dhubri to Sadiya – ~891 km
- National Waterway-3 (West Coast Canal, Kerala): Kottapuram to Kollam – ~205 km
- National Waterway-4 (Godavari & Krishna Rivers): Andhra Pradesh – ~1,000 km
- National Waterway-5 (Mahanadi & Brahmani): Odisha & West Bengal – ~600 km
These waterways handle cargo such as coal, cement, fertilizers, food grains, iron ore, and petroleum.
⚓ Coastal and Maritime Transport
India’s coastline connects 13 major and 200+ minor ports, forming a crucial link for both domestic coastal shipping and international trade. Major ports like Mumbai, Chennai, Visakhapatnam, Kochi, and Kandla serve as gateways for imports and exports, handling about 70% of India’s external trade by volume.
🚛 Goods Transportation: Backbone of Blue Logistics
Waterways serve as an energy-efficient and environmentally friendly medium for cargo movement. A single barge can carry the equivalent of 60 truckloads of cargo, consuming less than half the fuel and generating minimal emissions. Inland water transport has immense potential to move bulk and heavy goods — coal, steel, cement, food grains, fertilizers, and automobiles — especially over long distances.
🔹 Benefits for Goods Movement:
- Low Logistics Cost: 30–40% cheaper than road or rail for bulk cargo.
- Reduced Congestion: Shifts load from highways and railways.
- Fuel Efficiency: Lower fuel consumption per ton-km.
- Eco-friendly: Reduced carbon footprint and emissions.
- Scalable Capacity: Ideal for project cargo and over-dimensional consignments (ODC).
Companies like ABCC INDIA PROJECT CARGO CORPORATION use multimodal logistics networks integrating road, rail, and waterways to deliver heavy and oversized cargo safely across India’s industrial corridors.
🚢 Public Water Transport: Connecting Lives and Communities
Beyond cargo, India’s water transport plays a social role by connecting islands, coastal towns, and riverine communities. Ferries, boats, and passenger vessels operate across:
- Kerala’s Backwaters (NW-3): Kochi–Alappuzha ferry services.
- Assam & West Bengal Rivers: Brahmaputra ferries linking Majuli Island and rural districts.
- Goa & Andaman Islands: Passenger vessels for tourism and inter-island transport.
- Varanasi–Haldia Route: Now operational for passenger cruise tourism under JMVP.
This affordable and sustainable mode helps reduce rural isolation, promotes tourism, and supports regional economic activities.
🌉 Integration with Multimodal Logistics
Modern logistics demands seamless connectivity. The Sagarmala Project and PM Gati Shakti Mission integrate water transport with road, rail, and air networks to establish multimodal logistics hubs. This enables end-to-end freight movement and minimizes turnaround time.
For instance:
- Cargo from Haldia Port can be moved via barges to Patna (NW-1) and then by truck to northern industrial hubs.
- Coastal shipping connects Kandla–Cochin–Chennai with inland water terminals through interlinked freight corridors.
Such integration supports India’s target to reduce logistics cost from 13–14% of GDP to 8–9% by 2030.
⚙️ Challenges in Water Transport Development
Despite its potential, India’s water transport sector faces notable obstacles:
- Limited Navigable Depth: Seasonal water levels restrict year-round movement.
- Infrastructure Gaps: Lack of modern terminals, jetties, and storage facilities.
- Slow Fleet Modernization: Old vessels and inefficient propulsion systems.
- Administrative Overlaps: Multiple agencies managing ports, waterways, and shipping.
- Limited Public Awareness: Low passenger adoption due to safety and comfort concerns.
💡 Future Prospects & Government Initiatives
The Government of India, through Sagarmala, Jal Marg Vikas Project, and National Logistics Policy, aims to unlock India’s water transport capacity. Some of the flagship efforts include:
- Vessel Modernization: Support for building efficient barges and coastal ships.
- Digital Tracking: Implementation of River Information Systems (RIS).
- Port-Led Industrialization: Development of economic zones near major ports.
- Private Sector Participation: PPP projects in terminals, shipbuilding, and port logistics.
Future trends also point toward electric and hybrid vessels, smart port automation, and blue economy initiatives, aligning with India’s sustainability goals.
🌏 Waterways – The Future of Green Logistics
Water transport in India represents more than an alternative—it’s the foundation of a sustainable logistics revolution. By leveraging rivers and coasts for both public and cargo movement, India can decongest highways, reduce carbon emissions, and build a resilient multimodal supply chain. As industries, government, and logistics leaders like ABCC INDIA PROJECT CARGO CORPORATION collaborate on this mission, water transport will emerge as a central pillar in India’s journey toward greener, smarter, and more inclusive growth.
🌊 EVOLUTION OF WATER TRANSPORT IN INDIA (ANCIENT–2040)
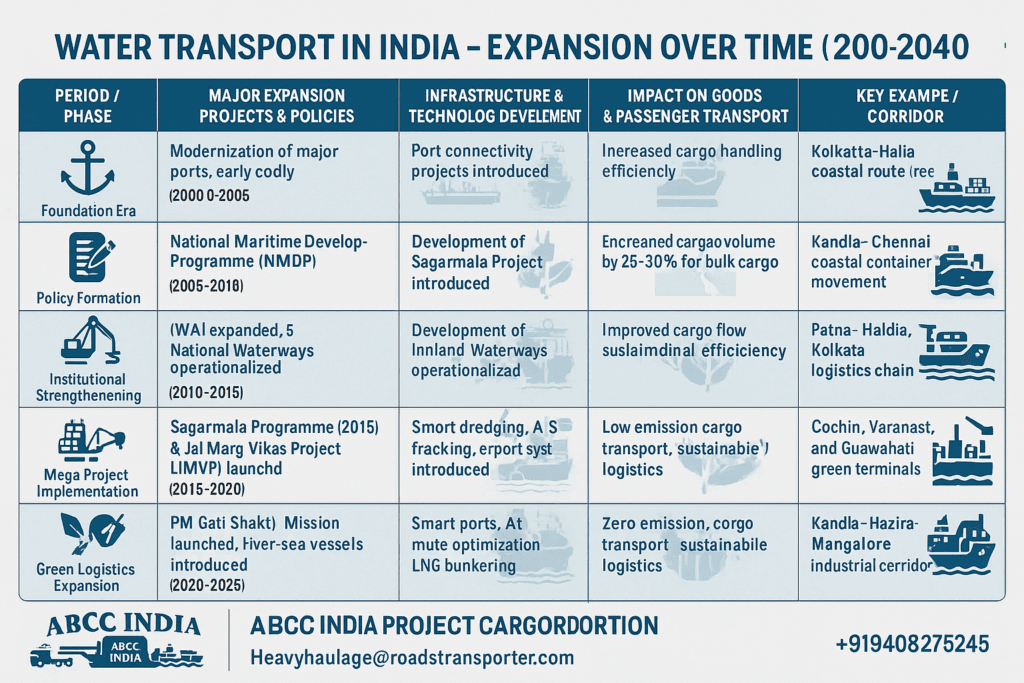
| 🕰️ Era / Timeline | ⚓ Major Developments | 🏗️ Infrastructure & Technology Milestones | 🌍 Impact on Public & Goods Transport |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ Ancient & Medieval Era (Before 1600 CE) | River-based trade on Ganga, Yamuna, Godavari, and coastal ports like Lothal, Muziris, and Tamralipti. | Wooden boats and sail vessels; small dockyards built along rivers. | Early maritime trade with Mesopotamia, Arabia, and Southeast Asia; cultural exchange and commerce flourished. |
| 2️⃣ Colonial Era (1600–1947) | British developed ports like Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai for resource export; inland canals built for goods transport. | Construction of Calcutta Port (1870), canal networks, and inland navigation routes. | India became a major maritime hub under British trade routes, though infrastructure favored exports. |
| 3️⃣ Early Post-Independence (1947–1980) | Establishment of major ports trust act (1963); focus on coastal shipping and port rebuilding. | Government set up 12 major ports; formation of the Inland Waterways Authority (preliminary work). | Limited inland navigation; primary focus on seaborne trade. |
| 4️⃣ Industrial Expansion Phase (1980–2000) | Creation of Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI, 1986); identification of first five National Waterways. | Modernization of Kolkata, Mumbai, Cochin ports; diesel-powered cargo barges introduced. | Began structured cargo movement along Ganga and Brahmaputra rivers. |
| 5️⃣ Modern Reforms (2000–2015) | Sagarmala Project conceptualized; National Maritime Agenda 2020 launched. | New cargo terminals, navigational aids, and port connectivity projects. | Cost-efficient cargo logistics; private players enter coastal shipping. |
| 6️⃣ Digital & Green Growth Era (2015–2025) | Implementation of Jal Marg Vikas Project (JMVP), Krishi Udan for river-air cargo, and revival of 111 National Waterways. | Inland terminals at Varanasi, Sahibganj, and Haldia; GPS-based vessel monitoring; modern dredging tech. | Boost in domestic trade, reduction in logistics costs, improved riverine passenger movement. |
| 7️⃣ Multimodal Integration Phase (2025–2035) | Integration with PM Gati Shakti, MMLPs, and Sagarmala Phase-II. | River-sea hybrid vessels; smart port automation; AI-based cargo routing. | Seamless logistics between river, road, rail, and air; rise in multimodal corridors. |
| 8️⃣ Future Vision 2040 (2035–2040) | India as a Blue Economy leader; expansion of electric and solar-powered vessels. | 200+ multimodal river ports, green energy terminals, hydrogen vessels. | Carbon-neutral cargo transport system; water transport as key national logistics pillar. |
🧭 SUMMARY INSIGHT
- India’s water transport has evolved from ancient sailboats to smart cargo corridors powered by digital navigation and green energy.
- The next phase (2040 Vision) focuses on sustainability, automation, and multimodal connectivity through projects like Sagarmala, Jal Marg Vikas, and National Logistics Policy.
🌊 WATER TRANSPORT IN INDIA — EXPANSION OVER TIME (2000–2040)
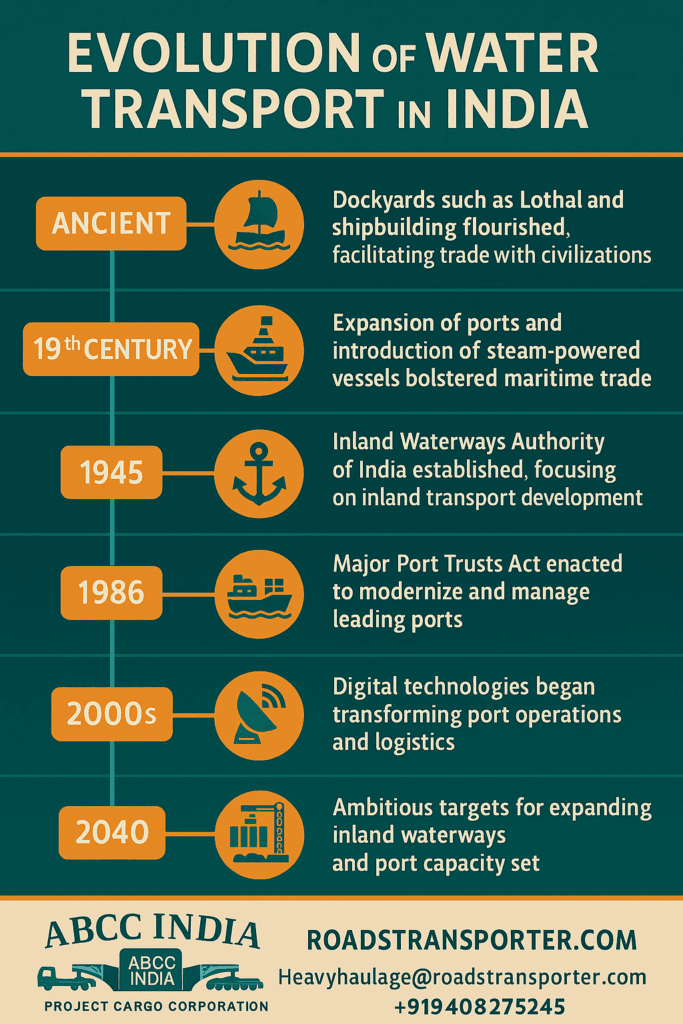
| 📅 Period / Phase | ⚓ Major Expansion Projects & Policies | 🏗️ Infrastructure & Technological Development | 🚢 Impact on Goods & Passenger Transport | 🌍 Key Example / Corridor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000–2005 (Foundation Era) | Modernization of major ports; early coastal cargo reforms | Port connectivity projects, dredging in Kolkata & Cochin | Increased cargo handling efficiency | Kolkata–Haldia coastal route revived |
| 2005–2010 (Policy Formation) | National Maritime Development Programme (NMDP) launched | Development of container terminals & coastal berths | Enhanced port capacity, faster cargo movement | Mumbai & Chennai port expansion |
| 2010–2015 (Institutional Strengthening) | Concept of Sagarmala Project introduced; inland navigation reviewed | IWAI expanded; 5 National Waterways operationalized | Coastal trade volume rose by 20% | Kandla–Cochin coastal container movement |
| 2015–2020 (Mega Project Implementation) | Sagarmala Programme (2015) & Jal Marg Vikas Project (JMVP) launched | Modern terminals at Varanasi, Haldia, Sahibganj; 111 NWs notified | Cost of logistics reduced by 25–30% for bulk cargo | NW-1 Ganga corridor operationalized |
| 2020–2025 (Digital & Multimodal Integration) | PM Gati Shakti Mission launched; river-sea vessels introduced | Smart dredging, AIS tracking, e-port systems | Improved cargo flow and multimodal efficiency | Patna–Haldia–Kolkata logistics chain |
| 2025–2030 (Green Logistics Expansion) | Electric & hybrid vessel policies introduced; PPP model for inland terminals | Solar-powered ports and electric barges | Low emission cargo transport; sustainable logistics | Cochin, Varanasi, and Guwahati green terminals |
| 2030–2035 (Industrial & Export Integration) | Integration with Industrial Corridors & SEZs under Sagarmala 2.0 | Smart ports, AI route optimization, LNG bunkering | 50% rise in coastal shipping share; export boost | Kandla–Hazira–Mangalore industrial corridor |
| 2035–2040 (Vision 2040 – Blue Economy Era) | India targets 20% modal share of waterways in logistics | Autonomous vessels, hydrogen-based port systems | Zero-emission, AI-controlled multimodal logistics | Ganga–Brahmaputra unified navigation corridor |
🧭 KEY INSIGHTS
- India’s water transport network has expanded from 5 operational waterways in 2000 to 111 National Waterways in 2024, aiming for seamless multimodal integration by 2040.
- The focus is on green shipping, digital logistics, and coastal–inland connectivity.
- Projects like Sagarmala, Jal Marg Vikas, and PM Gati Shakti are redefining the future of Indian logistics with sustainability and cost efficiency.
🌊 WATER TRANSPORT CONTRIBUTION IN MULTIMODAL LOGISTICS IN INDIA
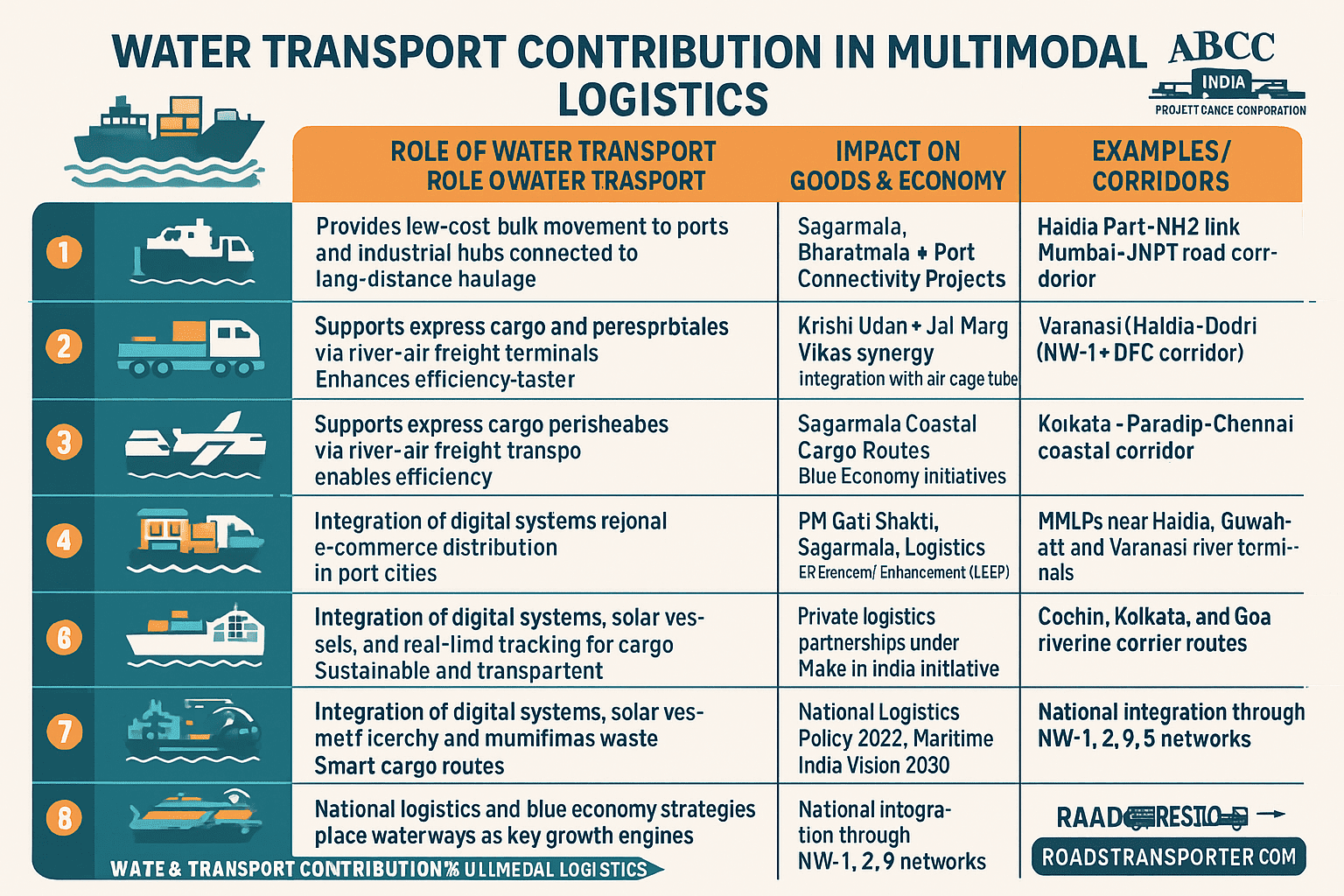
| 🚢 Multimodal Component | ⚓ Role of Water Transport | 🏗️ Supporting Infrastructure / Policies | 📦 Impact on Goods & Economy | 🌍 Examples / Corridors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ Water–Road Integration | Provides low-cost bulk movement to ports and industrial hubs, connected to highways for last-mile delivery. | Sagarmala, Bharatmala, and Port Connectivity Projects; new river-port highways. | Reduces highway congestion; faster door-to-door cargo delivery. | Haldia Port–NH2 link, Mumbai–JNPT road corridor. |
| 2️⃣ Water–Rail Linkage | Combines inland waterways with rail freight corridors for long-distance haulage. | Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFC) linked to river terminals and ports. | Enhances efficiency for coal, steel, and fertilizer transport. | Varanasi–Haldia–Dadri (NW-1 + DFC corridor). |
| 3️⃣ Water–Air Logistics | Supports express cargo and perishables via river-air freight terminals. | Krishi Udan + Jal Marg Vikas synergy; integration with air cargo hubs. | Faster export of agri-produce and pharma goods; minimizes wastage. | Varanasi (river terminal) linked with Lucknow Airport cargo hub. |
| 4️⃣ Water–Sea Coastal Corridors | Connects inland waterways to major seaports for import/export. | Sagarmala Coastal Cargo Routes, Blue Economy initiatives. | Reduces maritime freight time; better coastal industrial connectivity. | Kolkata–Paradip–Chennai coastal corridor. |
| 5️⃣ Water–Warehouse & MMLP Network | Waterway cargo linked to Multi Modal Logistics Parks (MMLPs) and warehouses near ports. | PM Gati Shakti, Sagarmala and Logistics Efficiency Enhancement Programme (LEEP). | Enables cross-docking, consolidation, and storage efficiency. | MMLPs near Haldia, Guwahati, and Varanasi river terminals. |
| 6️⃣ Water–E-Commerce & Express Logistics | Use of small cargo vessels for regional e-commerce distribution in port cities. | Private logistics partnerships under Make in India initiative. | Reduces delivery times for tier-2 and coastal cities. | Cochin, Kolkata, and Goa riverine courier routes. |
| 7️⃣ Green & Smart Multimodal Corridors | Integration of digital systems, solar vessels, and real-time tracking for cargo. | Digital Port Connectivity, AIS-based vessel monitoring, and Gati Shakti GIS integration. | Sustainable and transparent logistics system. | Smart cargo routes on NW-1 and NW-2. |
| 8️⃣ Policy & Economic Integration | National logistics and blue economy strategies place waterways as key growth engines. | National Logistics Policy 2022, Maritime India Vision 2030, and Sagarmala 2.0. | Waterways expected to handle 10–15% of total cargo by 2040. | National integration through NW-1, 2, 3, and 5 networks. |
🧭 KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Water transport acts as the backbone of India’s multimodal logistics, connecting ports, industries, and markets through cost-effective routes.
- Integration under PM Gati Shakti, Sagarmala, and National Logistics Policy ensures end-to-end cargo connectivity.
- This multimodal network strengthens India’s Blue Economy while reducing carbon emissions and logistics costs.
🚢 Major Water / Boat Accidents in India (2002 – 2023)
| 📅 Year | 📍 Location | ⚠️ Type / Cause | ⚰️ Deaths / Casualties | 📝 Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2002 | Kumarakom, Kerala | Boat capsizing (hitting sandbar) | 29 | Passenger boat sank near Kottayam-Muhamma route. |
| 2010 | Bhagirathi River, West Bengal | Overcrowded ferry hit sandbank | 74+ | Pilgrims ferry capsized; vessel capacity was far exceeded. |
| 2012 | Dhubri, Assam | Ferry capsizing during storm & overcrowding | 108+ | Ferry sank in Brahmaputra during storm. |
| 2014 | Hirakud Dam Reservoir, Odisha | Boat capsizing due to overloading | 31 | Motorboat with ~115 people capsized. |
| 2017 | Patna, Bihar | Boat capsizing (overcrowding) | 25 | Boat overturned near riverbank in Ganges. |
| 2023 | Tanur, Kerala | Recreational boat capsizing | 22 | “Atlantic” boat capsized off the Kerala coast. |
🌊 WATER TRANSPORT IN INDIA — PROBLEMS, REASONS, CHALLENGES & SOLUTIONS
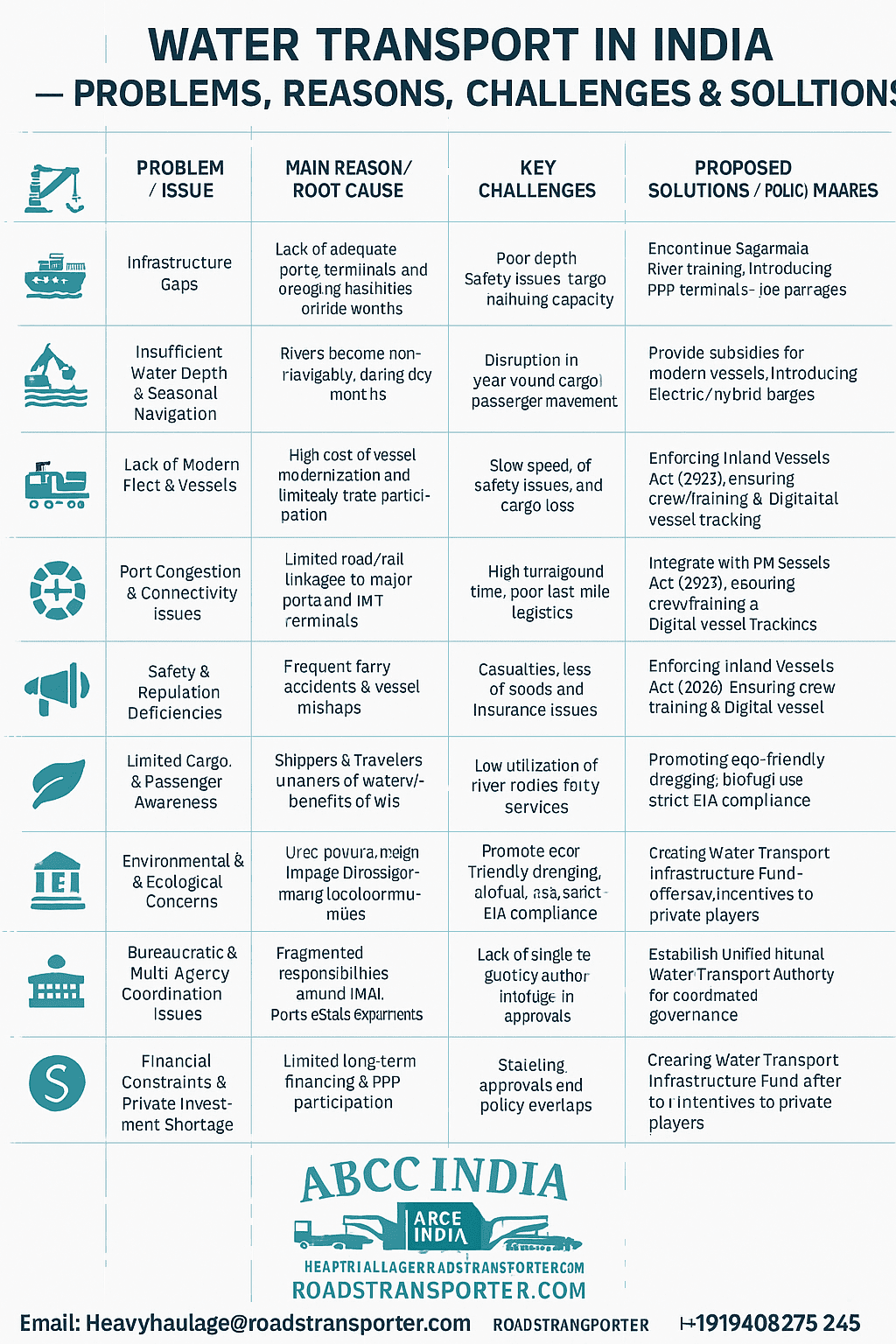
| ⚙️ Category | 🚨 Problem / Issue | 🔍 Main Reason / Root Cause | 🧩 Key Challenges | 💡 Proposed Solutions / Policy Measures |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ Infrastructure Gaps | Lack of adequate ports, terminals, and dredging facilities on rivers | Delayed execution and limited funding for IWT projects | Poor depth maintenance, low cargo handling capacity | Accelerate Sagarmala and Jal Marg Vikas implementation; promote PPP terminals |
| 2️⃣ Insufficient Water Depth & Seasonal Navigation | Rivers become non-navigable during dry months | Seasonal rainfall patterns and silt accumulation | Disruption in year-round cargo and passenger movement | Continuous dredging, river training, and water level regulation using barrages |
| 3️⃣ Lack of Modern Fleet & Vessels | Outdated boats and cargo barges with poor fuel efficiency | High cost of vessel modernization and limited private participation | Slow speed, safety issues, and cargo loss | Provide subsidy for modern vessels, introduce electric/hybrid barges |
| 4️⃣ Port Congestion & Connectivity Issues | Limited road/rail linkages to major ports and IWT terminals | Incomplete multimodal integration | High turnaround time and poor last-mile logistics | Integrate with PM Gati Shakti, MMLPs, and Bharatmala corridors |
| 5️⃣ Safety & Regulation Deficiencies | Frequent ferry accidents and vessel mishaps | Poor enforcement of safety norms and lack of trained manpower | Casualties, loss of goods, and insurance issues | Enforce Inland Vessels Act (2021), ensure crew training & digital vessel tracking |
| 6️⃣ Limited Cargo & Passenger Awareness | Shippers and travelers unaware of benefits of waterways | Historical preference for road and rail; lack of publicity | Low utilization of river routes and ferry services | Awareness campaigns, incentivize cargo movement via waterways |
| 7️⃣ Environmental & Ecological Concerns | River pollution, dredging impact on biodiversity | Improper waste disposal, oil leakage from vessels | Threat to aquatic life, resistance from local communities | Promote eco-friendly dredging, biofuel use, and strict EIA compliance |
| 8️⃣ Bureaucratic & Multi-Agency Coordination Issues | Fragmented responsibilities among IWAI, Ports, and State Departments | Lack of single regulatory authority | Delays in approvals and policy overlaps | Establish Unified National Water Transport Authority for coordinated governance |
| 9️⃣ Financial Constraints & Private Investment Shortage | Limited long-term financing and PPP participation | Low return on investment in waterway projects | Slow infrastructure development | Create Water Transport Infrastructure Fund; offer tax incentives to private players |
| 🔟 Climate & Disaster Vulnerability | Floods, cyclones, and erratic weather affect routes | Climate change impact on river flow and sea conditions | Route closures, cargo delays, higher risk | Develop resilient water transport design, integrate disaster forecasting systems |
🧭 KEY INSIGHTS
- India’s inland and coastal water transport is one of the greenest yet underutilized logistics assets.
- Effective integration of infrastructure, digital governance, and green energy can make waterways a reliable and economical mode.
- Collaboration between central–state agencies and private logistics firms like ABCC INDIA PROJECT CARGO CORPORATION can help realize the Blue Economy Vision 2040.
🏛️ GOVERNMENT CONTRIBUTION & BIG PROJECTS IN WATER TRANSPORTATION SERVICES IN INDIA

| 🚢 Project / Policy | 🏗️ Implementing Agency / Ministry | ⚙️ Objective / Focus Area | 💰 Investment / Budget (Approx.) | 🌍 Key Achievements / Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ Sagarmala Programme (2015–Present) | Ministry of Ports, Shipping & Waterways | Port-led development, coastal shipping, inland water transport (IWT) | ₹5.5 lakh crore (across 839 projects) | 234 port modernization projects; improved coastal logistics; reduced cargo cost by 25–30% |
| 2️⃣ Jal Marg Vikas Project (JMVP) | Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) with World Bank support | Develop NW-1 (Varanasi–Haldia) for commercial navigation | ₹4,633 crore | Multi-modal terminals at Varanasi, Haldia, Sahibganj; real-time river navigation & RIS system |
| 3️⃣ Sagarmala 2.0 (2023–) | Ministry of Ports, Shipping & Waterways | Green coastal economy, inland shipping promotion, skill development | ₹26,000 crore | New ferry routes, port infrastructure upgrades, and coastal community upliftment |
| 4️⃣ National Waterways Development Plan (111 NWs) | IWAI, Ministry of Shipping | Declared 111 National Waterways for cargo & passenger movement | ₹8,000 crore (Phase-wise) | 20+ waterways operationalized; improved freight efficiency |
| 5️⃣ Kochi Water Metro Project (2023) | Kerala Govt. + KfW (German funding) | Electric ferry-based urban mobility | ₹1,136 crore | India’s first electric ferry network; carbon-free public transport model |
| 6️⃣ Patna Water Metro & Ganga River Cruise Corridor | Bihar Govt. + IWAI | River-based passenger transport & tourism | ₹908 crore | Tourism promotion, improved urban connectivity |
| 7️⃣ Multi-Modal Terminals (Varanasi, Sahibganj, Haldia) | IWAI, Jal Marg Vikas Project | Seamless river–road–rail integration | ₹1,000 crore (combined) | Boosted inland cargo handling capacity to 3 MTPA |
| 8️⃣ Inland Vessels Act, 2021 | Parliament of India | Unified safety, training, and digital monitoring of vessels | Legislative reform | Modernized vessel certification, safety norms, and digital registry system |
| 9️⃣ PM Gati Shakti Mission (2021–) | Ministry of Commerce & Transport | Integration of waterways with roads, rail, air, and MMLPs | ₹100 lakh crore (overall) | Seamless multimodal connectivity; reduced turnaround time |
| 🔟 Maritime India Vision 2030 | Government of India | Long-term maritime infrastructure roadmap | ₹3 lakh crore | Green ports, automated terminals, and private partnership push |
🧭 KEY GOVERNMENT OUTCOMES
- Strengthened inland navigation and coastal shipping infrastructure through world-class port and terminal development.
- Integration of waterways into national logistics policy and multimodal transport corridors.
- Shift towards green, digital, and sustainable transport systems under the Blue Economy Vision 2040.
🚢 Private Companies’ Contribution in Water Transportation Services in India

| 🏷 Contribution Area | 🔧 Role / Activities | 🏢 Examples / Cases | 🌟 Impact / Value Added |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Barge / Inland Waterway Freight Operators | Private firms providing scheduled barge services, bulk cargo movement via rivers | Rhenus Logistics has signed an MoU with IWAI to roll out scheduled barge operations on NW-1, NW-2, and NW-16. | Brings global experience, scaling, improved reliability in inland water cargo movement |
| 2. Infrastructure / Terminal / Jetty Operators (PPP / Concessions) | Private firms operate or manage river terminals, jetties, or container handling inside waterways network | Summit Alliance Port East Gateway Pvt Ltd (a subsidiary of Bangladesh’s Summit Alliance Port) manages Indian river terminals (Garden Reach, Kalughat, Patna) under PPP with IWAI. | Improves cargo handling, storage, and integration with ports / customs operations |
| 3. Shipbuilding & Vessel Manufacturing | Private yards that build barges, dredgers, passenger boats, hulls for inland waterways | Timblo Drydocks Pvt Ltd in Goa: builds inland vessels such as cargo barges, pontoons, small river launches. | Boosts local manufacturing, reduces import dependence, provides specialized vessels for IWT |
| 4. Logistics & Integrated Services | Private logistics firms integrating inland waterways into multimodal solutions | Eka Infra offers navigable inland waterway services, combining planning, design and operations. Rhenus also promotes mixed waterway logistics solutions. | Makes water transport part of supply-chain offers, enabling clients to shift cargo to waterways |
| 5. Private Financing / Investment & PPP Participation | Capital investment in jetties, river terminals, concession models for operation | Private sector promoters appear in opportunity listings for IWT projects via India Investment Grid. | Helps share risk, speeds up infrastructure growth, encourages innovation |
🌐 MNC Contributions in Water Transport in India
| 🛠️ Contribution Area | 🔍 Role / Activity | 🏢 Example / MNC / Foreign Entity | 🌟 Impact / Value Added |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Barge Operations / Inland Freight | Operating barges / river freight services via MoUs with IWAI | Rhenus Group signed MoU with IWAI to run barge services on NW-1, NW-2, NW-16 & Indo-Bangladesh Protocol route. | Brings international logistics expertise, capacity, scale, and reliability to India’s inland waterways |
| 2. Terminal / River Terminal Management (PPP / Concession) | Operating river terminals / jetties under concession or PPP | Summit Alliance Port Limited (Bangladeshi MNC) operates and manages three Indian river terminals (Garden Reach in Kolkata, Kalughat in Patna) via its Indian subsidiary. | Improves terminal operations, customs integration, container handling, and connectivity at inland ports |
| 3. Investment & Capital Infusion | Funding projects, introducing new assets, investing in infrastructure | Rhenus plans to invest ~$100 million in Indian inland waterways and floating operations. | Enables faster scaling of water transport assets (barges, vessels, equipment) with foreign capital |
| 4. Technology & Operations Expertise Transfer | Providing operations, logistics, navigational, tracking, fleet management capabilities | Rhenus leverages its European inland waterways logistics experience to optimize Indian operations. | Brings best practices in scheduling, fleet utilization, safety, and cost management |
| 5. Cross-Border / Coastal Shipping Service | Operating global shipping lines linking Indian ports to international routes | Maersk Line India, MSC India, CMA CGM are major MNC shipping lines active in India’s maritime trade. | Enhances port throughput, provides containers and liner service options, links India’s coastal/sea transport to global networks |
🇮🇳 Transport Ministers of India (1947–present): Tenure & Notable Moves
| No | Minister (Portfolio title then) | Tenure (From–To) | What changed / New in the era (high level) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | John Mathai — Minister of Transport | 15 Aug 1947 – 22 Sep 1948 | Ministry of Transport created at Independence; groundwork for integrating movement sectors. |
| 2 | N. Gopalaswamy Ayyangar — Transport & Railways | 22 Sep 1948 – 13 May 1952 | Portfolio expanded to include Railways (renamed “Transport & Railways”). |
| 3 | Lal Bahadur Shastri — Transport & Railways | 13 May 1952 – 7 Dec 1956 | Consolidated policy across roads/rail during early Five-Year Plans. |
| 4 | Jagjivan Ram — Transport & Railways | 7 Dec 1956 – 17 Apr 1957 | Transition phase before 1957 reorganisation. |
| 5 | Lal Bahadur Shastri — Transport & Communications | 17 Apr 1957 – 28 Mar 1958 | Post-1957 bifurcation: Railways split out; Communications merged with Transport. |
| 6 | S. K. Patil — Transport & Communications | 29 Mar 1958 – 24 Aug 1959 | Continued integration with Posts/Telecom in one ministry. |
| 7 | Jawaharlal Nehru (PM) — Transport & Communications | 24 Aug 1959 – 2 Sep 1959 | Interim charge. |
| 8 | P. Subbarayan — Transport & Communications | 2 Sep 1959 – 10 Apr 1962 | Expansion of federal transport administration. |
| 9 | Jagjivan Ram — Transport & Communications | 10 Apr 1962 – 31 Aug 1963 | Final phase before Communications split (1963). |
| 10 | Raj Bahadur — Minister of Shipping (then Transport after split) | 10 Apr 1962 – 1 Sep 1963 (Shipping); 1 Sep 1963 – 24 Jan 1966 (Transport) | 1963: Communications separated; ministry retitled “Transport”. |
| 11 | Neelam Sanjiva Reddy — Transport & Aviation | 24 Jan 1966 – 13 Mar 1967 | Short-lived merger with Civil Aviation (Transport & Civil Aviation). |
| 12 | V. K. R. V. Rao — Shipping & Transport | 13 Mar 1967 – 14 Feb 1969 | Long “Shipping & Transport” era begins (1967–1985). |
| 13 | Kotha Raghuramaiah — Shipping & Transport | 14 Feb 1969 – 18 Mar 1971 | Infrastructure development continues under Transport-Shipping combine. |
| 14 | Raj Bahadur — Shipping & Transport | 18 Mar 1971 – 8 Nov 1973 | Port & road coordination phase. |
| 15 | Kamalapati Tripathi — Shipping & Transport | 8 Nov 1973 – 10 Feb 1975 | Continued combined portfolio stewardship. |
| 16 | Uma Shankar Dikshit — Shipping & Transport | 10 Feb 1975 – 1 Dec 1975 | Emergency-period administrative consolidation. |
| 17 | Gurdial Singh Dhillon — Shipping & Transport | 1 Dec 1975 – 24 Mar 1977 | Oversaw late-1970s port/road policies. |
| 18 | Morarji Desai (PM) — Shipping & Transport | 24 Mar 1977 – 7 Jun 1977; again 17 Jun 1977 – 14 Aug 1977 | Interim/PM charge during govt change. |
| 19 | Jagjivan Ram (Dy PM) — Shipping & Transport | 7 Jun 1977 – 17 Jun 1977 | Interim. |
| 20 | Chand Ram (MoS, Independent charge) — Shipping & Transport | 14 Aug 1977 – 28 Jul 1979 | MoS (I/C) heading portfolio. |
| 21 | Janeshwar Mishra (MoS, Independent charge) — Shipping & Transport | 30 Jul 1979 – 14 Jan 1980 | Interim through 1979–80 transition. |
| 22 | Anant Sharma — Shipping & Transport | 14 Jan 1980 – 19 Oct 1980 | Early 1980s transport coordination. |
| 23 | Veerendra Patil — Shipping & Transport | 19 Oct 1980 – 2 Sep 1982 and 7 Sep 1984 – 31 Oct 1984 | Two stints in the combined ministry. |
| 24 | C. M. Stephen — Shipping & Transport | 2 Sep 1982 – 2 Feb 1983 | — |
| 25 | Kotla Vijaya Bhaskara Reddy — Shipping & Transport | 2 Feb 1983 – 7 Sep 1984 | — |
| 26 | Ziaur Rahman Ansari (MoS, I/C) — Shipping & Transport | 31 Dec 1984 – 25 Sep 1985 | Leads into 1985 mega-merger. |
| 27 | Bansi Lal — Minister of Transport | 25 Sep 1985 – 4 Jun 1986 | 1985 mega-merger: Railways, Civil Aviation, and Shipping & Transport combined into one “Transport” super-ministry; assisted by MoS for each wing. |
| 28 | Rajiv Gandhi (PM) — Transport | 4 Jun 1986 – 24 Jun 1986 | Interim. |
| 29 | Mohsina Kidwai — Transport | 24 Jun 1986 – 22 Oct 1986 | 1986 split that created three ministries: Railways, Surface Transport, Civil Aviation. |
| 30 | (Surface Transport—several holders, MoS-I/C then cabinet) Rajesh Pilot; K. P. Unnikrishnan; Manubhai Kotadia; Jagdish Tytler; M. Rajasekara Murthy; T. G. Venkatraman; Sedapatti R. Muthiah; M. Thambidurai; Nitish Kumar; Jaswant Singh; Nitish Kumar (again); Rajnath Singh; Vajpayee (PM, interim) | 22 Oct 1986 – 7 Nov 2000 (various stints—see source table) | Era of Ministry of Surface Transport; policy groundwork that later split roads vs shipping (2000). |
| 31 | B. C. Khanduri — Road Transport & Highways | 7 Nov 2000 – 22 May 2004 | New MoRTH carved out (2000); NHDP momentum and safety focus. |
| 32 | T. R. Baalu — Shipping, Road Transport & Highways | 2 Oct 2004 – 22 May 2009 (was MoRTH May–Oct 2004) | 2004 re-merge (Shipping + Roads) into one ministry; port & highway expansion under UPA-I. |
| 33 | Kamal Nath — Road Transport & Highways | 28 May 2009 – 19 Jan 2011 | Post-2009 re-split; fast-track highway awards push. |
| 34 | C. P. Joshi — Road Transport & Highways | 19 Jan 2011 – 15 Jun 2013 | NH works & PPP pipeline stewardship. |
| 35 | (PM) Manmohan Singh — interim | 15–17 Jun 2013 | Interim. |
| 36 | Oscar Fernandes — Road Transport & Highways | 17 Jun 2013 – 26 May 2014 | Road safety & award continuity. |
| 37 | Nitin Jairam Gadkari — Road Transport & Highways (also held Shipping 2014–2019) | 27 May 2014 – Incumbent | Expressways & Bharatmala, FASTag roll-out, safety bill updates; Shipping split again (2019); Shipping renamed Ports, Shipping & Waterways (2020). |
Notes on portfolio changes (why titles keep changing)
- 1947: Ministry of Transport created.
- 1948: renamed Transport & Railways.
- 1957: split Railways; merged with Communications → Transport & Communications.
- 1963: Communications separated → Transport.
- 1966: merged with Civil Aviation briefly.
- 1967–85: Shipping & Transport combined.
- 1985: mega-merger → Transport (Rail + Surface + Civil Aviation) for a year.
- 1986: split again → Surface Transport (+ separate Railways & Civil Aviation).
- 2000: split Surface → Road Transport & Highways and Shipping.
- 2004: re-merged; 2009: split again; 2020: Shipping renamed Ports, Shipping & Waterways.
🚦 Transport Department of India
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Official Name & Ministry | The central body that oversees road transport, highways, vehicle regulation, transport policy is the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH). |
| Functions / Mandate | – Formulate policy on highways, road safety, vehicle regulations, transport research. – Develop & maintain National Highways, oversee agencies like NHAI. – Regulate transport laws (Motor Vehicles Act, etc.). – Coordinate with states on transport & road network. – Grant permissions & regulation for interstate transport, permits. – Vehicle registration, licensing, fitness, road safety oversight. |
| Organizational Structure | – Led by a Cabinet Minister (current: Nitin Gadkari) – Assisted by Ministers of State – Has departments / wings: Road Wing, Transport Wing, Planning & Monitoring, etc. – Agencies under MoRTH include NHAI, NHIDCL, CRRI, and others. |
| Key Acts / Laws | Motor Vehicles Act (1988), National Highways Act (1956), Road Transport Corporations Act, rules on vehicle fitness, pollution control, etc. |
| Role in Public Transport | The central ministry frames policy, sets standards, allocates funding. Execution of public transport (buses, urban transit) is typically done by state transport departments / corporations. |
| Role in Goods / Freight Transport | Works on road freight corridors, national highways facilitating goods movement across states. Gives permits, regulates heavy vehicle norms, axle loads, and highway infrastructure. |
| Challenges / Constraints | – Coordination with states – Funding large infrastructure – Ensuring enforcement across many jurisdictions – Balancing mobility, safety, and environmental concerns |
| Relation with State Transport Departments | The central ministry provides guidelines, funding, regulatory oversight. State transport departments handle implementation—vehicle registration, local transport regulations, bus operations, enforcing state laws. |
🚚 ABCC India Project Cargo Corporation
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Name / Business Identity | ABCC India Project Cargo Corporation — a private logistics & transport services firm. (roadstransporter.com) |
| Business / Services | – Project Cargo Transportation (heavy haulage) – Warehousing & logistics support – Route survey, project consultancy – Overweight / oversized consignment transport – Multi-modal solutions likely (road + other modes) (roadstransporter.com) |
| Scale & Infrastructure | They maintain fleets of tempo, trucks, trailers. They have network across India. (crane-locator.com) They are located in Pune (Transport Nagar, Nigdi) as per local address records. (Justdial) |
| Strength / Value Proposition | • Expertise in handling complex / heavy / project logistics • Customized route surveys and project consultancy • Flexibility, specialized equipment • Private sector efficiency, client focus • Likely to leverage multiple transport modes (road + perhaps connectivity to rail / ports) |
| Limitations / Challenges | • Regulatory dependence (permits, route clearances) • Infrastructure constraints (roads, bridge load limits) • High cost / investment in specialized fleet • Coordination with government agencies and compliance with transport laws |
| Relationship with Government / Regulation | • Needs to comply with central & state transport laws • Requires permits, clearances, route approvals • May partner with government in PPP projects or contracts for logistics • Regulated by the Ministry of Road Transport & Highways / state transport departments |
✅ Key Differences & Synergies
| Feature | Transport Department (Government) | ABCC India Project Cargo |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Policy, regulation, infrastructure development, oversight | Execution and delivery of transport/logistics services |
| Scope | National level, public goods, regulatory reach across states | Commercial, private client focus, niche in heavy / project cargo |
| Power | Legislative & regulatory authority | No regulatory authority; must operate within legal framework |
| Infrastructure creation | Builds roads, highways, sets standards, funds projects | Uses existing infrastructure; may invest in private assets (fleet, warehouses) |
| Stakeholders | Nation, citizens, states, public transport Ministries, agencies | Corporate clients, industries, project developers |
🚦 The Future of Transport in India: Evolution Toward Intelligent, Integrated Mobility
1️⃣ Overview: Transition from Traditional to Transformative Mobility
India’s transport ecosystem—once dominated by roads and railways—is moving toward a digitally-integrated, energy-efficient, and multi-modal future.
The government’s infrastructure push (through PM Gati Shakti, National Logistics Policy 2022, Bharatmala, Sagarmala, and UDAN) is complemented by private and global investments in EVs, green fuels, automation, and smart logistics.
By 2040, India is projected to handle nearly double its current freight volume, demanding cleaner, faster, and safer transport systems.
2️⃣ Future Pillars of Indian Transport
| 🔧 Pillar | 💡 Key Direction / Trend |
|---|---|
| Infrastructure Expansion | 80,000 km of highways, 111 national waterways, high-speed rail, and expanded metro networks to connect rural–urban India. |
| Electrification & Alternative Fuels | Shift from diesel to EV, CNG, LNG, bio-diesel, ethanol, hydrogen fuel for road, rail, and water fleets. |
| Digitalization & AI Integration | Implementation of IoT-based logistics, GPS-linked tracking, electronic tolling (FASTag 2.0), and AI-driven traffic management. |
| Multimodal Connectivity | Seamless linking of road + rail + air + water via logistics parks and digital freight corridors under the Gati Shakti framework. |
| Green Transport Goals | Carbon-neutral initiatives in ports, airports, and highways—electric buses, solar-powered terminals, and sustainable logistics hubs. |
| Urban Mobility Transformation | Widespread metro, water-metro, ropeway, and EV-bus adoption to reduce congestion and improve first-/last-mile connectivity. |
| Automation & Smart Safety | Development of autonomous driver-assist systems, e-licensing, predictive accident analytics, and national safety dashboards. |
3️⃣ Technological and Economic Enablers
- 5G & IoT connectivity: Real-time tracking of vehicles and goods.
- Big data & AI logistics: Dynamic route planning to minimize empty runs.
- Public–Private Partnerships (PPP): Co-funding of terminals, smart roads, and transport hubs.
- Start-ups & Innovation: Growth of Indian mobility tech firms in EV charging, delivery drones, and AI-driven fleet management.
- Skill Development: Need for specialized training in digital transport operations and green vehicle maintenance.
4️⃣ Challenges Shaping the Road Ahead
- Infrastructure strain — Maintaining quality across diverse geography.
- Energy transition cost — EV and hydrogen supply chains still expensive.
- Regulatory uniformity — Need for consistent rules across states.
- Safety & data privacy — Managing cybersecurity in connected vehicles.
- Behavioral shift — Adoption of shared mobility and public transport.
5️⃣ Long-Term Vision: “Integrated, Intelligent, Inclusive”
The long-term vision positions India as a global model for affordable, green mobility.
- Freight corridors to cut logistics cost from 14 % → 8 % of GDP.
- EV share in new vehicle sales projected > 40 % by 2035.
- Waterways and rail expected to handle > 50 % of freight by 2040.
- Urban air mobility (eVTOL, drones) and autonomous freight systems to become viable by late 2030s.
6️⃣ Conclusion
The future of transport in India will not be defined by speed alone—but by sustainability, technology, and coordination.
The nation’s progress depends on synergy between central policy, private innovation, and public adoption.
With integrated infrastructure, clean energy, and digital governance, India is steadily shifting from moving vehicles to moving intelligence—a leap that could redefine mobility for the next century.
🚦 TRANSPORT IN INDIA — SUMMARY
| 🚛 Mode of Transport | 🧭 Coverage & Network | ⚙️ Major Features / Use | ⚠️ Challenges / Issues | 🌱 Future Outlook / Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ Road Transport | Over 6.5 million km of roads (largest in world) | Flexible, door-to-door delivery; backbone for passenger & freight movement | Congestion, pollution, uneven maintenance, road safety issues | Expressways, EV trucks, logistics corridors, FASTag 2.0, intelligent traffic systems |
| 2️⃣ Rail Transport | 68,000+ km route network (4th largest globally) | Bulk freight (coal, cement, food grains), mass passenger movement | Overcrowding, aging infrastructure, delays | Dedicated Freight Corridors, high-speed rail, electrification, smart signaling |
| 3️⃣ Air Transport | 140+ airports (domestic & international) | Fastest passenger mode; high-value cargo & connectivity | High cost, limited regional penetration | Regional connectivity (UDAN), green airports, digital ticketing, cargo hubs |
| 4️⃣ Water Transport | 7,500 km coastline; 111 national waterways | Cheapest mode for bulk cargo, eco-friendly logistics | Shallow depth, poor terminals, low cargo awareness | Sagarmala, Jal Marg Vikas, electric ferries, inland multimodal hubs |
| 5️⃣ Pipeline Transport | 32,000+ km pipelines | Petroleum, gas, chemical flow over long distances | Limited coverage, leakage risk | Expansion to rural energy corridors, monitoring via IoT |
| 6️⃣ Multimodal Logistics | Integrated hubs (road–rail–port–air) | Reduces cost, improves time & fuel efficiency | Poor coordination among modes | PM Gati Shakti, MMLPs, digital freight integration |
| 7️⃣ Public Transport (Urban) | Metro, bus, water metro, EV fleet | Affordable mobility, urban connectivity | Funding gaps, urban congestion | Electric buses, ropeways, smart ticketing, transit-oriented development |
🧭 KEY INSIGHTS
- India’s transport ecosystem handles ~90% passenger traffic and ~65% freight by road.
- The National Logistics Policy 2022 targets reducing logistics cost from 14% to 8% of GDP.
- Integration under PM Gati Shakti and Digital India is driving a unified logistics vision.
- Future transport will be green, digital, and multimodal, led by innovations in EVs, data analytics, and smart governance.
Global Transport Sector Tax Changes for 2026
| Region (Country) | Transport Segment | Specific Tax Change | Tax Type | Cost Impact | Operational/Pricing Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North America (Canada) | Goods/Freight | Carbon price rising from C$95 to C$110 per tonne CO₂ (2025→2026) | Carbon tax (fuel levy) | ↑ | Higher carbon charge adds a few cents per liter to diesel/gasoline, raising transport fuel costscanada.ca. Trucking and logistics companies face moderately higher operating expenses, likely passed on in freight rates. |
| North America (USA) | Passenger/Public Transit | New regional sales tax (0.5%–1%) proposed (Nov 2026, San Francisco Bay Area) to fund transit operations | Sales tax (local) | ↑ | Would slightly increase consumer costs regionally, generating revenue to prevent major service cuts in Bay Area public transport (BART, Muni, etc.)kqed.org. Aims to stabilize transit service levels without sharp fare hikes. |
| North America (USA) | Goods/Freight | State carbon cap-and-invest program (e.g. Washington) raising fuel prices (~$0.50/gal diesel) | Emissions trading (fuel) | ↑ | Cap-and-trade auctions have added ~40–50¢ per gallon to gasoline/diesel priceswashingtonstatestandard.com. This increases trucking and delivery costs, likely driving up shipping rates and fuel surcharges in affected states. |
| South America (Brazil) | Goods/Freight | State GST (ICMS) on diesel fuel increased by R$0.05/L (from R$1.12→1.17) effective Jan 2026 | VAT on fuel (ICMS) | ↑ | Diesel prices will rise modestlyen.clickpetroleoegas.com.br, adding to domestic freight and logistics costs. Trucking firms may face higher fuel bills, potentially leading to higher freight charges or squeezed margins. |
| South America (Brazil) | Passenger (Private) | State GST (ICMS) on gasoline/ethanol up by R$0.10/L (from R$1.47→1.57) Jan 2026 | VAT on fuel (ICMS) | ↑ | Petrol (and ethanol) costs increase about 6–7%en.clickpetroleoegas.com.bren.clickpetroleoegas.com.br, which is expected to raise commuting costs and public transport fuel expenses. Likely to fuel broader inflation as transport and travel become costlier. |
| South America (Colombia) | Goods/Freight | New 10% VAT on gasoline and diesel from 2026 (was 0%; rising to 19% in 2027) | VAT on fuel | ↑ | Significant jump in fuel cost – roughly +COP432/gal for diesel, +COP384/gal for petrolitau.com.br. This tax hike will substantially increase operating costs for freight carriers and raise fares for passenger travel, with inflationary knock-on effects. |
| Europe (Germany) | Goods/Freight | National CO₂ pricing for transport fuels shifts to trading in 2026 (price floor €55, cap €65 per tonne) | Carbon ETS (fuel) | ↑ | After a fixed €55/t CO₂ price in 2025, the move to a market-based ETS in 2026 may push allowance prices toward the €65 capicapcarbonaction.comicapcarbonaction.com. Fuel suppliers could face higher costs (few eurocents per liter), marginally increasing diesel and petrol prices and logistics costs. |
| Europe (UK) | Passenger (Private) | Removal of electric vehicle (EV) road tax exemption from April 2025 (EVs now pay £10 first year, £165–£195 annually afterward) | Vehicle excise duty | ↑ | EV owners begin paying standard annual road taxesgov.uk, slightly raising the cost of owning EVs. This policy levels the playing field with petrol/diesel cars; impact on overall EV adoption is expected to be minimal due to the relatively low fee. |
| Africa (Nigeria) | Passenger (Private) | Fuel subsidy abolished mid-2023, with full market pricing of petrol going forward into 2026 (no new subsidy) | Subsidy removal | ↑ | Petrol pump prices roughly tripled (from ~₦189 to ₦557/L) when the subsidy endedreuters.com. Transport fares and costs of goods surged immediately, straining households and businesses but relieving a heavy fiscal burden on the government. |
| Africa (Kenya) | Goods/Freight | VAT on gasoline and diesel doubled from 8% to 16% (enacted July 2023, continued into 2026) | VAT on fuel | ↑ | Fuel costs climbed ~8% due to the higher VATcitizen.digital, directly increasing bus fares and freight trucking rates. The higher transport costs have fed into elevated prices for food and consumer goods, adding inflationary pressure. |
| Africa (South Africa) | Goods/Freight | Phase 2 of carbon tax from 2026: rate up to R236/tCO₂ (2025) with lower free allowances (10% cut) for emitters; fuel levy component rising (e.g. 17c/L diesel) | Carbon tax | ↑ | Tighter carbon tax regime raises effective emissions costs for fuel usersmoore-southafrica.commoore-southafrica.com. Petrol and diesel incur increased levies (e.g. +17c/L on diesel in 2025), pushing up operating costs for transport companies. Companies must improve efficiency or face higher expenses, though revenue recycling and allowances soften short-term impact. |
| Asia-Pacific (China) | Passenger (Private EVs) | New Energy Vehicle purchase tax incentive cut in 2026 – shifting from 100% exemption to 50% reduction (max ¥15k per vehicle) | Vehicle purchase tax | ↑ | EV buyers will pay a half-rate purchase tax from 2026 (about 5% vs 0% before)english.www.gov.cn. This ends the full tax holiday, increasing EV upfront prices modestly (up to ¥15,000 per car), though EVs remain tax-advantaged compared to gasoline vehicles. |
| Asia-Pacific (India) | Goods/Freight | GST on commercial trucks (goods transport vehicles) reduced from 28% to 18% (effective Sept 2025) | GST (sales tax) | ↓ | Lowers the cost of new lorries/trucks by cutting tax burdenhindustantimes.com. Fleet operators benefit from cheaper vehicle acquisition, which could translate into lower long-term freight costs or faster fleet upgrades (improving efficiency). |
| Asia-Pacific (India) | Passenger/Public Transit | GST on buses and public transport vehicles (≥10 seats) cut from 28% to 18% (Sept 2025) | GST (sales tax) | ↓ | Reduces capital costs for bus operatorshindustantimes.com, encouraging investment in public transport fleets. This tax relief helps transit agencies and could support affordable fares or service expansion due to lower vehicle purchase and leasing costs. |
| Asia-Pacific (Vietnam) | All (Fuel for transport) | Scheduled end of temporary fuel-tax cut – environmental tax on petrol, diesel reverting to full rates by 2026 (e.g. petrol from ₫2,000→₫4,000/L) | Environmental fuel tax | ↑ | Vietnam extended a 50% fuel-tax cut through 2025 to tame inflationvietnamlawmagazine.vn, but plans to restore the original rates in 2026. The return to full tax will roughly double the tax component of fuel prices, causing higher pump prices and transport costs after a year of relief. Businesses and consumers are expected to face renewed fuel-related inflationary pressures. |
| Asia-Pacific (Malaysia) | Goods/Freight | Introduction of national carbon tax by ~2026, alongside gradual removal of diesel subsidies (partial subsidy cuts started 2024) | Carbon tax & subsidy reform |
🇮🇳 INDIA – 2026 TRANSPORT SECTOR TAX & GST IMPACT CHART
| Transport Segment | Tax/Policy Change (2026) | Type of Tax / Rate (Old → New) | Cost Impact | Expected Operational / Pricing Effect (2026 onwards) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 🚚 Goods Transport – Road Freight (Trucks, LCVs, Containers) | GST on truck/carriage rental with operator (including fuel) cut | 18% → 5% | ↓ | Lowers logistics cost by 10–12%. Cheaper freight contracts for SMEs & industries; boosts organized road transport. |
| 🚛 Multimodal Transport (Road + Rail + Sea) | GST on multimodal transport reduced | 12% → 5% | ↓ | Reduces total logistics chain tax burden; encourages multimodal corridors (e.g., DFC + road integration). |
| 🚚 Transport of Goods by Road (GTA) | Simplified composite GST rate for GTA | Old: optional 5%/12% → Unified 5% | ↓ | Uniform low rate simplifies compliance; enhances competitiveness of small fleet owners. |
| 🛻 Commercial Vehicle Purchase (Trucks, Trailers, LCVs) | GST on commercial vehicles cut | 28% → 18% | ↓ | 10% cheaper truck/bus acquisition; faster fleet modernization (Euro VI, LNG, EV trucks). |
| 🚌 Public Bus Transport (Private/State Fleet) | GST on buses (≥10 seats) cut | 28% → 18% | ↓ | Lowers procurement cost for state and private bus operators; supports fleet expansion and fare stabilization. |
| 🚖 Taxi & Cab Services (Including App-based) | GST rate clarified / rationalized | 5% (no ITC) continues | ↔ | No change in rate; operators continue to collect 5% GST without input credit. |
| 🚆 Rail Freight Services | GST maintained at 5% (with ITC) | Unchanged | ↔ | Stable rate; keeps Indian Railways freight competitive against road sector. |
| ✈️ Air Cargo Services | GST retained | 18% (with ITC) | ↔ | No change; ITC available for exporters/importers. International cargo zero-rated under IGST. |
| ✈️ Air Passenger Transport (Domestic Flights) | GST unchanged | 5% (no ITC) for economy / 12% (with ITC)** for business | ↔ | No new taxes; ticket prices stable unless ATF excise revised. |
| ⛽ Fuel (Petrol / Diesel) | Remains outside GST; Central excise + State VAT continue | – | ↔ / ↑ (if crude ↑) | No GST yet on fuels; cost still influenced by oil market and excise/VAT changes. Govt review expected FY 2026–27. |
| 🔋 Electric Vehicles (EVs – Cars, Buses, LCVs) | GST retained at 5% + FAME-III support likely | 5% (unchanged) | ↓ | Continues to encourage EV adoption in passenger & cargo fleets; offsets fuel cost pressures. |
| 🛣️ Toll & Highway User Charges | NHAI tolls linked to WPI inflation (annual hike Apr 2026 ≈ 3–5%) | – | ↑ | Slight yearly toll hike adds marginal transport cost, particularly for long-haul freight. |
| 🚢 Inland Waterways & Coastal Cargo | GST on coastal cargo & barge services aligned | 12% → 5% | ↓ | Cheaper coastal shipping; supports Sagarmala multimodal logistics growth. |
| 🚄 Metro & Urban Rail | Passenger services continue exempt from GST | 0% (exempt) | ↔ | Keeps fares affordable; no new taxes expected. |
| 🏗️ Vehicle Body Building & Modification Industry | Uniform GST for fabrication / mounting of bodies | 18% (flat) | ↔ | Simplifies taxation for coach builders, trailer fabricators, and OEM suppliers. |
| 🧾 Marine & Transit Insurance Premium | GST standardized | 18% (flat) | ↔ | Uniform taxation for goods-in-transit policies; ensures input credit availability for logistics companies. |
🏁 Conclusion: The Journey of Indian Transport — Powered by Vision & Responsibility

India’s transport sector stands at the intersection of growth, innovation, and sustainability. From roads to railways, from waterways to air routes, the country’s mobility network has evolved into the lifeline of its economy and society.
The future of transport in India depends not just on new technologies or infrastructure—but on trustworthy execution, intelligent planning, and responsible logistics leadership.
At the heart of this transformation, ABCC INDIA PROJECT CARGO CORPORATION continues to play its part — ensuring that every load, route, and logistics challenge is handled with precision, safety, and speed.
With decades of experience in project cargo, multimodal logistics, and heavy haulage, ABCC India believes that transport is not merely movement—it is the momentum of the nation’s progress.
As India moves towards smart, green, and digital mobility, ABCC India remains committed to supporting industries, infrastructure, and communities through reliable, future-ready transportation services that connect not just places, but possibilities.
📧 Email: [email protected]
🌐 Website: ROADSTRANSPORTER.COM
📞 Helpline: +919408275245
🏢 ABCC INDIA PROJECT CARGO CORPORATION
“Driving India’s Growth… One Route at a Time.”